Aldolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (18 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
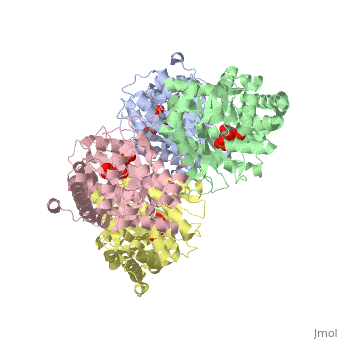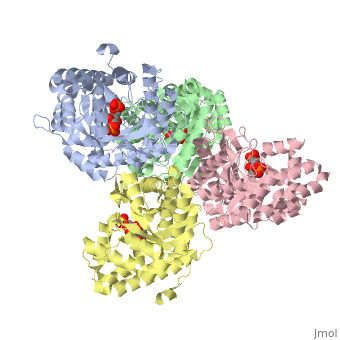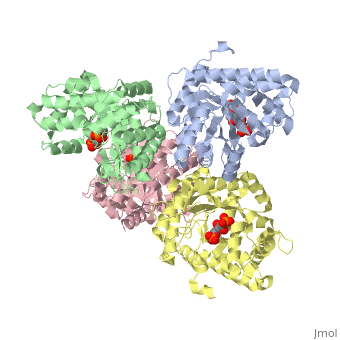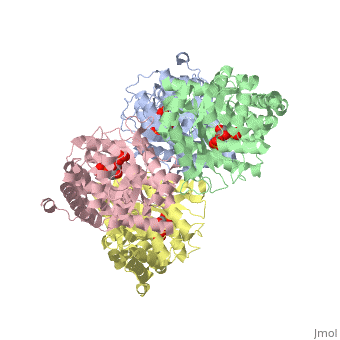
<StructureSection load='3mmt' size='340' side='right' caption='Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase tetramer complex with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, [[3mmt]]|' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3mmt' size='340' side='right' caption='Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase tetramer complex with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, [[3mmt]]|' scene=''> | ||
| + | '''Retro aldolase''' is an aldolase designed by directed evolution. | ||
| + | =Aldolase class I= | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Fructose-6-phosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of fructose-6-phosphate<ref>PMID:11120740</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase''' (FBPA) catalyzes the fourth step of glycolysis<ref>PMID:34458323</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase''' converts 2-deoxy-D-ribose-5-phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde<ref>PMID:25229427</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Dihydroneopterin aldolase''' catalyzes the conversion of 7,8-dihydropterin to 6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropterin. It is part of the folate synthesis <ref>PMID:15107504</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Sialic acid aldolase''' catalyzes the condensation of pyruvate and N-acetylmannosamine<ref>PMID:11674166</ref>. See [[N-acetylneuraminate lyase]].<br /> | ||
| + | '''Oxoadipate aldolase''' catalyzes the last step of the bacterial protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway<ref>PMID:20843800</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Oxovalerate aldolase''' catalyzes the conversion of 4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate to acetaldehyde and pyruvate<ref>PMID:8419288</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''2-keto-deoxydephosphogluconate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of 2-keto-deoxydephosphogluconate<ref>PMID:12876349</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase''' participates in the phthalide biosynthesis<ref>PMID:35845641</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | =Aldolase class II. Metal-dependent aldolase= | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatealdol to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) <ref>PMID:10712619</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the aldol condensation of DHAP with G3P to produce tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate<ref>PMID:11940603</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Fuculose-1-phosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of fuculose-1-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and lactaldehyde<ref>PMID:10821675</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''HpcH/HpaI aldolase''' catalyzes the conversion of 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-heptane-1,7-dioate into pyruvate and succinate. It is part of the aromatic compounds degradation<ref>PMID:17881002</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Oxoglutarate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate into pyruvate and glyoxylate. It belongs to the hydroxyproline degradation pathway<ref>PMID:21998747</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Threonine aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of threonine into glycine and acetaldehyde. It is part of the glycine, serine and threonine metabolism pathway<ref>PMID:13449064</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase''' participates in the degradation pathway of L-rhamnose <ref>PMID:18085797</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and glyoxylate It is part of the hydroxyproline degradation pathway<ref>PMID:21998747</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Hydroxyaspartate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of hydroxyaspartate to glyoxylate and glycine<ref>PMID:12835921</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Phenylserine aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of L-3-phenylserine to benzaldehyde and glycine<ref>PMID:16085854</ref>.<br /> | ||
= Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase = | = Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase = | ||
==Introduction and Structure== | ==Introduction and Structure== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 57: | ||
==Regulation== | ==Regulation== | ||
| - | The regulation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase is not well understood, but the understanding is | + | The regulation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase is not well understood, but the understanding is ever-increasing. As it is currently observed, aldolase C appears to be regulated mainly by the gene expression--the concentration of mRNA in the cytoplasm.<ref>Paolella, G, Buono, P, Mancini, F P, Izzo, P, and Salvatore, F. "Structure and expression of mouse aldolase genes." Eur. J. Biochem.. 156. (1986): 229-235.</ref> It is also known that adenosine 3',5'-cyclicmonophosphate (cAMP) affects the expression of the gene. cAMP concentration has been positively correlated with aldolase C expression. It is believed that cAMP acts upon a section of the promotor region, distal element D, causing the transcriptional promoter, NGFI-B, to bind. Once bound, the promoter activates the transcription of the gene coding for fructose bisphosphate aldolase.<ref>Buono, P, Cassano, S, Alfieri, A, Mancini, A, and Salvatore, F. "Human aldolase C gene expression is regulated by adenosine 30,50-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in PC12 cells." Gene. 291. (2002): 115-121.</ref> Given the inhibitory effects of an oxidant in the presence of aldolase, it is possible that this could be a mechanism of regulation of the enzyme. The deactivation that accompanies the oxidation of the surface thiol of Cys72 could be used intracellularly to slow the catalysis of the enzyme and regulate glycolysis.<ref name="kinetics" /> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | =3D structures of aldolase= | |
| - | + | [[Aldolase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[3nxf]], [[3o6y]], [[3ud6]], [[4pek]], [[4pej]], [[4pa8]] – RA – artificial gene<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ou1]] – SsRA<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
=Additional Resources= | =Additional Resources= | ||
For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Schurmann M, Sprenger GA. Fructose-6-phosphate aldolase is a novel class I aldolase from Escherichia coli and is related to a novel group of bacterial transaldolases. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 6;276(14):11055-61. Epub 2000 Dec 18. PMID:11120740 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008061200
- ↑ Pirovich DB, Da'dara AA, Skelly PJ. Multifunctional Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase as a Therapeutic Target. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Aug 11;8:719678. PMID:34458323 doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.719678
- ↑ Salleron L, Magistrelli G, Mary C, Fischer N, Bairoch A, Lane L. DERA is the human deoxyribose phosphate aldolase and is involved in stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1843(12):2913-25. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.007. Epub 2014 Sep 16. PMID:25229427 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.007
- ↑ Goyer A, Illarionova V, Roje S, Fischer M, Bacher A, Hanson AD. Folate biosynthesis in higher plants. cDNA cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of dihydroneopterin aldolases. Plant Physiol. 2004 May;135(1):103-11. Epub 2004 Apr 23. PMID:15107504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.038430
- ↑ Smith BJ, Lawrence MC, Barbosa JA. Substrate-Assisted Catalysis in Sialic Acid Aldolase. J Org Chem. 1999 Feb 5;64(3):945-949. PMID:11674166
- ↑ Wang W, Mazurkewich S, Kimber MS, Seah SY. Structural and kinetic characterization of 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxoglutarate (HMG)/4-carboxy-4-hydroxy-2-oxoadipate (CHA) aldolase: a protocatechuate degradation enzyme evolutionarily convergent with the HpaI and DmpG pyruvate aldolases. J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 15. PMID:20843800 doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.159509
- ↑ Powlowski J, Sahlman L, Shingler V. Purification and properties of the physically associated meta-cleavage pathway enzymes 4-hydroxy-2-ketovalerate aldolase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (acylating) from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):377-85. PMID:8419288
- ↑ Bell BJ, Watanabe L, Rios-Steiner JL, Tulinsky A, Lebioda L, Arni RK. Structure of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPG) aldolase from Pseudomonas putida. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003 Aug;59(Pt 8):1454-8. Epub 2003, Jul 23. PMID:12876349
- ↑ Feng WM, Liu P, Yan H, Yu G, Zhang S, Jiang S, Shang EX, Qian DW, Duan JA. Investigation of Enzymes in the Phthalide Biosynthetic Pathway in Angelica sinensis Using Integrative Metabolite Profiles and Transcriptome Analysis. Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 1;13:928760. PMID:35845641 doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.928760
- ↑ Zgiby SM, Thomson GJ, Qamar S, Berry A. Exploring substrate binding and discrimination in fructose1, 6-bisphosphate and tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases. Eur J Biochem. 2000 Mar;267(6):1858-68. PMID:10712619
- ↑ Hall DR, Bond CS, Leonard GA, Watt CI, Berry A, Hunter WN. Structure of tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Insight into chiral discrimination, mechanism, and specificity of class II aldolases. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):22018-24. Epub 2002 Apr 8. PMID:11940603 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M202464200
- ↑ Joerger AC, Gosse C, Fessner WD, Schulz GE. Catalytic action of fuculose 1-phosphate aldolase (class II) as derived from structure-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 2000 May 23;39(20):6033-41. PMID:10821675
- ↑ Rea D, Fulop V, Bugg TD, Roper DI. Structure and mechanism of HpcH: a metal ion dependent class II aldolase from the homoprotocatechuate degradation pathway of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 2;373(4):866-76. Epub 2007 Jun 26. PMID:17881002 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.048
- ↑ Riedel TJ, Johnson LC, Knight J, Hantgan RR, Holmes RP, Lowther WT. Structural and Biochemical Studies of Human 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate Aldolase: Implications for Hydroxyproline Metabolism in Primary Hyperoxaluria. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26021. Epub 2011 Oct 6. PMID:21998747 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026021
- ↑ KARASEK MA, GREENBERG DM. Studies on the properties of threonine aldolases. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jul;227(1):191-205. PMID:13449064
- ↑ Grueninger D, Schulz GE. Antenna domain mobility and enzymatic reaction of L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase. Biochemistry. 2008 Jan 15;47(2):607-14. Epub 2007 Dec 18. PMID:18085797 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi7012799
- ↑ Riedel TJ, Johnson LC, Knight J, Hantgan RR, Holmes RP, Lowther WT. Structural and Biochemical Studies of Human 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate Aldolase: Implications for Hydroxyproline Metabolism in Primary Hyperoxaluria. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26021. Epub 2011 Oct 6. PMID:21998747 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026021
- ↑ Liu JQ, Dairi T, Itoh N, Kataoka M, Shimizu S. A novel enzyme, D-3-hydroxyaspartate aldolase from Paracoccus denitrificans IFO 13301: purification, characterization, and gene cloning. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003 Jul;62(1):53-60. PMID:12835921 doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1238-2
- ↑ Misono H, Maeda H, Tuda K, Ueshima S, Miyazaki N, Nagata S. Characterization of an inducible phenylserine aldolase from Pseudomonas putida 24-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Aug;71(8):4602-9. PMID:16085854 doi:10.1128/AEM.71.8.4602-4609.2005
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Voet, D, Voet, J, & Pratt, C. (2008). Fundamentals of biochemistry, third edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- ↑ Protein: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from human (homo sapiens), muscle isozyme. (2009). Retrieved from http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Gefflaut, T., B. Casimir, J. Perie, and M. Willson. "Class I Aldolases: Substrate Specificity, Mechanism, Inhibitors and Structural Aspects." Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol.. 63. (1995): 301-340.
- ↑ Dalby A, Dauter Z, Littlechild JA. Crystal structure of human muscle aldolase complexed with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate: mechanistic implications. Protein Sci. 1999 Feb;8(2):291-7. PMID:10048322
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Sygusch, J., and Beaudry, D. "Allosteric communication in mammalian muscle aldolase." Biochem. J.. 327. (1997): 717-720.
- ↑ Paolella, G, Buono, P, Mancini, F P, Izzo, P, and Salvatore, F. "Structure and expression of mouse aldolase genes." Eur. J. Biochem.. 156. (1986): 229-235.
- ↑ Buono, P, Cassano, S, Alfieri, A, Mancini, A, and Salvatore, F. "Human aldolase C gene expression is regulated by adenosine 30,50-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in PC12 cells." Gene. 291. (2002): 115-121.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Sophie Mullinix, Jaime Prilusky, Austin Drake, David Canner