Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
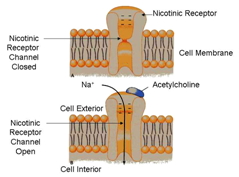
When in the presence of [[acetylcholine]], the receptor undergoes a conformational change opening up the channel to an influx of sodium (Na) within the cell. When this happens the cell undergoes a depolarization event that triggers an action potential to propagate along the rest of the cell stimulating, for example, a muscle response. | When in the presence of [[acetylcholine]], the receptor undergoes a conformational change opening up the channel to an influx of sodium (Na) within the cell. When this happens the cell undergoes a depolarization event that triggers an action potential to propagate along the rest of the cell stimulating, for example, a muscle response. | ||
| - | The opening of these channels only lasts for a millisecond due to [[cholinesterase]] being present and breaking down [[acetylcholine]] attached to the receptor causing the receptor to close again. Introduction of [[ | + | The opening of these channels only lasts for a millisecond due to [[cholinesterase]] being present and breaking down [[acetylcholine]] attached to the receptor causing the receptor to close again. Introduction of [[Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors]] can cause a depolarization block. It works by creating a prolonged refractory period in the depolarization event promoted by the opening of the receptor channel. |
=== Locations === | === Locations === | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
*[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | *[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
*[[Ionotropic receptors]] | *[[Ionotropic receptors]] | ||
| - | + | ||
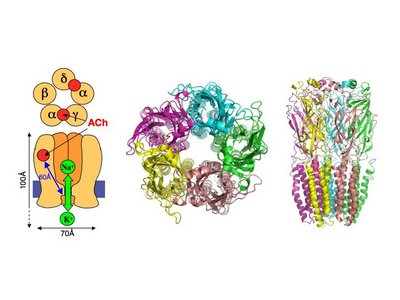
== 3D Structures of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor == | == 3D Structures of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor == | ||
| - | + | [[Acetyl choline receptor 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
1. Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Including Insecticides and Chemical Warfare Nerve Agents, Agency for Toxiz Substances and Disease Regulation accessed 5/2/14
2. Pierre-Jean Corringer and Jean-Pierre Changeux (2008) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Scholarpedia, 3(1):3468.
3. Adcock C, Smith GR, Sansom MS. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: from molecular model to single-channel conductance. Eur Biophys J. 2000;29:29–37.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, Alex Pennington