Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
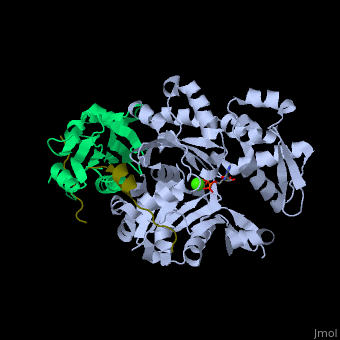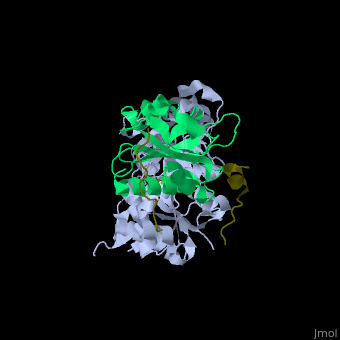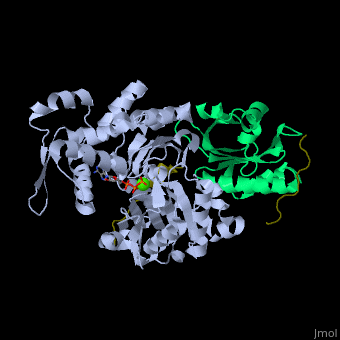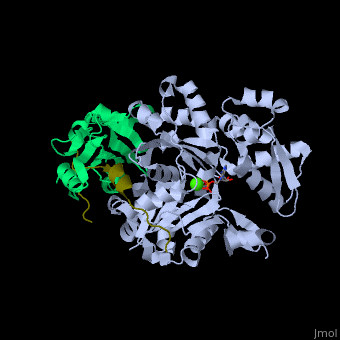
| - | <StructureSection load='' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human VASP (dark olive) complex with α-actin (cyan), profilin-1 (green), ATP (stick model) and Ca+2 ion (green), [[2pbd]]' scene='50/508423/Cv/7' > |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein''' (VASP) belongs to the Ena-VASP family. It binds proteins with E/DFPPPPXD/E motif and targets them to focal adhesion cell membranes. VASP is an actin- and profilin-binding protein<ref>PMID:16197368</ref>. VASP is associated with filament formation and promotes elongation. | '''Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein''' (VASP) belongs to the Ena-VASP family. It binds proteins with E/DFPPPPXD/E motif and targets them to focal adhesion cell membranes. VASP is an actin- and profilin-binding protein<ref>PMID:16197368</ref>. VASP is associated with filament formation and promotes elongation. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Structural highlights == | ==Structural highlights == | ||
| - | + | <scene name='50/508423/Cv/9'>Human VASP complex with α-actin, profilin-1, ATP (stick model) and Ca+2 ion</scene> ([[2pbd]]). VASP binds actin with a <scene name='50/508423/Cv/10'>poly-Pro site</scene><ref>PMID:17914456</ref>. | |
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structure of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein== | ==3D structure of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | [[1egx]] – hVASP EVH1 domain – human – NMR<BR /> | + | [[1egx]] – hVASP EVH1 domain 1-115 – human – NMR<BR /> |
| - | [[ | + | [[1use]] - hVASP tetramerization domain 335-379<br /> |
| - | [[2pav]], [[ | + | [[1usd]] - hVASP tetramerization domain (mutant)<br /> |
| + | [[2pav]], [[3chw]] – hVASP 199-214 + actin + profilin-1<br /> | ||
| + | [[2pbd]] – hVASP poly Pro domain 203-245 + actin + profilin-1<br /> | ||
| + | [[2v8c]] – hVASP 165-184 + profilin-2<br /> | ||
| + | [[8gat]], [[8gau]] – hVASP tetramerization domain/neuroaminidase + antibody – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structure of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein
Updated on 22-August-2024
1egx – hVASP EVH1 domain 1-115 – human – NMR
1use - hVASP tetramerization domain 335-379
1usd - hVASP tetramerization domain (mutant)
2pav, 3chw – hVASP 199-214 + actin + profilin-1
2pbd – hVASP poly Pro domain 203-245 + actin + profilin-1
2v8c – hVASP 165-184 + profilin-2
8gat, 8gau – hVASP tetramerization domain/neuroaminidase + antibody – Cryo EM
References
- ↑ Wentworth JK, Pula G, Poole AW. Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is phosphorylated on Ser157 by protein kinase C-dependent and -independent mechanisms in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem J. 2006 Jan 15;393(Pt 2):555-64. PMID:16197368 doi:http://dx.doi.org/BJ20050796
- ↑ Lee SY, Gertler FB, Goldberg MB. Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein restricts cell-to-cell spread of Shigella flexneri at the cell periphery. Microbiology. 2015 Nov;161(11):2149-60. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000173. Epub 2015 Sep , 9. PMID:26358985 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000173
- ↑ Ferron F, Rebowski G, Lee SH, Dominguez R. Structural basis for the recruitment of profilin-actin complexes during filament elongation by Ena/VASP. EMBO J. 2007 Oct 31;26(21):4597-606. Epub 2007 Oct 4. PMID:17914456