User:Brynn Baker/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Amylin == | == Amylin == | ||
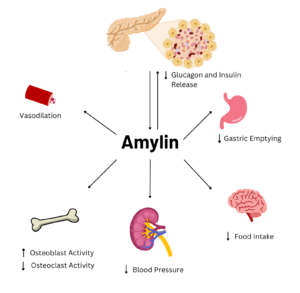
Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell beta cells] of pancreatic islets. It can cross the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood%E2%80%93brain_barrier blood-brain barrier] and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety. In doing so, it prevents spikes in blood glucose and overeating, making it a suitable target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes Type 2 Diabetes]. Type 2 Diabetes treatments and therapies. Seeing as Type 2 Diabetes is a major risk factor for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer's Disease], as Type 2 Diabetes cases continue to increase, there will likely be a spike in Alzheimer’s Disease as well. Therefore, it is vital that amylin, its receptor, and analogs such as pramlintide are understood to aid in rational drug design. | Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell beta cells] of pancreatic islets. It can cross the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood%E2%80%93brain_barrier blood-brain barrier] and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety. In doing so, it prevents spikes in blood glucose and overeating, making it a suitable target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes Type 2 Diabetes]. Type 2 Diabetes treatments and therapies. Seeing as Type 2 Diabetes is a major risk factor for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer's Disease], as Type 2 Diabetes cases continue to increase, there will likely be a spike in Alzheimer’s Disease as well. Therefore, it is vital that amylin, its receptor, and analogs such as pramlintide are understood to aid in rational drug design. | ||
| - | [[Image:AmylinFlowchart.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure | + | [[Image:AmylinFlowchart.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 2. Effects of Amylin in Humans]] |
The human amylin receptor is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-coupled protein receptor]. | The human amylin receptor is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-coupled protein receptor]. | ||
=== Structure === | === Structure === | ||
Revision as of 20:20, 9 April 2024
Homo sapiens Amylin3 Receptor, AMYR3
| |||||||||||
References
Student Contributors
- Brynn Baker
- Emily Berkman
- Sepp Hall