We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Prolyl Endopeptidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (25 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
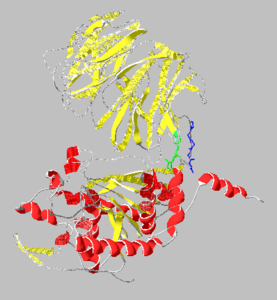
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' caption='Prolyl endopeptidase complex with Pro-(decarboxy-Pro)-type inhibitor (PDB entry [[3eq7]])' scene='38/382958/Cv/1'> |
| - | Prolyl endopeptidases (PEPs) are a class of serine proteases which cleave peptide bonds on the C-terminal side of internal proline residues.<ref name="Shan2">PMID:15738423</ref> | + | |
| + | '''Prolyl endopeptidases''' (PEPs) are a class of serine proteases which cleave peptide bonds on the C-terminal side of internal proline residues.<ref name="Shan2">PMID:15738423</ref> | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
[[Image:1yr2_ribbon2.png|thumb|left|300x300px|alt=Alt text|Catalytic(bottom) and β-propeller domains(top) with peptide linkages between the domains shown in green and blue]] | [[Image:1yr2_ribbon2.png|thumb|left|300x300px|alt=Alt text|Catalytic(bottom) and β-propeller domains(top) with peptide linkages between the domains shown in green and blue]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
Prolyl endopeptidases are relatively large enzymes(75 kDa) and contain two distinct domains: a catalytic domain and a β-propeller domain<ref name="Besedin">PMID:12658988</ref>. | Prolyl endopeptidases are relatively large enzymes(75 kDa) and contain two distinct domains: a catalytic domain and a β-propeller domain<ref name="Besedin">PMID:12658988</ref>. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
The catalytic domain mainly consists of an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha/beta_hydrolase_fold α/β hydrolase fold] which is a series of 8 strands connected by helices in a fold common to many enzymes. The catalytic domain was found to be much more conserved than the β-propeller domain(~50%).<ref name="Gass">PMID:17160352</ref> The catalytic site contains a catalytic triad of Ser-Asp-His and lies in a cavity near the interface to the β-propeller domain.<ref name="Shan2"/> | The catalytic domain mainly consists of an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha/beta_hydrolase_fold α/β hydrolase fold] which is a series of 8 strands connected by helices in a fold common to many enzymes. The catalytic domain was found to be much more conserved than the β-propeller domain(~50%).<ref name="Gass">PMID:17160352</ref> The catalytic site contains a catalytic triad of Ser-Asp-His and lies in a cavity near the interface to the β-propeller domain.<ref name="Shan2"/> | ||
| - | + | == Binding Mechanism == | |
From observed interactions between the β-propeller and catalytic domains several possible substrate binding mechanism have been proposed. | From observed interactions between the β-propeller and catalytic domains several possible substrate binding mechanism have been proposed. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
Both mechanistic binding theories account for the observed activity of PEP as being limited to acting on small peptides of less than 30 amino acids. | Both mechanistic binding theories account for the observed activity of PEP as being limited to acting on small peptides of less than 30 amino acids. | ||
| - | + | == Inhibition == | |
Initial classification of prolyl endopeptidases as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine_protease serine proteases] was due to their inhibition by [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diisopropyl_fluorophosphate DFP].<ref name="Besedin"/> | Initial classification of prolyl endopeptidases as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine_protease serine proteases] was due to their inhibition by [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diisopropyl_fluorophosphate DFP].<ref name="Besedin"/> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
=== Neurological Disorders === | === Neurological Disorders === | ||
As well as having a proposed role in the degradation of neuropeptides PEPs have also been linked to several specific neurological disorders. It has been found that patients suffering from depression had decreased PEP activity and those suffering from psychosis have increased PEP activity showing the importance of maintaining a balanced level of PEP activity in the brain. PEP inhibitors are a current point of research in hopes of finding ways to balance brain PEP activity.<ref name="Gass"/> | As well as having a proposed role in the degradation of neuropeptides PEPs have also been linked to several specific neurological disorders. It has been found that patients suffering from depression had decreased PEP activity and those suffering from psychosis have increased PEP activity showing the importance of maintaining a balanced level of PEP activity in the brain. PEP inhibitors are a current point of research in hopes of finding ways to balance brain PEP activity.<ref name="Gass"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The <scene name='38/382958/Cv/4'>active site of PEP contains the serine protease catalytic triad of Ser-His-Asp</scene><ref>PMID:19006380</ref>. Triad is colored in salmon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of prolyl endopeptidase== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Prolyl endopeptidase 3D structures]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<References/> | <References/> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Stacey Shantz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Andrea Gorrell, David Canner