Mannosidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (20 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
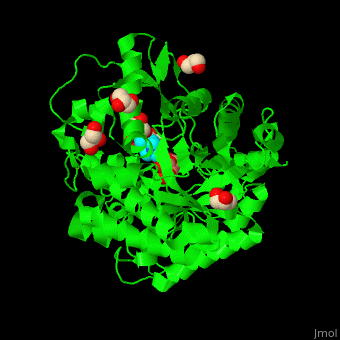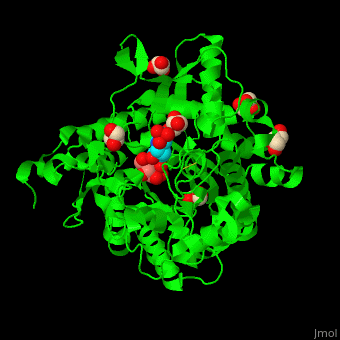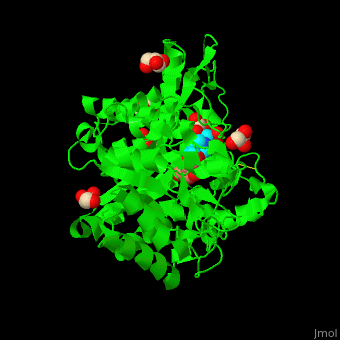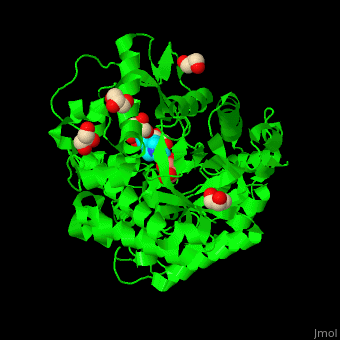
| - | + | <StructureSection load='4jie' size='350' side='right' caption='Rice β-mannosidase complex with β-mannose, glycerol and HEPES (PDB entry [[4jie]])' scene='45/458458/Cv/1'> | |
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Mannosidase''' (MAN) is an enzyme which hydrolyzes mannose. There are 2 kinds of MAN. | + | '''Mannosidase''' (MAN) is an enzyme which hydrolyzes mannose. There are 2 kinds of MAN. '''α-MAN''' which hydrolyzes α-mannose<ref>PMID:12634058</ref> and '''β-MAN''' which hydrolyzes β-1,4-linked manno-oligosaccharides<ref>PMID:10553664</ref>. α-MAN isozymes are classified as class I and II. |
| + | * '''Mannan endo-1,4-β-MAN''' hydrolyzes 1-4-β-D-mannosidic linkages in mannans, galactomannans and glucomannans. | ||
| + | * '''Endo-1,2-α-MAN''' is the Endo-acting glycoside hydrolase involved in N-glycan trimming located in the Golgi<ref>PMID:33154157</ref> | ||
| + | See some details in [[Molecular Playground/ERMan1]]. See also [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]]. | ||
| - | + | == Disease == | |
| + | α-mannosidosis is manifested by accumulation of mannose-containing oligosaccharides leading to mental retardation, hearing impairment, skeletal changes and immunodeficiency<ref>PMID:9915946</ref>. β-MAN deficiency called β-mannosidosis is a disorder of oligosaccharide metabolism<ref>PMID:12890191</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | <scene name='45/458458/Cv/5'>The active site of β-MAN contains β-mannose</scene><ref>PMID:24100330</ref>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
==3D structures of mannosidase== | ==3D structures of mannosidase== | ||
| + | [[Mannosidase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | == | + | == References == |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ===α-MAN class I=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1fmi]] - hαMAN I - human<br /> | ||
| - | [[1fo2]] - hαMAN I + deoxymannojirimycin<br /> | ||
| - | [[1fo3]] - hαMAN I+ kifunensine<br /> | ||
| - | [[1dl2]] - αMAN I catalytic domain + mannose - yeast<br /> | ||
| - | [[2ri8]] - PcαMAN I + glycerol – ''Penicillium citrinum''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1kre]], [[1kkt]] - PcαMAN I + mannose<br /> | ||
| - | [[2ri9]] - PcαMAN I + substrate analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[1krf]] - PcαMAN I + kifunensine + mannose<br /> | ||
| - | [[1x9d]] - hαMAN I residues 243-699 + polysaccharide analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[1nxc]] - αMAN I + mannose – mouse<br /> | ||
| - | [[1g6i]] - αMAN I + deoxymannojirimycin<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===α-MAN class II=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2wyh]] - SpαMAN II – ''Streptococcus pyrogenes''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3bub]], [[1hty]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain – ''Drosophila melanogaster''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3bud]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | [[3bui]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + Tris<br /> | ||
| - | [[3bup]], [[3buq]], [[3czs]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + mannose<br /> | ||
| - | [[3bvt]], [[3bvu]], [[3bvv]], [[3bvw]], [[3bvx]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + mannopyranoside<br /> | ||
| - | [[1r33]], [[1r34]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + mannopyranoside<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ddf]], [[3ddg]], [[2f18]], [[2f1a]], [[2f1b]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + pyrrolidin<br /> | ||
| - | [[2alw]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + noeuromycin<br /> | ||
| - | [[3cv5]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + polysaccharide<br /> | ||
| - | [[3czn]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + polysaccharide<br /> | ||
| - | [[2wyi]] - SpαMAN II + swainsonine<br /> | ||
| - | [[3blb]], [[1hww]] - DmαMAN II + swainsonine<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ejp]], [[3ejq]], [[3ejr]], [[3ejs]], [[3ejt]], [[3eju]], [[2ow6]], [[2ow7]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + swainsonine analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[3dx0]], [[3dx2]], [[2f7o]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + mannostatine<br /> | ||
| - | [[3dx1]], [[3dx3]], [[3dx4]], [[2f7p]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + mannostatine analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[3d4y]], [[3d4z]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + imidazole derivative<br /> | ||
| - | [[3d50]], [[3d51]], [[3d52]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2fyv]], [[2f7q]], [[2f7r]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + amino-salacinol carboxylate analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[1tqv]], [[1tqw]], [[1tqs]], [[1tqt]], [[1tqu]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + seleno-salacinol<br /> | ||
| - | [[1ps3]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + kifunensine<br /> | ||
| - | [[1qwn]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + intermediate<br /> | ||
| - | [[1hxk]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain + deoxymannojirimycin<br /> | ||
| - | [[1qwu]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + guloside<br /> | ||
| - | [[1qx1]] - DmαMAN II catalytic domain (mutant) + mannosyl | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===β-MAN=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2je8]] - BtβMAN residues 26-864 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2wbk]] - BtβMAN residues 26-864 + mannopyranoside <br /> | ||
| - | [[2vqt]], [[2vr4]], [[2vjx]], [[2vl4]], [[2vmf]], [[2vo5]], [[2vot]], [[2vqu]] - BtβMAN residues 26-864 + piperidine derivative<br /> | ||
| - | [[1oh4]], [[1of4]] - TmβMAN catalytic domain + mannose – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1of3]] - TmβMAN catalytic domain<br /> | ||
| - | [[1gvy]] - βMAN (mutant) + mannotrioside – ''Pseudomonas cellulose''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1uz4]] - CmβMAN + inhibitor – ''Cellvibrio mixtus''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1uuq]] - CmβMAN<br /> | ||
| - | [[2c0h]] - βMAN (mutant) – blue mussel<br /> | ||
| - | [[2whk]] - βMAN – ''Bacillus subtilis'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Heikinheimo P, Helland R, Leiros HK, Leiros I, Karlsen S, Evjen G, Ravelli R, Schoehn G, Ruigrok R, Tollersrud OK, McSweeney S, Hough E. The structure of bovine lysosomal alpha-mannosidase suggests a novel mechanism for low-pH activation. J Mol Biol. 2003 Mar 28;327(3):631-44. PMID:12634058
- ↑ Ademark P, Lundqvist J, Hagglund P, Tenkanen M, Torto N, Tjerneld F, Stalbrand H. Hydrolytic properties of a beta-mannosidase purified from Aspergillus niger. J Biotechnol. 1999 Oct 8;75(2-3):281-9. PMID:10553664
- ↑ Sobala LF, Fernandes PZ, Hakki Z, Thompson AJ, Howe JD, Hill M, Zitzmann N, Davies S, Stamataki Z, Butters TD, Alonzi DS, Williams SJ, Davies GJ. Structure of human endo-alpha-1,2-mannosidase (MANEA), an antiviral host-glycosylation target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 5. pii: 2013620117. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.2013620117. PMID:33154157 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2013620117
- ↑ Berg T, Riise HM, Hansen GM, Malm D, Tranebjaerg L, Tollersrud OK, Nilssen O. Spectrum of mutations in alpha-mannosidosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Jan;64(1):77-88. PMID:9915946 doi:http://dx.doi.org/S0002-9297(07)61660-7
- ↑ Uchino Y, Fukushige T, Yotsumoto S, Hashiguchi T, Taguchi H, Suzuki N, Konohana I, Kanzaki T. Morphological and biochemical studies of human beta-mannosidosis: identification of a novel beta-mannosidase gene mutation. Br J Dermatol. 2003 Jul;149(1):23-9. PMID:12890191
- ↑ Tankrathok A, Iglesias-Fernandez J, Luang S, Robinson RC, Kimura A, Rovira C, Hrmova M, Ketudat Cairns JR. Structural analysis and insights into the glycon specificity of the rice GH1 Os7BGlu26 beta-D-mannosidase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Oct;69(Pt 10):2124-35. doi:, 10.1107/S0907444913020568. Epub 2013 Sep 20. PMID:24100330 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0907444913020568