GLP-1
From Proteopedia
m (GLP-1 moved to Glucagon-like peptide 1: help with search) |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | '''Glucagon-like peptide 1''' (GLP-1) is a hormone involved in insulin regulation. It was discovered when researchers found that glucose in the digestive tract led to higher insulin levels than the same amount of glucose administered directly in the blood stream<ref>PMID: 31767182</ref>. GLP-1 is produced in specialized cells in the intestine and in the pancreas, is released into the blood and has effects on cells in the pancreas, in the brain, and in many other organs. The half-life of GLP-1 is on the order of minutes, so it exerts a short-term effect unless continuously produced. | |
| - | <StructureSection size='340' side='right' scene=' | + | <StructureSection size='340' side='right' scene='10/1067195/Glp1_only/1'> |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
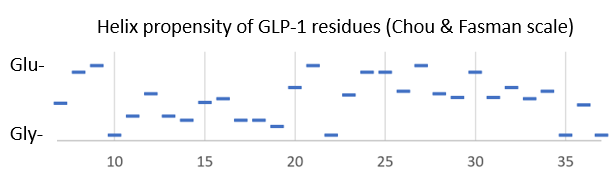
| - | Bound to the GLP-1 receptor, GLP-1 has an <scene name='10/1067195/Glp1_only/1'> | + | Bound to the GLP-1 receptor, GLP-1 has an alpha-helical structure <scene name='10/1067195/Glp1_only/1'>(reload initial scene)</scene> that is <scene name='10/1067195/Cv1/1'>bent</scene> near glycine 22 in some complexes. In solution, GLP-1 is <scene name='10/1067195/Glp-1_solution/1'>alpha-helical in its center</scene> according to NMR data when in the presence of helix-stabilizers, and fairly unstructured otherwise<ref>DOI:10.1002/mrc.880</ref>. Looking at the helix-propensity of the peptide sequence, the N-terminal part of Glp-1 (7-37) is less likely to be alpha-helical than the C-terminal half. |
| - | == Synthesis == | + | [[Image:GLP1 helix propensity.PNG]] |
| - | + | ||
| + | == Synthesis through proglucagon processing== | ||
| + | <scene name='10/1067195/Proglucagon/1'>Proglucagon</scene> is a prohormone made of 177 amino acids (in humans). In the polypeptide form, it is inactive until processed to yield mature hormones. Proglucagon is found in the human body, specifically in L-cells (within the gut) and 𝜶-cells (within the pancreas). | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is broken down using specific enzymes called prohormone convertases (PCs). These convertases are endopeptidases (they can act in the middle of an extended peptide), different from exopeptidases DPP-4 and CPE, which also play a role in GLP-1 synthesis and degradation. | ||
| + | In healthy individuals, PCs produce GLP-1 precursors in L-cells and glucagon precursors in 𝜶-cells. These then are trimmed on the C-terminal side by carboxypeptidase E (CPE), and sometimes the C-terminus is amidated<ref>PMID: 11375130</ref>. Other pathways of proglucagon yield other products such as GRPP, and IP-1 in the pancreas and Glicentin, GRRP, Oxyntomodulin, and GLP-2 in the intestines <ref>PMID: 19116373</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Glucagon and GLP-1 work to balance the levels of sugar in the blood. However, when a person has type 2 diabetes, they struggle to lower blood sugar on their own, due to a resistance to insulin. As a result of diabetes, proglucagon processes differently in order to adapt. For people with type 2 diabetes, proglucagon may yield GLP-1 in 𝜶-cells rather than glucagon<ref>PMID: 34280055</ref>. | ||
== Degradation == | == Degradation == | ||
| - | GLP-1 is initially degraded by [[dipeptidyl peptidase IV]]. | + | GLP-1 (7-39) is initially <scene name='10/1067195/Glp1_only/3'>degraded</scene> by [[dipeptidyl peptidase IV]] to yield GLP-1 (9-37) (<scene name='10/1067195/Glp1_only/2'>detail</scene>). For a discussion how this affects the half-life of GLP-1 and synthetic analogs, see the [[semaglutide]] article. |
== Binding to receptor == | == Binding to receptor == | ||
| - | GLP-1 binds to the extracellular side of | + | GLP-1 binds to the extracellular side of its receptor. By <scene name='84/841095/Cv1/1'>binding</scene> to the receptor, GLP-1 acts as agonist, leading to conformational change and intracellular consequences. For more information about the receptor, see [[GLP-1R]]. |
== Consequences of receptor binding == | == Consequences of receptor binding == | ||
| + | In the pancreas, GLP-1 plays a critical role in glucose regulation through its glucose-dependent insulin secretion. It stimulates insulin release only when blood glucose levels are elevated, preventing hypoglycemia. In the brain, GLP-1 receptor agonists play a significant role in regulating feeding behaviors and appetite<ref>PMID: 34975402</ref>. In the heart, GLP-1 receptor activation has several cardio-protective effects. It reduces oxidative stress (unstable molecules with not enough antioxidants to neutralize) and improves cardiac function during low blood flow events. These and other actions make GLP-1 beneficial for patients with type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease<ref>PMID: 17928588</ref>. | ||
| + | ==3D structures of glucagon-like peptide== | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | [[1dor]] - hGLP-1 residues 7-36 - human - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[6vcb]], [[6x18]], [[7duq]], [[9ivg]] - hGLP-1 + GLP-1 receptor + Gs complex + nanobody - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | [[2l63]], [[2l64]] - hGLP-2 residues 146-178 - NMR<br /> | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | == Student contributors == | ||
| + | This page was created as a two-week project of an undergraduate biochemistry course. Karsten Theis would like to acknowledge contributors Jamie, Travon Patterson, Spencer J. Edwards, Pam, Summer, and Hyacinth Osei. | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a hormone involved in insulin regulation. It was discovered when researchers found that glucose in the digestive tract led to higher insulin levels than the same amount of glucose administered directly in the blood stream[1]. GLP-1 is produced in specialized cells in the intestine and in the pancreas, is released into the blood and has effects on cells in the pancreas, in the brain, and in many other organs. The half-life of GLP-1 is on the order of minutes, so it exerts a short-term effect unless continuously produced.
| |||||||||||
Student contributors
This page was created as a two-week project of an undergraduate biochemistry course. Karsten Theis would like to acknowledge contributors Jamie, Travon Patterson, Spencer J. Edwards, Pam, Summer, and Hyacinth Osei.
References
- ↑ Müller TD, Finan B, Bloom SR, D'Alessio D, Drucker DJ, Flatt PR, Fritsche A, Gribble F, Grill HJ, Habener JF, Holst JJ, Langhans W, Meier JJ, Nauck MA, Perez-Tilve D, Pocai A, Reimann F, Sandoval DA, Schwartz TW, Seeley RJ, Stemmer K, Tang-Christensen M, Woods SC, DiMarchi RD, Tschöp MH. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol Metab. 2019 Dec;30:72-130. PMID:31767182 doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2019.09.010
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mrc.880
- ↑ Friis-Hansen L, Lacourse KA, Samuelson LC, Holst JJ. Attenuated processing of proglucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 in carboxypeptidase E-deficient mice. J Endocrinol. 2001 Jun;169(3):595-602. PMID:11375130 doi:10.1677/joe.0.1690595
- ↑ Ali S, Drucker DJ. Benefits and limitations of reducing glucagon action for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Mar;296(3):E415-21. PMID:19116373 doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90887.2008
- ↑ Ramzy A, Kieffer TJ. Altered islet prohormone processing: a cause or consequence of diabetes? Physiol Rev. 2022 Jan 1;102(1):155-208. PMID:34280055 doi:10.1152/physrev.00008.2021
- ↑ Chen XY, Chen L, Yang W, Xie AM. GLP-1 Suppresses Feeding Behaviors and Modulates Neuronal Electrophysiological Properties in Multiple Brain Regions. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Dec 17;14:793004. PMID:34975402 doi:10.3389/fnmol.2021.793004
- ↑ Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. 2007 Oct;87(4):1409-39. PMID:17928588 doi:10.1152/physrev.00034.2006