Acetyl-CoA synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
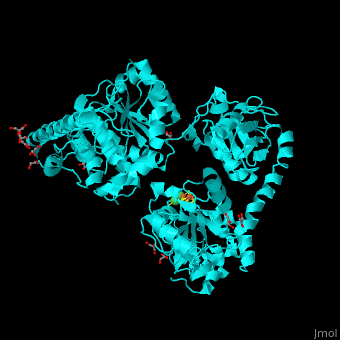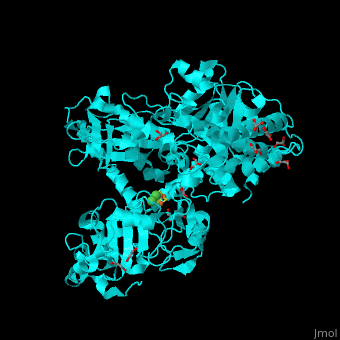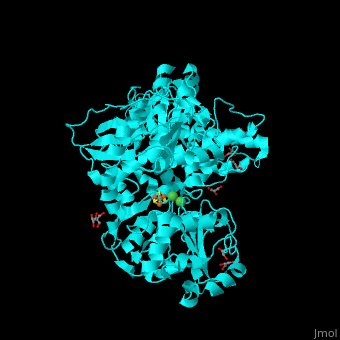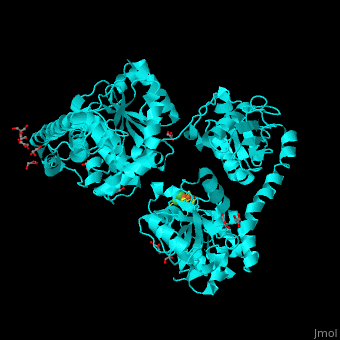
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='49/492892/Cv/8' caption='Acetyl-CoA synthase IV subunit α with Fe4S4 center complex with glycerol (stick model) and Ni+2 ions (green) [[1ru3]]'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='49/492892/Cv/8' caption='Acetyl-CoA synthase IV subunit α with Fe4S4 center complex with glycerol (stick model) and Ni+2 ions (green) [[1ru3]]'> | ||
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* '''ACS-III''' uses pyruvate as the source of CO2 and 2 electrons to produce acetyl-CoA.<br /> | * '''ACS-III''' uses pyruvate as the source of CO2 and 2 electrons to produce acetyl-CoA.<br /> | ||
* '''ACS-IV''' catabolizes CO to CO2. <br /> | * '''ACS-IV''' catabolizes CO to CO2. <br /> | ||
| - | ACS can form a bifunctional entity with carbon monoxide dehydrogenase ('''CODH/ACS'''). CODH/ACS is part of the | + | ACS can form a bifunctional entity with [[carbon monoxide dehydrogenase]] ('''CODH/ACS'''). CODH/ACS is part of the [[Wood-Ljungdahl pathway]] of [[Carbon Fixation|carbon fixation]] using CO and methyl group to produce acetyl-CoA. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
ACS-I and ACS-II contain 5 subunits: α, β, γ, δ, ε. ACS-III is composed of 2 proteins: 2α+2β and γ+δ. ACS-IV is composed of α monomer. | ACS-I and ACS-II contain 5 subunits: α, β, γ, δ, ε. ACS-III is composed of 2 proteins: 2α+2β and γ+δ. ACS-IV is composed of α monomer. | ||
| - | *<scene name='49/492892/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='49/492892/Cv/11'>Fe4S4 center and 2 Ni+2 ions form interactions with 6 cysteine residues</scene> in Acetyl-CoA synthase IV subunit α from ''Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans'' ([[1ru3]]).<ref>PMID:14699043</ref> Water molecules shown as red spheres. |
| - | + | ||
==3D structures of acetyl-CoA synthase== | ==3D structures of acetyl-CoA synthase== | ||
| + | [[Acetyl-CoA synthase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | <b>References</b><br> | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Category: Topic Page]] | [[Category: Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Svetlitchnyi V, Dobbek H, Meyer-Klaucke W, Meins T, Thiele B, Romer P, Huber R, Meyer O. A functional Ni-Ni-[4Fe-4S] cluster in the monomeric acetyl-CoA synthase from Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 13;101(2):446-51. Epub 2003 Dec 29. PMID:14699043 doi:10.1073/pnas.0304262101