TPH
From Proteopedia
(New page: ==Tryptophan hydroxylase== Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) (tryptophan 5-monooxygenase, EC 1.14.16.4) catalyses the reaction between tryptophan, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and O2 to gi...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Tryptophan hydroxylase== | ==Tryptophan hydroxylase== | ||
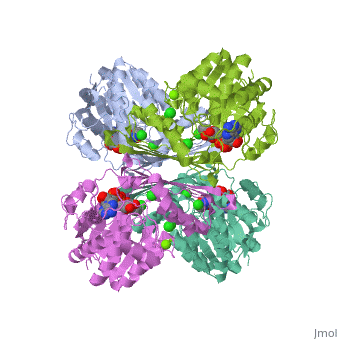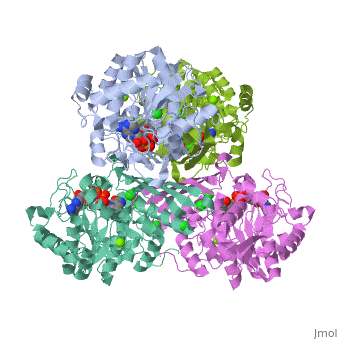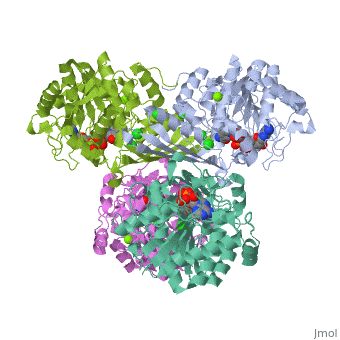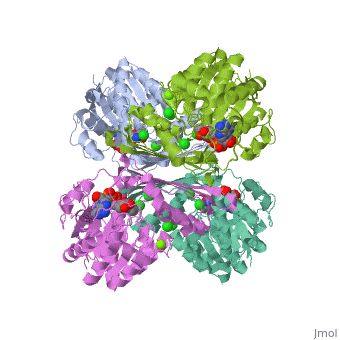
Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) (tryptophan 5-monooxygenase, EC 1.14.16.4) catalyses the reaction between tryptophan, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and O2 to give 5-hydroxytryptophan and 4a-hydroxy-tetrahydrobiopterin (4a-hydroxy-BH4. This reaction is the first and rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of serotonin (See scheme). | Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) (tryptophan 5-monooxygenase, EC 1.14.16.4) catalyses the reaction between tryptophan, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and O2 to give 5-hydroxytryptophan and 4a-hydroxy-tetrahydrobiopterin (4a-hydroxy-BH4. This reaction is the first and rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of serotonin (See scheme). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Together with phenylalanine hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.1) and tyrosine hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.2), TPH form the small enzyme family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAH) []. These enzymes all contain iron and use BH4 as a co-substrate in the hydroxylation of their respective aromatic amino acids [ , , ]. Additionally all mammalian AAAH form homotetramers and each monomer consists of three domains. These domains are the N-terminal regulatory domain (100-150 residues), the catalytic domain (approximately 315 residues) and the C-terminal tetramerisation domain (approximately 30-40 residues) [ , , , ]. | ||
| + | |||
This is a placeholder text to help you get started in | This is a placeholder text to help you get started in | ||
Revision as of 08:19, 3 April 2009
Tryptophan hydroxylase
Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) (tryptophan 5-monooxygenase, EC 1.14.16.4) catalyses the reaction between tryptophan, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and O2 to give 5-hydroxytryptophan and 4a-hydroxy-tetrahydrobiopterin (4a-hydroxy-BH4. This reaction is the first and rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of serotonin (See scheme).
Together with phenylalanine hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.1) and tyrosine hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.2), TPH form the small enzyme family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAH) []. These enzymes all contain iron and use BH4 as a co-substrate in the hydroxylation of their respective aromatic amino acids [ , , ]. Additionally all mammalian AAAH form homotetramers and each monomer consists of three domains. These domains are the N-terminal regulatory domain (100-150 residues), the catalytic domain (approximately 315 residues) and the C-terminal tetramerisation domain (approximately 30-40 residues) [ , , , ].
This is a placeholder text to help you get started in
placing a Jmol applet on your page. At any time, click
"Show Preview" at the bottom of this page to see how it goes.
Replace the PDB id (use lowercase!) after the STRUCTURE_ and after PDB= to load and display another structure.
| |||||||||
| 3cin, resolution 1.70Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Gene: | TM1419, TM_1419 (Thermotoga maritima MSB8) | ||||||||
| Activity: | Inositol-3-phosphate synthase, with EC number 5.5.1.4 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum, TOPSAN | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||