Electrostatic potential maps
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→See Also) |
(→See Also) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Electrostatic interactions]] in Proteopedia. | *[[Electrostatic interactions]] in Proteopedia. | ||
| + | *[[Jmol/Electrostatic potential]] methods. | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isopotential_map Isopotential Map in Wikipedia] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isopotential_map Isopotential Map in Wikipedia] | ||
*[http://compbio.clemson.edu/sapp/delphi_webserver/ Delphi Web Server] | *[http://compbio.clemson.edu/sapp/delphi_webserver/ Delphi Web Server] | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 25 August 2024
It is revealing to visualize the distribution of electrostatic charges, electrostatic potential, on molecular surfaces. Most protein-protein and protein-ligand interactions are largely electrostatic in nature, via hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions. Their strengths are modulated by the nature of the solvent: pure water or high ionic strength aqueous solution.
Gallery
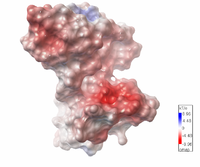 | Electrostatic potential map of 1tsj made with the Embedded Python Molecular Viewer from the Center for Computational Structural Biology of the Scripps Research Institute.
Click on the image to enlarge. |
See Also
- Electrostatic interactions in Proteopedia.
- Jmol/Electrostatic potential methods.
- Isopotential Map in Wikipedia
- Delphi Web Server
