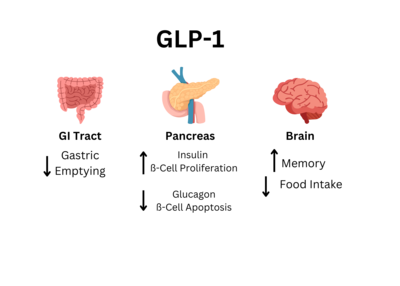
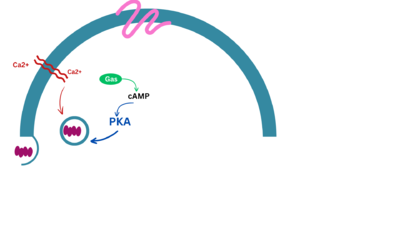
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor or GLP1-R uses the glucagon-like peptide to signal the body to secrete insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion. When glucose levels in the blood rise (usually after consuming food), GLP-1R activates, creating a signaling cascade to signal cAMP. After the signaling cascade, the final result is the secretion of insulin to the rest of the body. Discovered in 1990s while trying to understand the mechanism of GLP-1 action. [1] The structure was determined using cryogenic electron microscopy.
Function
GLP-1R works in conjunction with GIP-R to maintain blood glucose levels after the ingestion of food. It is imperative for these receptors to work well so diseases like diabetes and obesity do not ensue.
Disease
Diabetes and Obesity
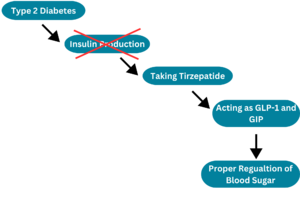
Type II Diabetes is when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin for the body.[2] This in turn makes the blood glucose level dangerously low. When the sugar levels in our blood become too low people can become dizzy and tired. On the other hand, when blood sugar levels become too high then can become feverish and sick.
Ligand and Receptor Interactions
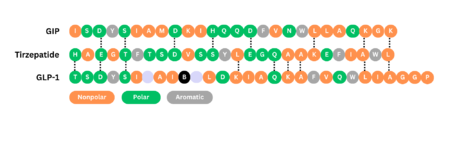
Sequence Alignment starts at residue 7
Hormone Interactions
uses pi stacking and hydrophilic interactions to dock into the receptor.
Drug Interactions
Relevance
Tirzepatide and other GLP-1R related antagonist drugs help to regulate blood glucose levels.[3] Although these drugs can make remarkable changes, the long term effects of GLP-1R related drugs are unknown. There have been some hints toward thyroid cancers but this was only shown in mice during trial periods.
References
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
- ↑ Coskun T, Sloop KW, Loghin C, Alsina-Fernandez J, Urva S, Bokvist KB, Cui X, Briere DA, Cabrera O, Roell WC, Kuchibhotla U, Moyers JS, Benson CT, Gimeno RE, D'Alessio DA, Haupt A. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol Metab. 2018 Dec;18:3-14. PMID:30473097 doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2018.09.009
- ↑ Mayendraraj A, Rosenkilde MM, Gasbjerg LS. GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells interactions and co-stimulation. Peptides. 2022 May;151:170749. PMID:35065096 doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170749
- ↑ Seino Y, Fukushima M, Yabe D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J Diabetes Investig. 2010 Apr 22;1(1-2):8-23. PMID:24843404 doi:10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x
- ↑ Sun B, Willard FS, Feng D, Alsina-Fernandez J, Chen Q, Vieth M, Ho JD, Showalter AD, Stutsman C, Ding L, Suter TM, Dunbar JD, Carpenter JW, Mohammed FA, Aihara E, Brown RA, Bueno AB, Emmerson PJ, Moyers JS, Kobilka TS, Coghlan MP, Kobilka BK, Sloop KW. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 29;119(13):e2116506119. PMID:35333651 doi:10.1073/pnas.2116506119