Ubiquitin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (39 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human ubiquitin (green) complex with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 (deep sky blue), [[3k9p]]' scene='41/417541/Cv/3' > | |
| - | + | == Function == | |
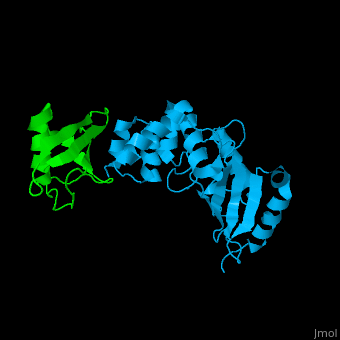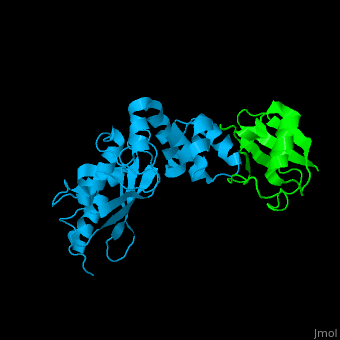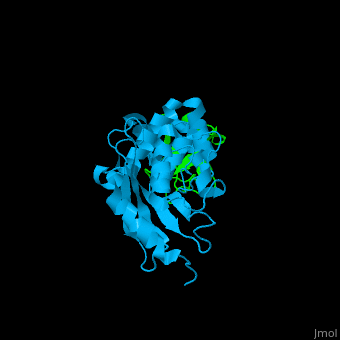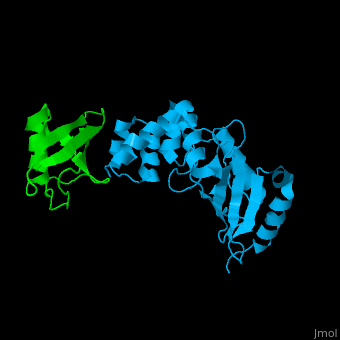
| - | + | [[Ubiquitin]] (UBB) is found in almost all cells. It binds to proteins tagging them for destruction in the proteasome. UBB is activated by the UBB-activating enzymes E1, E2 and E3. '''Ubiquitin+1''' is a frameshifted mutant of UBB observed in several diseases. A dimer of UBB (DiUBB) is formed by linkage of K48 to the C-terminus of a second UBB molecule. '''Polyubiquitin''' (polyUBB) is a chain of ubiquitin molecules bound by peptide bonds. PolyUBB can be formed by lysine residues: K6, K11, K27, 29, K33, K48, and K63. Different lysine linkages convey different functions to polyUBB. Lys48- linked polyUBB and LYs11-linked polyUBB are associated with proteasome degradation; Lys63-linked and Lys-6 polyUBB are associated with non-proteolytic functions<ref>PMID:18438605</ref>. At least 4 UBB molecules are needed to tag a protein for the proteasome<ref>PMID:9759494</ref>. <scene name='41/417541/Cv/4'>Human ubiquitin interactions with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2</scene> ([[3k9p]]). For details see<br /> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Ubiquitin]] (UBB) is found in almost all cells. It binds to proteins tagging them for destruction in the proteasome. UBB is activated by the UBB-activating enzymes E1, E2 and E3. | + | |
* [[Ubiquitin Structure & Function]]<br /> | * [[Ubiquitin Structure & Function]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Ubiquitin and Ubiquitination]]<br /> | ||
* [[Ubiquitin salt bridge discussion]]<br /> | * [[Ubiquitin salt bridge discussion]]<br /> | ||
* [[Ubiquitin chains]]. | * [[Ubiquitin chains]]. | ||
| - | + | Professors Ciechanover, Hershko and Rose received the '''Nobel Prize''' in 2004 for their discovery of the process by which ubiquitin mediates protein proteolysis<ref>PMID:15646859</ref>. | |
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
| - | See: | + | See also: |
| - | + | *[[Tumor susceptibility gene 101]] | |
| - | + | *[[SUMO]] | |
| - | + | == Disease == | |
| - | + | The UBB-proteasome system deregulation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson disease, Huntington disease, Prion-like lethal disorders and in genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis, angelman's syndrome, Liddle syndrome and many cancers<ref>PMID:18937370</ref>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | == | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | ==[[3D structures of ubiquitin]]== |
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Li W, Ye Y. Polyubiquitin chains: functions, structures, and mechanisms. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Aug;65(15):2397-406. PMID:18438605 doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8090-6
- ↑ Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425-79. PMID:9759494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.425
- ↑ Neefjes J, Groothuis TA, Dantuma NP. [The 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2004 Dec 25;148(52):2579-82 PMID:15646859
- ↑ Paul S. Dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in multiple disease conditions: therapeutic approaches. Bioessays. 2008 Nov;30(11-12):1172-84. doi: 10.1002/bies.20852. PMID:18937370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bies.20852
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky