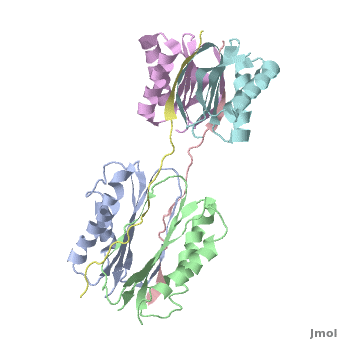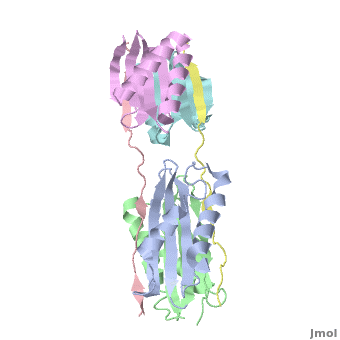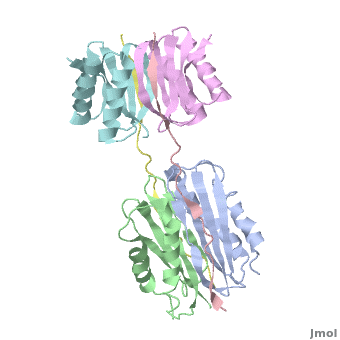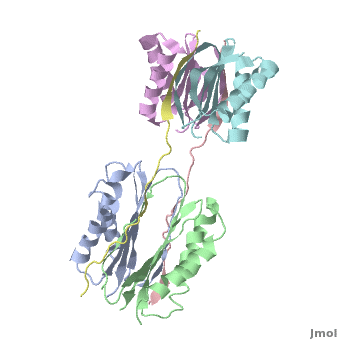
Dynein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load="" size="350" color="" spin="on" Scene='Dynein/Dynein/3' caption='Dynein light (grey, magenta, cyan and green) and intermediate (pink and yellow) chains, [[3fm7]]' > | |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''Dynein''' is a motor protein which walks along the microtubule toward its minus end, i.e. it is a minus-end directed motor. Dyneins are classified as cytoplasmic (DYNC) or axonemal. The Dyneins are composed of heavy, intermediate and light chains. For discussion of the DYNC inter mediate and light chains see: [[Dynein light and intermediate chain]]. | ||
| - | + | '''Dynein''' is a motor protein which walks along the microtubule toward its minus end, i.e. it is a minus-end directed motor. Dyneins are classified as cytoplasmic (DYNC) or axonemal. The '''cytoplasmic dyneins''' are composed of heavy, intermediate and light chains. They drive processes like cell migration, spindle organisation and chromosome separation in mitosis. For discussion of the DYNC intermediate and light chains see: [[Dynein light and intermediate chain]]. '''Axonemal dynein''' has only heavy chain and is involved in cilia and flagella movement. | |
| + | ==Quaternary Structure of Drosophila melanogaster IC/Tctex-1/LC8; Allosteric Interactions of Dynein Light Chains with Dynein Intermediate Chain== | ||
| + | Cytoplasmic Dynein is a motorprotein, which plays an important role in many cellular processes as vesicular transport, mitosis , and cell migration. | ||
| + | Dynein consists of four homodimeric subunits named heavychain (HC) (~530kDa), intermediate chain (IC) (74kDa), light intermediate chain (LIC) (two members, 30 and 50kDa), and light chain (LC) (three members, 10, 12, and 14kDa). On the C-terminal region the HCs bind to mircrotubules and they hydrolyse ATP to generate force towards the minus end of the microtubule. On the N-terminal region they self-associate with the LICs and the ICs. Also the LICs and the ICs associate together. And the ICs bind to the LCs as the following article describes. The whole comlpex then binds to cargo. | ||
| + | Earlier research considered that every LC subunit binds cargo like transcription factors, signaling molecules, and scaffolding proteins, and links this cargo to the motor complex. This would allow the retrograde transport of the cargo along microtubules through the cytoplasm. Recent structural and thermodynamic studies do not support this mechanism. Due to the fact that the LC binding IC parts block the major cargo binding sites on the LC. However, in this article we want to focus on the interaction between the LC and the IC. | ||
| + | ===Structural Analysis=== | ||
| + | ====Overall Structure==== | ||
| + | The '''overall structure''' of this part of the Dynein complex consists of two homodimeric LCs named <scene name='Sandbox_al/Subunit_of_tctex1/4'>TcTex1</scene> and <scene name='Sandbox_al/Lc8/4'>LC8</scene> and two parts of the <scene name='Sandbox_al/Ic_strands/1'>IC</scene>. The associating sites of the IC strands are β-sheets. Every subunit of every light chain interacts with one β-strand of one part of the IC. This IC β-sheet lies in a <scene name='Sandbox_al/Cleft_for_cargo_and_ic_in_lcs/2'>cleft</scene> on the outside of the LC dimer. The IC strands run roughly parallel to the fold axis of the LCs. In fact the binding sites of LC8 and TcTex1 are not parallel and so the IC strand shows a bend. | ||
| + | ====Intermediate Chain==== | ||
| + | The '''intermediate chain''' residues LEU<sub>110</sub>-SER-VAL<sub>112</sub> and ASN<sub>119</sub>-ILE<sub>120</sub> (<scene name='Sandbox_al/Residues_110_112_119_120/3'>show residues1</scene>) interact with TcTex1 and TYR<sub>128</sub>-THR-LYS-GLN-THR-GLN<sub>133</sub> (<scene name='Sandbox_al/Residues_128_133/2'>show residues2</scene>) interact wit LC8. Each associating part undergoes a disorder-to-order transition to form β-strands incorporating the β-sheets in the LC. | ||
| + | ====TcTex1==== | ||
| + | The structure of '''TcTex1''' consists, as shown in the band diagram, of two α-helices ((a) and (b)) and five β-sheets ((c)-(g)). The α-helices are found exposed to the outside of the globular subunit and so they consist of charged and polar residues on the solvent exposed side whereas the buried residues are mostly aliphatic. Also every second residue of the solvent exposed β-sheet (f) is polar and the others apolar. | ||
| + | The binding sites of TcTex1 are the β-sheets (d) and (e). As said before they lie in a cleft on the outside and due to that the IC (or cargo) binds with hydrophobic residues to it. | ||
| + | [[Image:TcTexscheme.jpg|thumb|center|400px|Band diagram of TcTex1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====LC8==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''LC8''' consists of two α-helices and four β-sheets as shown in the band diagram. We find analogical to TcTex1 the globular assembly. And as in TcTex1 the α-helices are found on the solvent exposed side with polar residues to the outside and aliphatic residues to the center of the subunit. β-sheet (a) is also solvent exposed but unlike the solvent exposed β-sheet in TcTex1 the residues looking into the solvent are not charged. Contrariwise, they are aliphatic. | ||
| + | [[Image:LC8scheme.jpg|thumb|center|400px|Band diagram of LC8]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Discussion==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Latest structural research on Dynein has brought a different view on the behaviour of the Dynein-LC and its association with the IC. It was thought that the LCs bind cargo to the Dynein complex. Due to the fact that the IC binds at the same cleft as cargo would, there is a conflict between the two binding partners and we have to consider a new scenario for the interaction between LCs and the motor complex. | ||
| + | Dynein transports different cargo and to have influence on this transports could be interesting as it could be the case in stopping the transport of viral products. But as we see our previous knowledge is limited and so further research on this multisubunit protein is preferable. | ||
== 3D Structures of Dynein == | == 3D Structures of Dynein == | ||
| + | [[Dynein 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | == | + | ==References== |
| - | + | '''Structure''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | *Hall,Karplus&Barbar (2009), "Multivalency in the assembly of intrinsically disordered dynein intermediate chain", J.Biol.Chem. ([http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3FM7 3fm7]) [http://www.jbc.org/content/early/2009/09/16/jbc.M109.048587.full.pdf+html?sid=8cdf6ae5-0f32-4225-bb59-df5236613627 jbc.M109.048587] | |
| - | + | '''Informations''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | *Williams et al. (2007), "Structural and thermodynamic characterization of a cytoplasmic dynein light chain-intermediate chain complex", PNAS no.24 vol.104 [http://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.0703614104 10028-10033] | |
| - | [ | + | *Lightcap et al. (2008), "Biochemical and Structural Characterization of the Pak1-LC8 Interaction", J.Biol.Chem. [http://www.jbc.org/content/283/40/27314.full.pdf+html?sid=46ed0632-4da5-434f-803f-e88d6310d517 jbc.M800758200] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Created with the participation of [[User:Alexander Grosse-Honebrink|Alexander Grosse-Honebrink]]. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
Structure
- Hall,Karplus&Barbar (2009), "Multivalency in the assembly of intrinsically disordered dynein intermediate chain", J.Biol.Chem. (3fm7) jbc.M109.048587
Informations
- Williams et al. (2007), "Structural and thermodynamic characterization of a cytoplasmic dynein light chain-intermediate chain complex", PNAS no.24 vol.104 10028-10033
- Lightcap et al. (2008), "Biochemical and Structural Characterization of the Pak1-LC8 Interaction", J.Biol.Chem. jbc.M800758200
Created with the participation of Alexander Grosse-Honebrink.