Fructokinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='48/484862/Cv/2' caption='Fructokinase with ADP and Fructose bound in the active site [[3lm9]]'> | |
| - | + | == Function == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
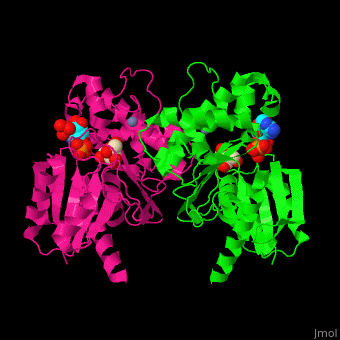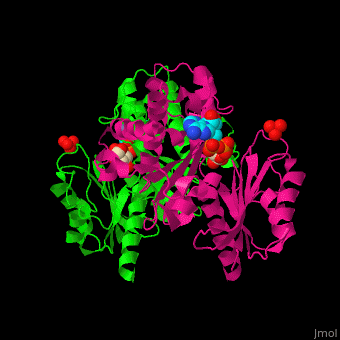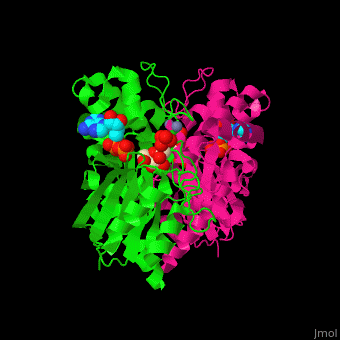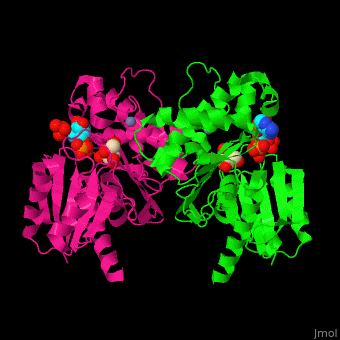
| + | '''Fructokinase''' (FRK) catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose to fructose-1-phosphate using ATP as phosphate source in plants, bacteria and animals. In plants and bacteria FRK regulates starch synthesis. In animals it produces oxalate and its precursors<ref>PMID:3009653</ref>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='48/484862/Cv/6'>Fructokinase with ADP and fructose bound in the active site</scene> ([[3lm9]]). Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Inhibitors of FRK C may block sugar-associated metabolic syndromes<ref>PMID:23439477</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Disease == | ||
| + | |||
| + | FRK deficiency in the liver causes the inherited metabolic disorder Fructosuria<ref>PMID:2992452</ref>. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of fructokinase== | ==3D structures of fructokinase== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
[[2qhp]] – FRK – ''Bacterioides thetaiotamicron''<br /> | [[2qhp]] – FRK – ''Bacterioides thetaiotamicron''<br /> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 22: | ||
[[3lki]] – XfFRK + ATP<br /> | [[3lki]] – XfFRK + ATP<br /> | ||
[[3lm9]] - BsFRK + ATP + fructose – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> | [[3lm9]] - BsFRK + ATP + fructose – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ohr]] - BsFRK + ADP | + | [[3ohr]] - BsFRK + ADP<br /> |
| + | [[2v78]], [[2var]] – FRK – ''Sulfolobus solfataricus''<br /> | ||
| + | [[3c8u]] – FRK – ''Silicibacter''<br /> | ||
| + | [[5ey7]] – VcFRK – ''Vibrio cholerae''<br /> | ||
| + | [[5f11]] – VcFRK + fructose <br /> | ||
| + | [[5f0z]], [[5ygg]] – VcFRK + fructose + ADP<br /> | ||
| + | [[5eyn]] – VcFRK + fructose + ADP + BeF3<br /> | ||
| + | [[7cf8]], [[7cfa]] – FRK – ''Mycobacterium marinum''<br /> | ||
| + | [[4u7x]] – BaFRK – ''Brucella abortus''<br /> | ||
| + | [[4wjm]] – BaFRK + AMPPNP<br /> | ||
| + | For Hepatic fructokinase see [[Ketohexokinase]] | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of fructokinase
Updated on 07-July-2025
2qhp – FRK – Bacterioides thetaiotamicron
3ljs – XfFRK – Xylella fastidiosa
3hj6 – FRK – Halothermothrix orenii
3lki – XfFRK + ATP
3lm9 - BsFRK + ATP + fructose – Bacillus subtilis
3ohr - BsFRK + ADP
2v78, 2var – FRK – Sulfolobus solfataricus
3c8u – FRK – Silicibacter
5ey7 – VcFRK – Vibrio cholerae
5f11 – VcFRK + fructose
5f0z, 5ygg – VcFRK + fructose + ADP
5eyn – VcFRK + fructose + ADP + BeF3
7cf8, 7cfa – FRK – Mycobacterium marinum
4u7x – BaFRK – Brucella abortus
4wjm – BaFRK + AMPPNP
For Hepatic fructokinase see Ketohexokinase
References
- ↑ James HM, Williams SG, Bais R, Rofe AM, Edwards JB, Conyers RA. The metabolic production of oxalate from xylitol: activities of transketolase, transaldolase, fructokinase and aldolase in liver, kidney, brain, heart and muscle in the rat, mouse, guinea pig, rabbit and human. Int J Vitam Nutr Res Suppl. 1985;28:29-46. PMID:3009653
- ↑ Johnson RJ, Rivard C, Lanaspa MA, Otabachian-Smith S, Ishimoto T, Cicerchi C, Cheeke PR, Macintosh B, Hess T. Fructokinase, Fructans, Intestinal Permeability, and Metabolic Syndrome: An Equine Connection? J Equine Vet Sci. 2013 Feb;33(2):120-126. PMID:23439477 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jevs.2012.05.004
- ↑ Phillips MI, Davies DR. The mechanism of guanosine triphosphate depletion in the liver after a fructose load. The role of fructokinase. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):667-71. PMID:2992452