Alcohol dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (11 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
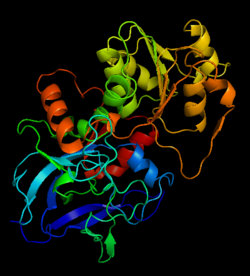
[[Image:1htb2.png|thumb|left|250px|Structure of Alcohol Dehydrogenase]] | [[Image:1htb2.png|thumb|left|250px|Structure of Alcohol Dehydrogenase]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | ==Function== | ||
| + | |||
'''Alcohol dehydrogenase''' (ADH, EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1]) is an 80kDa enzyme that catalyzes the 4th step in the metabolism of fructose before [[glycolysis]]. In the 4th step, glyceraldehyde is converted to the glycolytic intermediate DHAP by the NADH-dependent, ADH catalyzed reduction to glycerol.<ref>Voet, et. al. ''Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition''. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.</ref> ADH catalyzes the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to their corresponding aldehydes and ketones through a mechanism that involves the removal of a hydrogen. More detailed discussions in<br /> | '''Alcohol dehydrogenase''' (ADH, EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1]) is an 80kDa enzyme that catalyzes the 4th step in the metabolism of fructose before [[glycolysis]]. In the 4th step, glyceraldehyde is converted to the glycolytic intermediate DHAP by the NADH-dependent, ADH catalyzed reduction to glycerol.<ref>Voet, et. al. ''Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition''. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.</ref> ADH catalyzes the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to their corresponding aldehydes and ketones through a mechanism that involves the removal of a hydrogen. More detailed discussions in<br /> | ||
| Line 9: | Line 12: | ||
*[[Alcohol dehydrogenase from Clostridium beijerinckii]]<br /> | *[[Alcohol dehydrogenase from Clostridium beijerinckii]]<br /> | ||
*[[Alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica]]<br /> | *[[Alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[ALDH2]]<br /> | ||
*[[D275P mutant of alcohol dehydrogenase from protozoa Entamoeba histolytica]]<br /> | *[[D275P mutant of alcohol dehydrogenase from protozoa Entamoeba histolytica]]<br /> | ||
*[[Horse Liver Alcohol Dehydrogenase]]<br /> | *[[Horse Liver Alcohol Dehydrogenase]]<br /> | ||
*[[Contribution of Pro275 to the Thermostability of the Alcohol Dehydrogenases]]. | *[[Contribution of Pro275 to the Thermostability of the Alcohol Dehydrogenases]]. | ||
'''Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' (HADH) catalyzes the conversion of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA to 3-oxoacyl-CoA. NAD is the cofactor of HADH activity. HADH oxidates straight-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoAs in the β-oxidation pathway of fatty acid metabolism. HADH is classified according to its substrate ads short chain (SHCDH) and long chain HADH. HADH deficiency is a genetic disorder. | '''Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' (HADH) catalyzes the conversion of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA to 3-oxoacyl-CoA. NAD is the cofactor of HADH activity. HADH oxidates straight-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoAs in the β-oxidation pathway of fatty acid metabolism. HADH is classified according to its substrate ads short chain (SHCDH) and long chain HADH. HADH deficiency is a genetic disorder. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''alcohol dehydrogenase I, II, III, IV''' differ by their tissue specificity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Secondary alcohol dehydrogenase''' catalyses the reduction of acetone to isopropanol<ref>PMID: 22686835</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''NADP-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase''' catalyses the redox equilibria between aldehydes or ketones and the corresponding primary or secondary alcohols <ref>PMID: 8349550</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Quinone-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase''' oxidizes primary, secondary alcohols, aldehydes, polysaccharides and cyclodextrins <ref>PMID: 26440996</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Quinohemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase''' have pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) as the prosthetic group <ref>PMID: 15234265</ref>. | ||
For chimeras of alcohol dehydrogenase see<br /> | For chimeras of alcohol dehydrogenase see<br /> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 37: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Structure== | ||
| - | |||
| - | The initial scene (<scene name='Birrer_Sandbox_2/Whole_adh_molecule/3'>Domains of ADH</scene>) shows an overview of the molecule, allowing for a general look at the tertiary structure of alcohol dehydrogenase (it is complexed with Cl, Pyz, NAD, and Zn). A second scene (<scene name='Birrer_Sandbox_2/Close_look_at_ligand/2'>Closer Look at Subunit</scene>) shows a close view of the ligand within each subunit. Labels have been placed on NAD, CL, and Zn to clearly establish the structure. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | Within alcohol dehydrogenase, <scene name='Birrer_Sandbox_2/The_active_site/1'>the active</scene> site of alcohol dehydrogenase has three important residues, Phe 93, Leu 57, and Leu 116. These three residues work together to bind to the alcohol substrate.<ref>''Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase''. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm></ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | Zn plays an important role in the catalysis. It funtions by electrostatically stabilizing the oxygen in alcohol during the reaction, which causes the alcohol to be more acidic. At the <scene name='Birrer_Sandbox_2/Zinc_binding_site/1'>Zinc Binding Site</scene>, Zinc coordinates with Cys 146, Cys 174, and His 67.<ref>''Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase''. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 <http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm></ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | NAD functions as a cosubstrate in the dehydration. NAD binds to numerous residues in a series of beta-alpha-beta folds. <scene name='Birrer_Sandbox_2/Nad_binding_site/1'>NAD Binding Region</scene> shows the domain where NAD binds, and many of the residues with which it interacts are selected. | ||
| - | <ref>''Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase''. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | Alcohol dehydrogenase exists as a dimer with a zinc molecule complexed in each of the subunits. It has a SCOP catagory of an alpha and beta protein. At the N-terminal, there is a domain that is all beta; however, the C-Terminal domain is alpha and beta, so the catagory is alpha and beta. The C-Terminal core has 3 layers of alpha/beta/alpha and parallel beta sheets of 6 strands.<ref>''Protein: Alcohol dehydrogenase from Human (Homo sapiens), different isozymes''. SCOP. 2009. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20060914235939/http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.d.c.b.b.c.html></ref> | ||
| - | |||
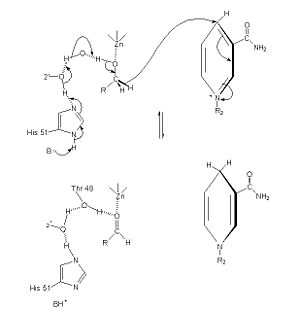
==Reaction and Mechanism== | ==Reaction and Mechanism== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 76: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of alcohol dehydrogenase== | ||
| + | [[Alcohol dehydrogenase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
| - | For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | + | For additional information, see: |
| - | + | *[[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | |
| - | + | *[[Horse Liver Alcohol Dehydrogenase]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[1uay]] - HADH II – ''Thermus thermophilus''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1zej]], [[3ctv]] - HADH – ''Archaeoglobus fulgidus''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1zcj]] - rHADH <BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2x58]] - rHADH + CoA <BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2et6]] – HADH (mutant) – ''Candida tropicalis'' | ||
| - | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
For additional information, see:
References
- ↑ Voet, et. al. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.
- ↑ Sutak R, Hrdy I, Dolezal P, Cabala R, Sedinova M, Lewin J, Harant K, Muller M, Tachezy J. Secondary alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the reduction of exogenous acetone to 2-propanol in Trichomonas vaginalis. FEBS J. 2012 Aug;279(15):2768-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08661.x. Epub, 2012 Jul 9. PMID:22686835 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08661.x
- ↑ Ismaiel AA, Zhu CX, Colby GD, Chen JS. Purification and characterization of a primary-secondary alcohol dehydrogenase from two strains of Clostridium beijerinckii. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5097-105. PMID:8349550
- ↑ Rozeboom HJ, Yu S, Mikkelsen R, Nikolaev I, Mulder HJ, Dijkstra BW. Crystal structure of quinone-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase from Pseudogluconobacter saccharoketogenes. A versatile dehydrogenase oxidizing alcohols and carbohydrates. Protein Sci. 2015 Oct 6. doi: 10.1002/pro.2818. PMID:26440996 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pro.2818
- ↑ Toyama H, Mathews FS, Adachi O, Matsushita K. Quinohemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenases: structure, function, and physiology. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004 Aug 1;428(1):10-21. PMID:15234265 doi:10.1016/j.abb.2004.03.037
- ↑ Voet, et. al. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.
- ↑ Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm>
- ↑ Protein: Alcohol Dehydrogenase. The College of Saint Benedict and Saint John's University. 1 March 2010 < http://web.archive.org/web/20080307193453/http://www.users.csbsju.edu/~hjakubow/classes/rasmolchime/99ch331proj/alcoholdehydro/index.htm>
- ↑ Voet, et. al. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: 3rd Edition. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008.
- ↑ Dickinson FM, Monger GP. A study of the kinetics and mechanism of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with a variety of substrates. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):261-70. PMID:4352908
- ↑ Dickinson FM, Monger GP. A study of the kinetics and mechanism of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with a variety of substrates. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):261-70. PMID:4352908
- ↑ Bille V, Remacle J. Simple-kinetic descriptions of alcohol dehydrogenase after immobilization on tresyl-chloride-activated agarose. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):343-8. PMID:3769934
- ↑ Dickinson FM, Monger GP. A study of the kinetics and mechanism of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with a variety of substrates. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):261-70. PMID:4352908
- ↑ Blomstrand R, Ostling-Wintzell H, Lof A, McMartin K, Tolf BR, Hedstrom KG. Pyrazoles as inhibitors of alcohol oxidation and as important tools in alcohol research: an approach to therapy against methanol poisoning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3499-503. PMID:115004
- ↑ Alcohol Dehydrogenase. Worthington Biochemical Corporation . 31 March 2010 < http://http://www.worthington-biochem.com/ADH/default.html>
- ↑ Alcohol Dehydrogenase.Worthington Biochemical Corporation . 31 March 2010 < http://http://www.worthington-biochem.com/ADH/default.html>
- ↑ Goihberg E, Dym O, Tel-Or S, Levin I, Peretz M, Burstein Y. A single proline substitution is critical for the thermostabilization of Clostridium beijerinckii alcohol dehydrogenase. Proteins. 2007 Jan 1;66(1):196-204. PMID:17063493 doi:10.1002/prot.21170
- ↑ Goihberg E, Dym O, Tel-Or S, Shimon L, Frolow F, Peretz M, Burstein Y. Thermal stabilization of the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase by a single proline substitution. Proteins. 2008 Feb 7;. PMID:18260103 doi:10.1002/prot.21946
- ↑ Goihberg E, Peretz M, Tel-Or S, Dym O, Shimon L, Frolow F, Burstein Y. Biochemical and Structural Properties of Chimeras Constructed by Exchange of Cofactor-Binding Domains in Alcohol Dehydrogenases from Thermophilic and Mesophilic Microorganisms. Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 9. PMID:20102159 doi:10.1021/bi901730x
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, David Birrer