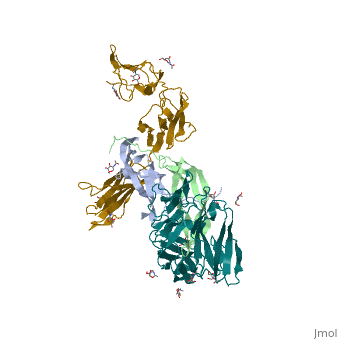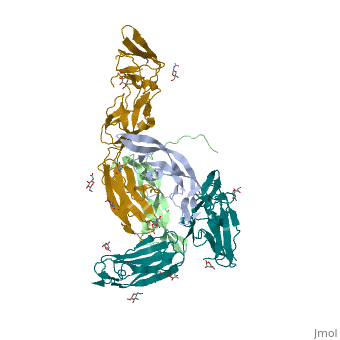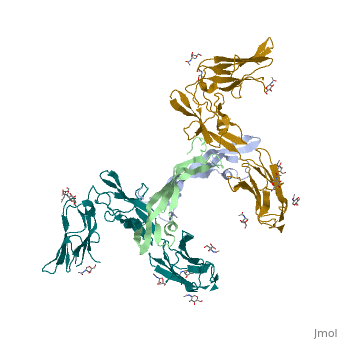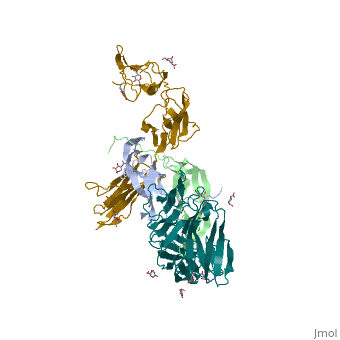
Platelet-derived growth factors and receptors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
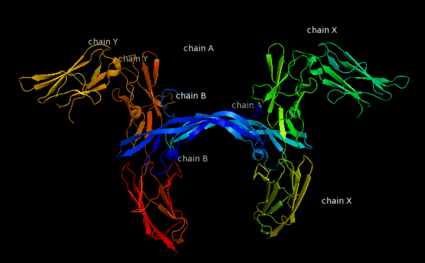
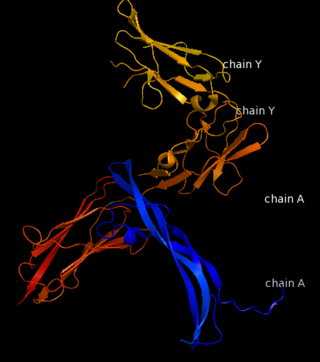
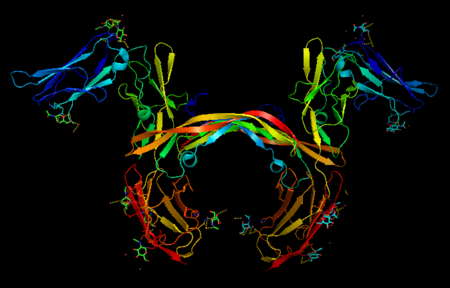
| - | '''Platelet-derived growth factor receptors, PDGF-R''', are cell surface [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|tyrosine kinase receptors]] for members of the platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs). PDGF (Chains A and B) is a 172 amino acid sequence consisting of one alpha helix and eight beta-pleated sheets. PDGF function as disulfide-linked dimers. PDGFs have a cysteine-knot-fold growth factor domain of ∼100 amino acids involved in receptor-binding and dimerization. The synthesis and processing of PDGFs is highly regulated. There are two forms of PDGF-R, alpha and beta, which are each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor binds to the receptor, PDGF-R homodimerizes or heterodimerizes<ref>PMID:1315403</ref>. The PDGF-R is a 289 amino acid sequence consisting of two alpha helices and twenty-nine beta-pleated sheets. Together these form the PDGF-R complex<ref>PMID:20534510</ref> . | + | '''Platelet-derived growth factor receptors, PDGF-R''', are cell surface [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|tyrosine kinase receptors]] for members of the '''platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs)'''. PDGF (Chains A and B) is a 172 amino acid sequence consisting of one alpha helix and eight beta-pleated sheets. PDGF function as disulfide-linked dimers. PDGFs have a cysteine-knot-fold growth factor domain of ∼100 amino acids involved in receptor-binding and dimerization. The synthesis and processing of PDGFs is highly regulated. There are two forms of PDGF-R, alpha and beta, which are each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor binds to the receptor, PDGF-R homodimerizes or heterodimerizes<ref>PMID:1315403</ref>. The PDGF-R is a 289 amino acid sequence consisting of two alpha helices and twenty-nine beta-pleated sheets. Together these form the PDGF-R complex<ref>PMID:20534510</ref> . |
[[Image:Labeled PDGF-R_r.png|left|425px]] | [[Image:Labeled PDGF-R_r.png|left|425px]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
Pharmaceutical research has been targeting inhibiting PDGF-PDGFR signaling as a potential for anti-cancer treatments. Strategies of blocking signaling at the cellular level include neutralizing antibiodies for PDGF ligands and receptors, aptamers which are oligonucleic acid or peptide molecules that bind to a specific target molecule, N-terminal processing-deficient PDGFs, and soluble receptors without the kinase domain. | Pharmaceutical research has been targeting inhibiting PDGF-PDGFR signaling as a potential for anti-cancer treatments. Strategies of blocking signaling at the cellular level include neutralizing antibiodies for PDGF ligands and receptors, aptamers which are oligonucleic acid or peptide molecules that bind to a specific target molecule, N-terminal processing-deficient PDGFs, and soluble receptors without the kinase domain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[PDGFR inhibitors]]. | ||
== Quiz == | == Quiz == | ||
| Line 110: | Line 112: | ||
**[[3mjk]] – hPDGF subunit A – human<br /> | **[[3mjk]] – hPDGF subunit A – human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4qci]] – hPDGF subunit B + antibody <br /> | + | **[[4qci]] , [[6t9e]]– hPDGF subunit B + antibody <br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1pdg]] – hPDGF BB <br /> |
**[[4hqu]], [[4hqx]] – hPDGF BB + DNA<br /> | **[[4hqu]], [[4hqx]] – hPDGF BB + DNA<br /> | ||
*Platelet-derived growth factor receptor | *Platelet-derived growth factor receptor | ||
| - | **[[5k5x]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain <br /> | + | **[[5k5x]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain 550-696, 769-973<br /> |
**[[6a32]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain (mutant)<br /> | **[[6a32]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[5grn]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain + pyridine derivative <br /> | **[[5grn]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain + pyridine derivative <br /> | ||
| - | [[6jok]], [[6jol]] – hPDGF-R-a residues 550-696, 769-973 + cancer drug<br /> | + | **[[6jok]], [[6jol]] – hPDGF-R-a residues 550-696, 769-973 + cancer drug<br /> |
| - | [[6joi]], [[6joj]] – hPDGF-R-a residues 550-696, 769-973 (mutant) + cancer drug<br /> | + | **[[6joi]], [[6joj]] – hPDGF-R-a residues 550-696, 769-973 (mutant) + cancer drug<br /> |
| + | **[[7ram]] – hPDGF-R-a 1-524 + HCMV glycoproteins - CryoEM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7lbf]] – hPDGF-R-a 1-524 + HCMV glycoproteins + antibody - CryoEM<br /> | ||
**[[3mjg]] – hPDGF-R-β residues 33-314 + PDGF subunit B<br /> | **[[3mjg]] – hPDGF-R-β residues 33-314 + PDGF subunit B<br /> | ||
**[[2l6w]] – hPDGF-R-β residues 526-563 - NMR<br /> | **[[2l6w]] – hPDGF-R-β residues 526-563 - NMR<br /> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of platelet-derived growth factor receptor
Updated on 05-January-2025
References
- ↑ Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes. Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):571-4. PMID:1315403
- ↑ Shim AH, Liu H, Focia PJ, Chen X, Lin PC, He X. Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11307-12. Epub 2010 Jun 2. PMID:20534510
- ↑ Heldin CH, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: three isoforms and two receptor types. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):108-11. PMID:2543106
- ↑ Williams LT. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564-70. PMID:2538922
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Lisa Tice, Michal Harel, Angel Herraez, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky