Core-binding factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
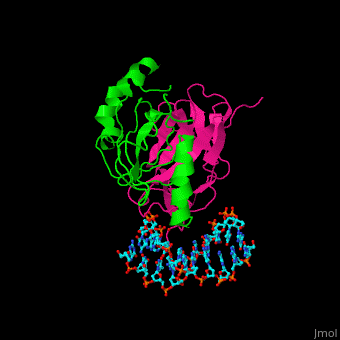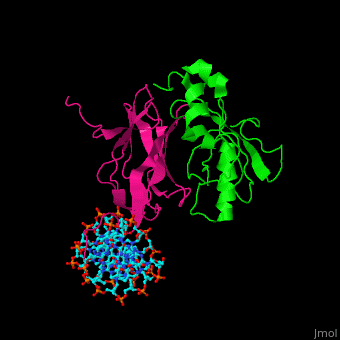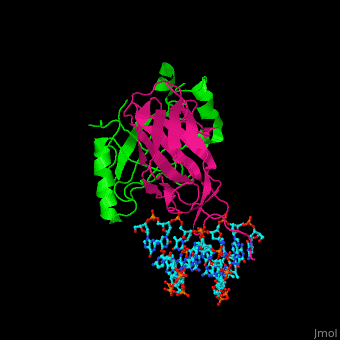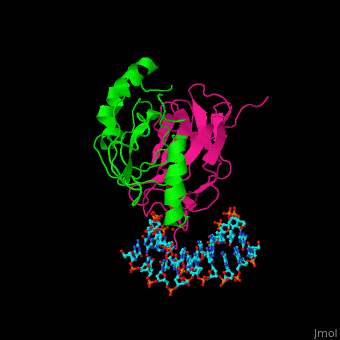
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human CBFα runt domain (magenta) complex with CBFβ heterodimerization domain (green) and DNA (PDB code [[1h9d]])' scene='70/708082/Cv/1'> |
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Core-binding factor''' (CBF) is a heterodimeric transcription factor which is composed of <scene name='70/708082/Cv/2'>α chain which binds DNA and a regulatory β chain</scene>. CBF binds to various enhancers and promoters including murine leukemia virus and polyomavirus enhancer. <ref>PMID:11276260</ref> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Mutations in CBF β are implicated in breast cancer. Rearrangements of CBF α and β genes are implicated in acute myeloid leukemia. | Mutations in CBF β are implicated in breast cancer. Rearrangements of CBF α and β genes are implicated in acute myeloid leukemia. | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Relevance == | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | |||
| + | CBF α contains a DNA-binding runt domain (residues 50-177). | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | *Core-binding factor α | + | *Core-binding factor α subunit |
**[[1ean]], [[1ljm]] – hCBFα runt domain - human<br /> | **[[1ean]], [[1ljm]] – hCBFα runt domain - human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1cmo]] – hCBFα runt domain (mutant) - NMR<br /> | + | **[[1cmo]], [[2n7b]] – hCBFα runt domain (mutant) - NMR<br /> |
**[[1co1]] – hCBFα runt domain - NMR<br /> | **[[1co1]] – hCBFα runt domain - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1eao]], [[1eaq]], [[2j6w]] – mCBFα runt domain (mutant) - mouse<br /> | **[[1eao]], [[1eaq]], [[2j6w]] – mCBFα runt domain (mutant) - mouse<br /> | ||
**[[1hjc]] – mCBFα runt domain + DNA <br /> | **[[1hjc]] – mCBFα runt domain + DNA <br /> | ||
**[[1hjb]] – mCBFα runt domain + hEBP β + DNA<br /> | **[[1hjb]] – mCBFα runt domain + hEBP β + DNA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4l0y]], [[4l0z]], [[4l18]], [[ | + | **[[4l0y]], [[4l0z]], [[4l18]], [[3wu1]] – mCBFα runt domain + hETS1 + DNA<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | *Core-binding factor β subunit | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[4n9f]] – hCBFb + cullin-5 + elongin-B + virion infectivity factor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6p59]] – hCBFb + elongin-B + elongin-C + virion infectivity factor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nil]] – hCBFb + A3F complex + virion infectivity factor – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8e40]], [[8h0i]], [[8j62]] – hCBFb + APOBEC + virion infectivity factor + RNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8cx0]], [[8cx1]], [[8cx2]] – hCBFb + elongin-B + elongin-C + APOBEC + virion infectivity factor + RNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8fvi]] – hCBFb + APOBEC + virion infectivity factor + cullin 5 + RNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8fvj]] – hCBFb + elongin-B + elongin-C + virion infectivity factor + cullin 5 – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8szk]] – hCBFb + elongin-B + elongin-C + virion infectivity factor + cullin 5 + RNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6vg2]], [[6vg8]], [[6vgd]], [[6vge]], [[6vgg]] – hCBFb + Runx2 + FLI1 + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ilf]] – mCBFb<br /> | ||
| - | *Core-binding factor α+β | + | *Core-binding factor α+β subunits |
**[[1e50]] – hCBFα runt domain + hCBFβ heterodimerization domain<br /> | **[[1e50]] – hCBFα runt domain + hCBFβ heterodimerization domain<br /> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 55: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of core-binding factor
Updated on 09-February-2025
References
- ↑ Bravo J, Li Z, Speck NA, Warren AJ. The leukemia-associated AML1 (Runx1)--CBF beta complex functions as a DNA-induced molecular clamp. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Apr;8(4):371-8. PMID:11276260 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/86264