Plasminogen activator
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Plasminogen activator''' (PLA) is a serine protease which converts plasminogen to plasmin. TPA structure contains heavy and light chains (HC, LC). PLA is inhibited by PLA inhibitor 1 and 2. | '''Plasminogen activator''' (PLA) is a serine protease which converts plasminogen to plasmin. TPA structure contains heavy and light chains (HC, LC). PLA is inhibited by PLA inhibitor 1 and 2. | ||
| - | *'''Tissue PLA''' (TPA) which is involved in breakdown of blood clots | + | *'''Tissue PLA''' (TPA) which is involved in breakdown of blood clots. |
| + | *'''Urokinase-type PLA''' see [[Urokinase]].<br /> | ||
*'''Coagulase/fibrinolysin''' is a plasminogen activator from ''Yersinia pestis'' which possesses coagulase activity is responsible for degradation of plasmid-coded outer membrane proteins<ref>PMID:2843471</ref>. | *'''Coagulase/fibrinolysin''' is a plasminogen activator from ''Yersinia pestis'' which possesses coagulase activity is responsible for degradation of plasmid-coded outer membrane proteins<ref>PMID:2843471</ref>. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
Treatment with tissue PLA for acute ischemic stroke is beneficial<ref>PMID:7477192</ref>. | Treatment with tissue PLA for acute ischemic stroke is beneficial<ref>PMID:7477192</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
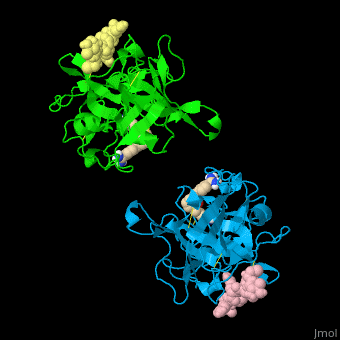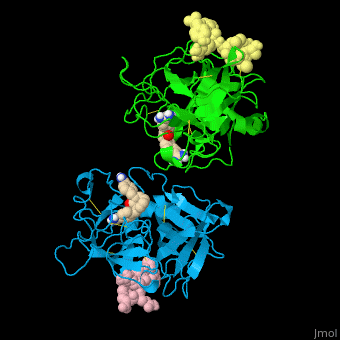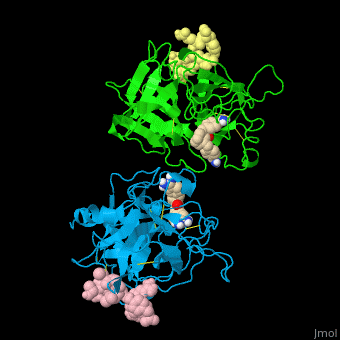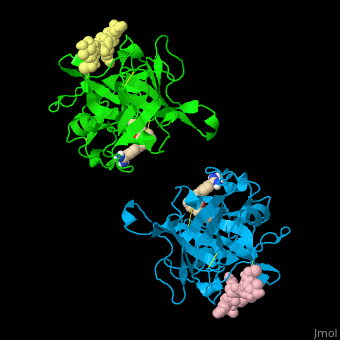
| - | *<scene name='47/476004/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='47/476004/Cv/4'>Interactions between tissue plasminogen activator light chain catalytic domain and heavy chain catalytic domain fragment</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
| - | *<scene name='47/476004/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='47/476004/Cv/5'>Benzamidine binding site</scene>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of plasminogen activator== | ==3D structures of plasminogen activator== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
**[[1bqy]] – PLA – Pit viper | **[[1bqy]] – PLA – Pit viper | ||
| - | *Tissue plasminogen activator | + | *Tissue plasminogen activator; Domains – fibrin-binding 36-85; kringle 1 69-153; kringle 2 209-298; catalytic 311-561 |
**[[1a5h]] – hTPA HC+LC + benzamidine – human<br /> | **[[1a5h]] – hTPA HC+LC + benzamidine – human<br /> | ||
**[[1rtf]] - hTPA HC+LC<br /> | **[[1rtf]] - hTPA HC+LC<br /> | ||
**[[1tpg]] – hTPA F1-G - NMR<br /> | **[[1tpg]] – hTPA F1-G - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1bda]] – hTPA catalytic domain (mutant) + EGR-CMK<br /> | ||
**[[1pk2]] – hTPA kringle 2 domain + 6-aminohexanoic acid – NMR<br /> | **[[1pk2]] – hTPA kringle 2 domain + 6-aminohexanoic acid – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1tpk]], [[1pml]] - hTPA kringle 2 domain<br /> | **[[1tpk]], [[1pml]] - hTPA kringle 2 domain<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1kdu]] - hTPA kringle domain – NMR<br /> | + | **[[1kdu]] - hTPA kringle 1 domain – NMR<br /> |
**[[1tpm]], [[1tpn]] - hTPA fibrin-binding domain – NMR<br /> | **[[1tpm]], [[1tpn]] - hTPA fibrin-binding domain – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1bda]] – hTPA catalytic domain (mutant) + EGR-CMK<br /> |
| - | + | **[[5brr]], [[5zlz]] - hTPA catalytic domain (mutant) + plasminogen activator inhibitor 1<br /> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
*Coagulase/fibrinolysin | *Coagulase/fibrinolysin | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of plasminogen activator
Updated on 21-July-2024
References
- ↑ Sodeinde OA, Sample AK, Brubaker RR, Goguen JD. Plasminogen activator/coagulase gene of Yersinia pestis is responsible for degradation of plasmid-encoded outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2749-52. PMID:2843471
- ↑ . Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 14;333(24):1581-7. PMID:7477192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199512143332401