Latrophilin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Latrophilin''' (LAT) or '''adhesion G protein-coupled receptor''' is the major brain receptor for α-latroxin - a black widow spidertoxin which stimulates strong neuronal exocytosis in vertebrates<ref>PMID:21618826</ref>. LAT is cleaved proteolitically into 2 fragments which reassociate upon binding an agonist and upon reassociation cause release of calcium from intracellular stores and massive release of neurotransmitter. | '''Latrophilin''' (LAT) or '''adhesion G protein-coupled receptor''' is the major brain receptor for α-latroxin - a black widow spidertoxin which stimulates strong neuronal exocytosis in vertebrates<ref>PMID:21618826</ref>. LAT is cleaved proteolitically into 2 fragments which reassociate upon binding an agonist and upon reassociation cause release of calcium from intracellular stores and massive release of neurotransmitter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Latrophilin-1''' is required for some inhibitory synaptic connections <ref>PMID:38684366</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Latrophilin-3''' mediates synapse formation in the hypoccampus<ref>PMID:38233523</ref>. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 12: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
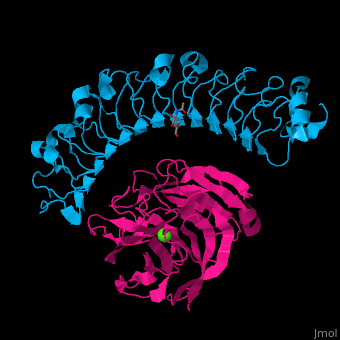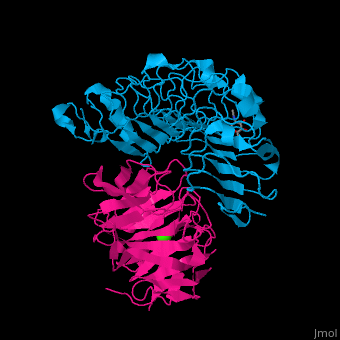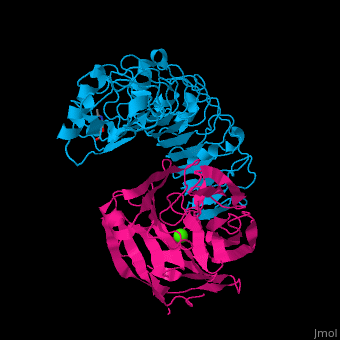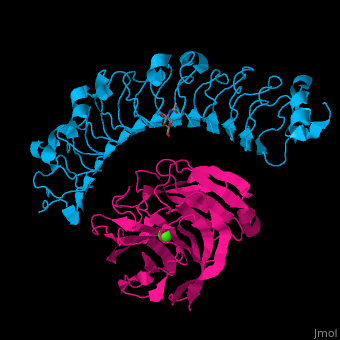
| - | The high-affinity of the LAT-3/FLRT3 complex is achieved by a combination of interactions between the <scene name='74/748875/Cv/ | + | The high-affinity of the LAT-3/FLRT3 complex is achieved by a combination of interactions between the <scene name='74/748875/Cv/4'>round face of LAT-3 and the concave surface of FLRT3</scene><ref>PMID:26235030</ref>. <scene name='74/748875/Cv/5'>All interactions</scene>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ==3D structures of | + | ==3D structures of latrophilin== |
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| Line 22: | Line 25: | ||
**[[2jxa]] – mLAT-1 Gal_lectin domain + rhamnose - NMR<br /> | **[[2jxa]] – mLAT-1 Gal_lectin domain + rhamnose - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | *Latrophilin-3 | + | *Latrophilin-3; Domains – lectin 97-198; olfactomedin 199-495; GAIN and HormR 496-1160 |
**[[5ftt]], [[5ftu]] – hLAT-3 + FLRT2 + netrin receptor - human<br /> | **[[5ftt]], [[5ftu]] – hLAT-3 + FLRT2 + netrin receptor - human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4rmk]], [[4rml]] – hLAT-3 olfactomedin domain <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5afb]] – hLAT-3 olfactomedin and lectin domains <br /> | ||
**[[5cmn]] – hLAT-3 olfactomedin domain + FLRT3<br /> | **[[5cmn]] – hLAT-3 olfactomedin domain + FLRT3<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8djg]] – hLAT-3 residues 24-126 + antibody<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7wy5]], [[7wy8]], [[7wyb]] – hLAT-3 + nanobody + GS – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7sf7]] – hLAT-3 residues 842-1138 + GS – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7x10]] – hLAT-3 + Scfv + GS – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8vti]] – hLAT-3 GAIN and HormR domains 490-1160 + antibody – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[4yeb]] – mLAT-3 + FLRT3 <br /> | **[[4yeb]] – mLAT-3 + FLRT3 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6jbu]] – mLAT-3 olfactomedin domain + FLRT3<br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6ska]], [[6ske]], [[6vhh]] – mLAT-3 olfactomedin domain + teneurin-2<br /> |
}} | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of latrophilin
Updated on 26-October-2025
References
- ↑ Silva JP, Ushkaryov YA. The latrophilins, "split-personality" receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;706:59-75. PMID:21618826
- ↑ Matúš D, Lopez JM, Sando RC, Südhof TC. Essential Role of Latrophilin-1 Adhesion GPCR Nanoclusters in Inhibitory Synapses. J Neurosci. 2024 Jun 5;44(23):e1978232024. PMID:38684366 doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1978-23.2024
- ↑ Wang S, DeLeon C, Sun W, Quake SR, Roth BL, Südhof TC. Alternative splicing of latrophilin-3 controls synapse formation. Nature. 2024 Feb;626(7997):128-135. PMID:38233523 doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06913-9
- ↑ Arcos-Burgos M, Jain M, Acosta MT, Shively S, Stanescu H, Wallis D, Domene S, Velez JI, Karkera JD, Balog J, Berg K, Kleta R, Gahl WA, Roessler E, Long R, Lie J, Pineda D, Londono AC, Palacio JD, Arbelaez A, Lopera F, Elia J, Hakonarson H, Johansson S, Knappskog PM, Haavik J, Ribases M, Cormand B, Bayes M, Casas M, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Hervas A, Maher BS, Faraone SV, Seitz C, Freitag CM, Palmason H, Meyer J, Romanos M, Walitza S, Hemminger U, Warnke A, Romanos J, Renner T, Jacob C, Lesch KP, Swanson J, Vortmeyer A, Bailey-Wilson JE, Castellanos FX, Muenke M. A common variant of the latrophilin 3 gene, LPHN3, confers susceptibility to ADHD and predicts effectiveness of stimulant medication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Nov;15(11):1053-66. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.6. Epub 2010 Feb, 16. PMID:20157310 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.6
- ↑ Lu YC, Nazarko OV, Sando R 3rd, Salzman GS, Sudhof TC, Arac D. Structural Basis of Latrophilin-FLRT-UNC5 Interaction in Cell Adhesion. Structure. 2015 Jul 28. pii: S0969-2126(15)00277-4. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.06.024. PMID:26235030 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.06.024