Aminopeptidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (42 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/1' caption='Bacterial leucine aminopeptidase complex with 8-hydroxyquinoline, glycerol, SCN, Zn+2 (magenta), Na+ (cyan) and Cl- (green) ions (PDB code [[3vh9]])'> |
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | [[Aminopeptidase|Aminopeptidases]] (AP) ([[EC]] 3) are metal - mostly Zn-dependent enzymes involved in the digestion of proteins. '''Cytosol AP''' (Cyt-AP) and '''AP N''' (APN) remove N-terminal amino acids. The AP are classified by the amino acid which they hydrolyze. Other types of AP are:<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Cold-activated AP''' (Col-AP)<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Heat stable AP''' from ''Thermus thermophilus'' (AmpT)<br /> | ||
| + | * '''AP from ''Staphylococcus aureus''''' (AmpS)<br /> | ||
| + | * '''SGAP''' from ''Stereomyces griseus''. See details in [[Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)]].<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Alanine aminopeptidase''' is called '''aminopeptidase N'''. See details in [[Aminopeptidase N]].<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Aminopeptidase C''' is a Phe aminopeptidase from ''Aspergillus niger''<ref>PMID:12571053</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Deblocking aminopeptidase''' (DAP) is an exoprotease aminopeptidase which can release N-terminal amino acids from blocked peptides<ref>PMID:21670507</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Beta-peptidyl AP''' (BapA) cleaves N-terminal β-homoamino acid from peptides of length 2 to 6.<ref>PMID:8440407</ref><br />. | ||
| + | * '''M1 family AP''' are Zn+2 containing amino peptidases<ref>PMID:25530263</ref><br /> | ||
| + | Aminopeptidases catalyze a release of an N-terminal amino acid from a peptide, amide, or arylamide. | ||
| - | {{TOC limit|limit=2}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Clear}} | ||
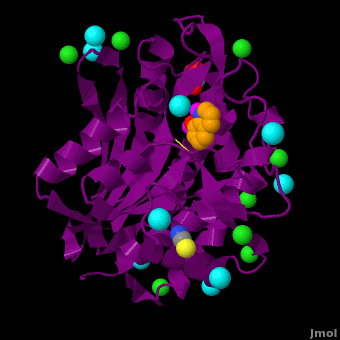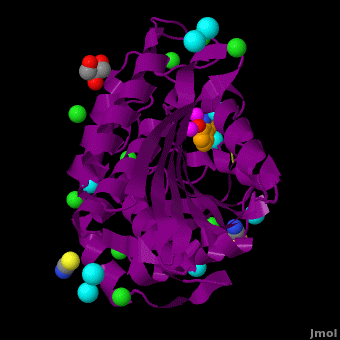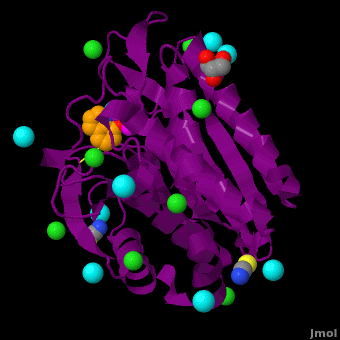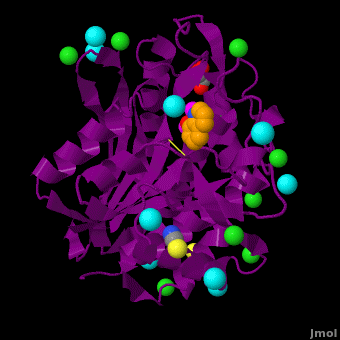
== Aminopeptidase from ''Aeromonas proteolytica''<ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-012-0873-4</ref> == | == Aminopeptidase from ''Aeromonas proteolytica''<ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-012-0873-4</ref> == | ||
| - | <Structure load='VH9.pdb' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Dinuclear Zinc(II) Peptidase, an Aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica' scene='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/1' /> | ||
The selective inhibition of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/2'>aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica (AAP)</scene>, a <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/3'>dinuclear Zn2+</scene> hydrolase, by <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/10'>8-quinolinol (8-hydroxyquinoline, 8-HQ)</scene> derivatives is reported. Based on our findings about 8-HQ-based Zn<sup>2+</sup> fluorophores, it was hypothesized that 8-HQ derivatives have the potential to function as specific inhibitors of Zn<sup>2+</sup> enzymes, especially dinuclear Zn<sup>2+</sup> hydrolases. Inhibitory assays of 8-HQ derivatives against AAP disclosed that the 8-HQ and 5-substituted 8-HQ′s are competitive inhibitors for AAP with inhibition constants (''K''i) of 0.16—29 μM at pH 8.0. <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/11'>X-ray crystal structure analysis of an AAP with 8-HQ complex</scene> (1.3 Å resolution) as well as fluorescence titrations of these drugs with AAP confirmed that <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/13'>8-hydroxyquinoline binds to AAP in the 'Pyr-out' mode</scene>, in which the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/15'>hydroxide anion of 8-HQ bridges two Zn2+ (Zn1 and Zn2)</scene> in the active site of AAP and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/17'>nitrogen atom of 8-HQ coordinates to Zn1</scene> (PDB code: [[3vh9]]). <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/18'>Overlap of active site</scene> of <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">free AAP (colored green)</span> containing Zn<sup>2+</sup>-bound <font color='red'><b>water molecule (H2O or OH-; red sphere)</b></font> ([[1rtq]]) bridging two Zn<sup>2+</sup> and <font color='darkmagenta'><b>AAP–8-HQ complex (darkmagenta,</b></font> [[3vh9]]). <font color='magenta'><b>Two Zn<sup>2+</sup> are depicted as magenta spheres</b></font>. | The selective inhibition of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/2'>aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica (AAP)</scene>, a <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/3'>dinuclear Zn2+</scene> hydrolase, by <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/10'>8-quinolinol (8-hydroxyquinoline, 8-HQ)</scene> derivatives is reported. Based on our findings about 8-HQ-based Zn<sup>2+</sup> fluorophores, it was hypothesized that 8-HQ derivatives have the potential to function as specific inhibitors of Zn<sup>2+</sup> enzymes, especially dinuclear Zn<sup>2+</sup> hydrolases. Inhibitory assays of 8-HQ derivatives against AAP disclosed that the 8-HQ and 5-substituted 8-HQ′s are competitive inhibitors for AAP with inhibition constants (''K''i) of 0.16—29 μM at pH 8.0. <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/11'>X-ray crystal structure analysis of an AAP with 8-HQ complex</scene> (1.3 Å resolution) as well as fluorescence titrations of these drugs with AAP confirmed that <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/13'>8-hydroxyquinoline binds to AAP in the 'Pyr-out' mode</scene>, in which the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/15'>hydroxide anion of 8-HQ bridges two Zn2+ (Zn1 and Zn2)</scene> in the active site of AAP and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/17'>nitrogen atom of 8-HQ coordinates to Zn1</scene> (PDB code: [[3vh9]]). <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/18'>Overlap of active site</scene> of <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">free AAP (colored green)</span> containing Zn<sup>2+</sup>-bound <font color='red'><b>water molecule (H2O or OH-; red sphere)</b></font> ([[1rtq]]) bridging two Zn<sup>2+</sup> and <font color='darkmagenta'><b>AAP–8-HQ complex (darkmagenta,</b></font> [[3vh9]]). <font color='magenta'><b>Two Zn<sup>2+</sup> are depicted as magenta spheres</b></font>. | ||
| - | |||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
== ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase == | == ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase == | ||
| - | <applet load='1xjo' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Structure of S. griseus Aminopeptidase, [[1xjo]]' /> | ||
''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline.<br/> | ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline.<br/> | ||
| + | The <scene name='Aminopeptidase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme. See details of SGAP in [[Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)]]. | ||
| - | The <scene name='Aminopeptidase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme. See details of SGAP in [[Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)]]. | ||
| - | {{Clear}} | ||
== 3D Structures of Aminopeptidase == | == 3D Structures of Aminopeptidase == | ||
| + | [[Aminopeptidase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
For additional information, see:
Amino Acid Synthesis & Metabolism
Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)
References
- ↑ Basten DE, Dekker PJ, Schaap PJ. Aminopeptidase C of Aspergillus niger is a novel phenylalanine aminopeptidase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Feb;69(2):1246-50. PMID:12571053 doi:10.1128/AEM.69.2.1246-1250.2003
- ↑ Jia B, Lee S, Pham BP, Kwack JM, Jin H, Li J, Wang Y, Cheong GW. Biochemical characterization of deblocking aminopeptidases from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(6):1160-6. PMID:21670507 doi:10.1271/bbb.110114
- ↑ Taylor A. Aminopeptidases: structure and function. FASEB J. 1993 Feb 1;7(2):290-8. PMID:8440407
- ↑ Cadel S, Darmon C, Pernier J, Hervé G, Foulon T. The M1 family of vertebrate aminopeptidases: role of evolutionarily conserved tyrosines in the enzymatic mechanism of aminopeptidase B. Biochimie. 2015 Feb;109:67-77. PMID:25530263 doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2014.12.009
- ↑ Hanaya K, Suetsugu M, Saijo S, Yamato I, Aoki S. Potent inhibition of dinuclear zinc(II) peptidase, an aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica, by 8-quinolinol derivatives: inhibitor design based on Zn(2+) fluorophores, kinetic, and X-ray crystallographic study. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Feb 5. PMID:22311113 doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0873-4
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Eran Hodis