Elongation factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (35 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
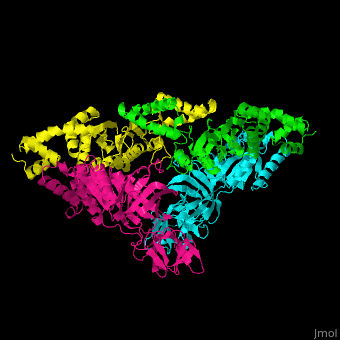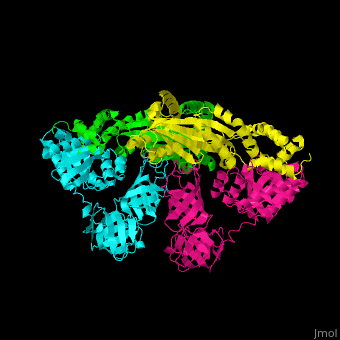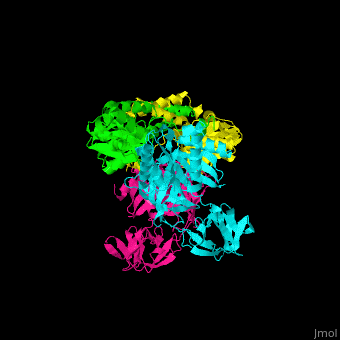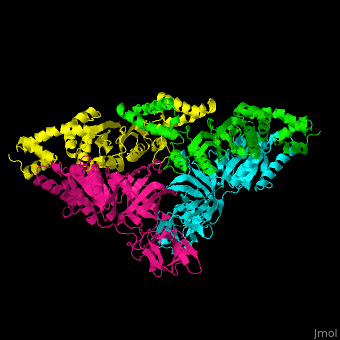
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of EF-Tu (cyan and magenta) with EF-Ts (green and yellow) (PDB entry [[1efu]])' scene='51/517376/Cv/1'> |
| + | __FORCETOC__ | ||
| - | + | == Function == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | '''Elongation factors''' (EF) facilitate translational elongation during the formation of peptide bonds in the ribosome.<br /> | |
| + | * '''EF-selB''' is selenocysteine-specific EF. See [[SelB]]<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-Tu or EF 1-α''' (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic EF. EF-Tu contributes to translational accuracy. It catalyzes the addition of aminoacyl tRNA<ref>PMID:20798060</ref>. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''EF-Ts or EF 1-β''' (elongation factor thermo stable) catalyzes the release of GDP from EF-Tu.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-G''' translocates the peptidyl tRNA from the A site to the P site while moving the mRNA through the ribosome.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-SII''' helps RNA polymerase II to bypass blocks to elongation.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-ELL2''' enhances polyadenylation and exon skipping with the gene encoding the immunoglobulin heavy-chain complex.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-GreA or GreB''' are cleavage factors allowing the resumption of elongation.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-NusA''' recruits translesion DNA polymerases to gaps encountered during translation.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-P''' alters the ribosome affinity to aminoacyl-tRNA.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-1 γ''' acts during the delivery of aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-2''' promotes the translocation of the nascent protein chain from the A site to the P site on the ribosome<ref>PMID:16246167</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-3''' is a unique EF in fungi hence it provides an anti-fungal drug target. See [[HEAT Repeat]]<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF Spt4, Spt5, Spt6''' are conserved among eukaryotes. They modulate the chromatin structure.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''EF-CA150''' is believed to play a role in coupling transcription and splicing.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Elongin complex''' or '''SIII''' activates elongation by RNA polymerase II by suppressing transient pausing of the enzyme<ref>PMID:7660129</ref>. The complex is composed of elongin A, B and C. '''Elongin A''' (EloA) is the active component of the complex. '''Elongin B and C''' (EloBC) are the regulatory subunits of it. '''Von Hippel-Landau tumor suppressor protein''' (VHL) binds to EloBC and inhibits transcriptional elongation.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Negative EF''' (NELF) are involved in regulating the pausing of RNA Pol II polymerase transcripton<ref>PMID:38401543</ref>.<br /> | ||
| - | = | + | <scene name='51/517376/Cv/4'>Complex EF-Tu with EF-Ts is heterotetramer</scene>, or, more exactly <scene name='51/517376/Cv/5'>heterodimer of homodimers</scene> (PDB entry [[1efu]]).<ref>PMID:8596629</ref> |
| - | + | ==3D structures of elongation factor== | |
| - | + | [[Elongation factor 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ''EF-Tu complex with nucleotide'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1efu]] – EcEF + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1exm]] – TtEF + GTP analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[1eft]] – TaEF + GNP – ''Thermus aquaticus''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1tui]] – TaEF + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1d2e]] – bEF + GDP – bovine<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1jny]], [[1skq]] – SsEF + GDP – ''Sulfolobus solfataricus'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | ''EF-Tu with EF-Ts'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1efu]] – EcEF + EcEF-Ts<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1aip]] - TtEF + TtEF-Ts - ''Thermus thermophilus''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1xb2]] – bEF + EF-Ts - bovine<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1f60]] – yEF + EF-Ts C terminal<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1g7c]] - yEF + EF-Ts C terminal + GDPNP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1ije]], [[1ijf]] - yEF + EF-Ts C terminal + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2b7b]] - yEF + EF-Ts C terminal (mutant) + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2b7c]] - yEF + EF-Ts C terminal (mutant) | ||
| - | |||
| - | ''EF-Tu in the ribosome'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[3eq3]], [[3eq4]] – EcEF in 80S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3izv]], [[3izw]] - EcEF in 30S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1zc8]], [[3dwu]] – TtEF in 70S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2wrn]], [[2wrq]], [[2xqd]], [[2y0u]], [[2y0w]], [[2y0y]], [[2y10]], [[2y12]], [[2y14]], [[2y16]], [[2y18]] - TtEF in 70S ribosome | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-SII=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1tfi]] – hEF – human – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3ndq]] - hEF domain II<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1enw]] – yEF domain II – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1eo0]] - yEF domain I – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2xex]] – SaEF – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1pqv]], [[1y1v]] – yEF + RNA polymerase II<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1y1y]], [[3gtm]] – yEF + RNA polymerase II + RNA<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1wjt]] – mEF N terminal – mouse – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-ELL2=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2e5n]] – hEF N2 domain - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-G=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1efg]], [[1elo]], [[1ktv]], [[1wdt]], [[2dy1]] – TtEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1pn6]], [[3izp]] – TtEF – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1fnm]], [[2bm0]], [[2bm1]] – TtEF (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| - | [[2xex]] – SaEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3zz0]], [[3zzt]], [[3zzu]] – SaEF (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| - | [[2bv3]] - TtEF (mutant) + GTP analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[2j7k]] - TtEF (mutant) + GDP analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[2om7]], [[2wri]], [[2wrk]] – TtEF in 70S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2xsy]], [[2xuy]] - TtEF in 70S ribosome<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1dar]], [[2efg]] – TtEF + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1jqm]], [[1jqs]] – EcEF + L11 – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1zn0]], [[2rdo]], [[3j0e]], [[3j18]] – EcEF in 30S ribosome – Cryo-EM<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-GreA/GreB=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2pn0]] – EF – ''Nitrosomonas europaea''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2p4v]] – EcEF-GreB | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-NusA=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1wcl]], [[1wcn]] – EcEF C terminal – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2kwp]] - EcEF N terminal – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2jzb]] – EcEF + RNA polymerase subunit α - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-P=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1ueb]] – TtEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3huw]], [[3huy]] – TtEF in 70S ribosome<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3oyy]] – EF – ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3a5z]] – EcEF + lysyl-tRNA synthetase | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-Ts=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1tfe]] – TtEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1b64]] – hEF guanine exchange factor domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2cp9]] – UBA domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1gh8]] – EF – ''Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum'' – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2yy3]] – EF – ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2uz8]] – hEF (mutant) | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-1G=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1nhy]] – yEF N terminal | ||
| - | [[1pbu]] – hEF C terminal (mutant) - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-2=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1n0v]] – yEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1u2r]] – yEF + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1n0u]], [[2e1r]], [[2npf]] – yEF + antifungal drug<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1zm2]], [[1zm3]], [[1zm4]], [[1zm9]], [[3b78]], [[3b82]], [[3b8h]], [[2zit]] – yEF + exotoxin<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1s1h]] - yEF + antifungal drug in 40S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2p8w]], [[2p8x]], [[3dny]] - yEF in 80S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2p8y]], [[2p8z]] - yEF+ antifungal drug in 80S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-3=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2ix3]] – yEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2iwh]] – yEF + ADPNP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2iw3]] – yEF + ADP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2ix8]] – yEF in 80S ribosome – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-SelB=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1lva]] – MtEF C terminal – ''Moorella thermoacetica''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2v9v]] – MtEF winged helix domain<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1wsu]], [[2uwm]] – MtEF + RNA<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2ply]] – MtEF (mutant) + RNA<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1wb2]] – MmEF – ''Methanococcus maripaludis''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1wb3]] – MmEF + GTP analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[4ac9]] – MmEF + GDP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2pjp]] – EcEF + RNA | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-Spt5=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2do3]], [[2e6z]], [[2e70]] – hEF KOW motif – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2exu]] – yEF<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3h7h]] – hEF + hEF-Spt4 | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-Spt6=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[3gxw]], [[3gxx]], [[3pjp]] – EF SH2 domain – ''Candida glabrata''<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3psf]], [[3psi]] – yEF core domain<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3psj]], [[3psk]] – yEF SH2 domain<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2l3t]] - yEF SH2 domain]] - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3oak]] – yEF + transcription factor IWS1 | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===EF-CA150=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2dod]], [[2doe]], [[2dof]], [[2e71]], [[2kiq]], [[2kis]] – hEF FF domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3hfh]] – hEF FF domain<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2ysi]]– mEF WW domain - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Elongin BC complex=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1lqb]] – hEloBC + von-Hippel Lindau disease tumor suppressor + hypoxia inducible factor 1 α<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3zrc]], [[3ztc]], [[3ztd]], [[3zun]] - hEloBC + von-Hippel Lindau disease tumor suppressor + inhibitor<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3zrf]] - hEloBC + von-Hippel Lindau disease tumor suppressor<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2c9w]], [[2izv]], [[2jz3]] – hEloBC + suppressor of cytokine signaling<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3dcg]] – hEloBC + virion infectivity factor<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2xai]] - hEloBC + ankyrin repeat<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2fnj]] - mEloBC + GUSTAVUS | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Takeshita D, Tomita K. Assembly of Q{beta} viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 7;107(36):15733-8. Epub 2010 Aug 23. PMID:20798060 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006559107
- ↑ Jorgensen R, Merrill AR, Andersen GR. The life and death of translation elongation factor 2. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):1-6. PMID:16246167 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST20060001
- ↑ Aso T, Lane WS, Conaway JW, Conaway RC. Elongin (SIII): a multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1439-43. PMID:7660129
- ↑ Su BG, Vos SM. Distinct negative elongation factor conformations regulate RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing. Mol Cell. 2024 Apr 4;84(7):1243-1256.e5. PMID:38401543 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2024.01.023
- ↑ Kawashima T, Berthet-Colominas C, Wulff M, Cusack S, Leberman R. The structure of the Escherichia coli EF-Tu.EF-Ts complex at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1996 Feb 8;379(6565):511-8. PMID:8596629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/379511a0