Ozonolysis
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<applet load='1ea5' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' /> | <applet load='1ea5' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Ozonolysis stepone.jpg]] | ||
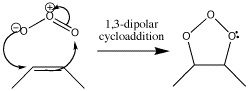
This is <scene name='Ozonolysis/Ozonolysis_step_1/4'>step one</scene> of ozonolysis. | This is <scene name='Ozonolysis/Ozonolysis_step_1/4'>step one</scene> of ozonolysis. | ||
Revision as of 08:36, 28 May 2008
Ozonolysis is a type of cycloaddition which destroys bonds. It starts with a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition but eventually becomes a method of cleaving π bonds in an oxidative fashion, so that they end up as two carbonyl groups. The reagent for this reaction is ozone, O3.
Reaction
|
This is of ozonolysis.
This is of ozonolysis.
This is of ozonolysis.
This is of ozonolysis.
This is the
This should do something
This should forgo transition
Image:Ozonolysis mechanism1.jpg
Acknowledgements
The animations of the ozonolysis reaction, as well as the 2D images of the reaction mechanism, were created by Nick Greeves. Many more reactions are viewable in an intuitive manner at http://www.chemtube3d.com.