Glutathione Reductase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: Glutathione reductase, also known as GSH reductase, is found in the human cells and converts oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to two molecules of reduced gluthatione (GSH) <ref name="main">...) |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | Glutathione reductase, also known as GSH reductase, is found in the human cells and converts oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to two molecules of reduced | + | '''Glutathione reductase''', also known as GSH reductase, is found in the human cells and converts oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to two molecules of reduced gluthatione (GSH) <ref name="main">PMID:18638483</ref>. EC:[http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/EC1/8/1/7.html 1.8.1.7]. For more details see [[Molecular Playground/Glutathione Reductase]]. |
| - | + | ||
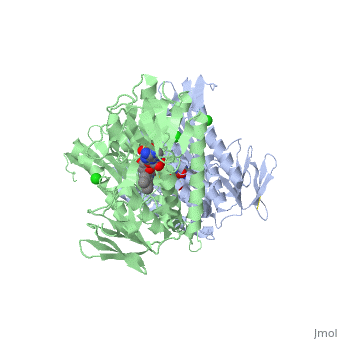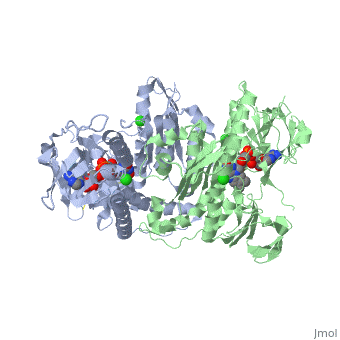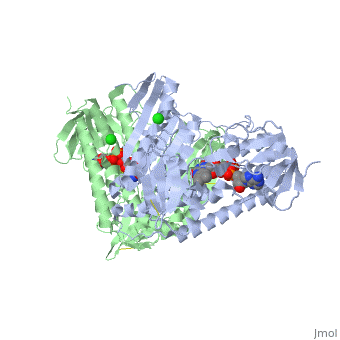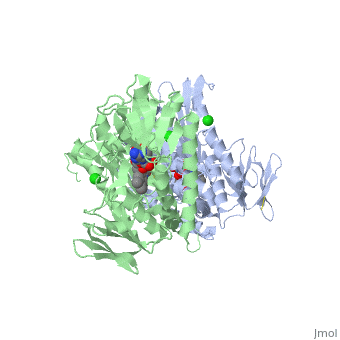
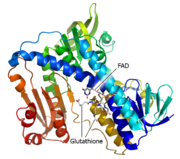
| + | <StructureSection load='3o0h' size='340' side='right' caption='Glutathione reductase dimer complex with FAD and chloride ion, [[3o0h]]' scene=''> | ||
| + | |||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
| - | Glutathione reductase belongs to the larger family of | + | Glutathione reductase belongs to the larger family of flavoezymes, which use a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) or flavin mononucleotide (FMN) in catalysis<ref name="main"/>. It is a disulfide oxiodreductase homodimer of 52kD monomers of which, each has four domains<ref name="main"/>: |
(<scene name='Sandbox_181/Fad_ndp_highlight/1'>FAD and NADPH Highlighted</scene>) | (<scene name='Sandbox_181/Fad_ndp_highlight/1'>FAD and NADPH Highlighted</scene>) | ||
| - | 1. NADPH-binding domain (yellow), | + | 1. NADPH-binding domain (yellow), residues 158-293 |
| - | 2. FAD-binding domain (red), | + | 2. FAD-binding domain (red) residues 1-157, |
| - | 3. dimerization domain. | + | 3. dimerization domain, residues 365-478. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Glutathione reductase.png|thumb|left|alt=Alt text|Glutathione Reductase]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
It is a thermostable protein as it retains 100% of its function up to 65 degrees Celsius attributing to the importance of its function in the cell <ref>PMID: 2044390</ref>. It is encoded by a single gene ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=summary&list_uids=2936 GeneID:2936], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=138300 MIM 138300]) located on chromosome 8p21.1 <ref name="kelner">PMID:10708558</ref>. It consists of 13 exons spanning 50kb<ref name="kelner"/> | It is a thermostable protein as it retains 100% of its function up to 65 degrees Celsius attributing to the importance of its function in the cell <ref>PMID: 2044390</ref>. It is encoded by a single gene ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=summary&list_uids=2936 GeneID:2936], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=138300 MIM 138300]) located on chromosome 8p21.1 <ref name="kelner">PMID:10708558</ref>. It consists of 13 exons spanning 50kb<ref name="kelner"/> | ||
| - | + | For glutathione reductase with nitrotyrosine modification see [[Nitrotyrosine]]. | |
| - | + | ||
| + | =Topology= | ||
| + | GSH reductase has a central five-stranded parallel beta-sheet (β1, β2, β3, β7 and β8) <ref name="Dym">PMID:11514662</ref>. This central β-sheet is surrounded by α-helices 1 and 2 with a crossover connection of a three-stranded antiparallel β-sheet (β4-6) <ref name="Dym"/>. | ||
| - | + | =Compression and Hydride Transfer= | |
Compression has been shown to play a role in enzyme catalysis and X-ray structure of NADPH complex of GSH reductase shows the C4 atom to be only 3.3 Angstrom from the flavin N5 atom<ref name="main"/>. This is closer than one would predict with van der Waals interactions. Compression of the NADPH-bound complex is first evidenced in the decrease in the level of motion of the active site atoms in the complex<ref name="main"/>. Second, it was observed that the van der Waals radii overlapped in the active site, tightly fixing flavin<ref name="main"/>. It is fixed from both sides as flavin N5 to nicotinamide C4 distance is 3.29 Angstrom and the flavin C4a to Cys63-SG distance is 3.29 Angstrom <ref name="main"/>. Third, the flavin ring system shifts in the two reduced structures, with the binding of NADPH pushing the flavin N5 about 0.3 Angstrom towards the thiolate<ref name="main"/>. This provides a structural explanation for how the thiolate-flavin charge transfer intensity is increased by the binding of NADPH <ref name="main"/>. Finally, the last evidence for compression involves the planarity of the nicotinamide group which shows distortion at atom N1 <ref name="main"/>. | Compression has been shown to play a role in enzyme catalysis and X-ray structure of NADPH complex of GSH reductase shows the C4 atom to be only 3.3 Angstrom from the flavin N5 atom<ref name="main"/>. This is closer than one would predict with van der Waals interactions. Compression of the NADPH-bound complex is first evidenced in the decrease in the level of motion of the active site atoms in the complex<ref name="main"/>. Second, it was observed that the van der Waals radii overlapped in the active site, tightly fixing flavin<ref name="main"/>. It is fixed from both sides as flavin N5 to nicotinamide C4 distance is 3.29 Angstrom and the flavin C4a to Cys63-SG distance is 3.29 Angstrom <ref name="main"/>. Third, the flavin ring system shifts in the two reduced structures, with the binding of NADPH pushing the flavin N5 about 0.3 Angstrom towards the thiolate<ref name="main"/>. This provides a structural explanation for how the thiolate-flavin charge transfer intensity is increased by the binding of NADPH <ref name="main"/>. Finally, the last evidence for compression involves the planarity of the nicotinamide group which shows distortion at atom N1 <ref name="main"/>. | ||
=Reaction= | =Reaction= | ||
| - | [[Image:Glutathione _reductase_mechanism.gif|thumb|Reaction]] | + | [[Image:Glutathione _reductase_mechanism.gif|left|thumb|Reaction]] |
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
The action of glutathione reductase proceeds through a cyclic series of structures in differing redox states<ref name="main"/>. NADPH binds causing a transient reduction of flavin and this reduced flavin consequently reduces Cys58-Cys63 disulfide bond, forming a short lived covalent intermediate with Cys63<ref name="main"/>. Following this, a stable charge-transfer complex between flavin and the Cys63 thiolate forms<ref name="main"/>. After formation the NADP+ dissociates and is replaced by another NADPH<ref name="main"/>. This is the end of the reductive first half of the mechanism and the oxidative half is initiated upon the binding of GSSG<ref name="main"/>. The Cys58 in glutathione reductase attacks CysI of the GSSG to form a mixed disulfide between the first GS and Cys58<ref name="main"/>. The second GSH is the free to leave and the disulfide bond is reformed between Cys58 and Cys63 of glutathione reductase. Finally, the first molecule of GSH is released<ref name="main"/>. The glutathione reductase is then able to be recycled to allow for the binding of NADPH once again<ref name="main"/>. | The action of glutathione reductase proceeds through a cyclic series of structures in differing redox states<ref name="main"/>. NADPH binds causing a transient reduction of flavin and this reduced flavin consequently reduces Cys58-Cys63 disulfide bond, forming a short lived covalent intermediate with Cys63<ref name="main"/>. Following this, a stable charge-transfer complex between flavin and the Cys63 thiolate forms<ref name="main"/>. After formation the NADP+ dissociates and is replaced by another NADPH<ref name="main"/>. This is the end of the reductive first half of the mechanism and the oxidative half is initiated upon the binding of GSSG<ref name="main"/>. The Cys58 in glutathione reductase attacks CysI of the GSSG to form a mixed disulfide between the first GS and Cys58<ref name="main"/>. The second GSH is the free to leave and the disulfide bond is reformed between Cys58 and Cys63 of glutathione reductase. Finally, the first molecule of GSH is released<ref name="main"/>. The glutathione reductase is then able to be recycled to allow for the binding of NADPH once again<ref name="main"/>. | ||
| - | |||
=Function= | =Function= | ||
For proper functioning and prevention of damage to a cell, GSH plays an essential role in preventing oxidative stress in human cells<ref name="another">PMID:16111877</ref>. GSH directly scavenges hydroxyl radicals and singlet oxygens, plays a role as a cofactor in several detoxifying enzymes, participates in amino acid transport through the plasma membrane, and can regenerate important antioxidants such as Vitamins E and C to their reactive forms <ref name="another"/>. The antioxidant capacity of glutathione is linked to the redox state of GSSG/2GSH inside the cell<ref>PMID: 12809732 </ref>. The function of GSH reductase is to maintain this narrow redox state of high reduced to oxidized ratio of GSH in the cell<ref>PMID: 16111877 </ref>. | For proper functioning and prevention of damage to a cell, GSH plays an essential role in preventing oxidative stress in human cells<ref name="another">PMID:16111877</ref>. GSH directly scavenges hydroxyl radicals and singlet oxygens, plays a role as a cofactor in several detoxifying enzymes, participates in amino acid transport through the plasma membrane, and can regenerate important antioxidants such as Vitamins E and C to their reactive forms <ref name="another"/>. The antioxidant capacity of glutathione is linked to the redox state of GSSG/2GSH inside the cell<ref>PMID: 12809732 </ref>. The function of GSH reductase is to maintain this narrow redox state of high reduced to oxidized ratio of GSH in the cell<ref>PMID: 16111877 </ref>. | ||
| - | + | =Mutation Derived Deficiency= | |
Ultimately, a mutation in the single-copy gene coding for GSH reductase affecting its activity would disrupt the redox state of the GSSG/2GSH in the cell. If GSH were unable to be regenerated from GSSG the cellular environment would become more oxidising, a phenomenon shown to be associated will the onset of cellular apoptosis at a moderate oxidizing environment and necrosis at higher oxidizing cellular environments<ref>PMID: 10716996 </ref>. | Ultimately, a mutation in the single-copy gene coding for GSH reductase affecting its activity would disrupt the redox state of the GSSG/2GSH in the cell. If GSH were unable to be regenerated from GSSG the cellular environment would become more oxidising, a phenomenon shown to be associated will the onset of cellular apoptosis at a moderate oxidizing environment and necrosis at higher oxidizing cellular environments<ref>PMID: 10716996 </ref>. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
A second mutation in the GSH reductase gene truncated GSH reductase at Trp287 by changing the TGG codon for Trp287 into a premature TGA stop codon <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. The folding-initiating helix 11 of residues 439 to 454 is then missing, causing the improper folding and an inactive enzyme <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. Additionally, Gly330 is exchanged for a GCG codon for alanine <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. The exchange of glycine to alanine affects catalysis and stability of GSH reductase by disrupting the proper FAD binding necessitating the presence of higher concentrations of FAD to saturate the apoenzyme <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. | A second mutation in the GSH reductase gene truncated GSH reductase at Trp287 by changing the TGG codon for Trp287 into a premature TGA stop codon <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. The folding-initiating helix 11 of residues 439 to 454 is then missing, causing the improper folding and an inactive enzyme <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. Additionally, Gly330 is exchanged for a GCG codon for alanine <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. The exchange of glycine to alanine affects catalysis and stability of GSH reductase by disrupting the proper FAD binding necessitating the presence of higher concentrations of FAD to saturate the apoenzyme <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. | ||
| - | + | =Dietary Deficiency= | |
| - | + | ||
In addition to mutation, an insufficient intake to riboflavin (Vitamin B12) through the diet results in the GSH reductase remaining as an inactive apoenzyme <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. A deficiency in FAD is usually only found in malnourished populations and these populations make up the more common occurrence of a GSH reductase deficiency<ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. The clinical symptoms of cataracts, favism and reduced lifespans of red blood cells are also seen in dietary deficiency of RSH reductase<ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. | In addition to mutation, an insufficient intake to riboflavin (Vitamin B12) through the diet results in the GSH reductase remaining as an inactive apoenzyme <ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. A deficiency in FAD is usually only found in malnourished populations and these populations make up the more common occurrence of a GSH reductase deficiency<ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. The clinical symptoms of cataracts, favism and reduced lifespans of red blood cells are also seen in dietary deficiency of RSH reductase<ref name="Kamerbeek"/>. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | =3D structures of glutathione reductase= | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Glutathione reductase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1grb]], [[1grg]], [[1k4q]], [[3djg]], [[3djj]], [[3dk4]], [[3dk8]], [[3dk9]] – hGR – human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1grt]], [[2grt]], [[3grt]], [[4grt]], [[5grt]] - hGR (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1alg]] – hGR interface domain helix – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1onf]] – GR – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ger]], [[1ges]], [[1get]], [[1geu]] – GR – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5v36]] – GS – ''Streptococcus mutans''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6du7]] – GS – ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6n7f]] – GS – ''Streptococcus pyogenes''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5u1o]] – GS – ''Vibrio parahaemolyticus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6b4o]] – GS – ''Entercoccus faecalis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3o0h]] - GR – ''Bartonella henselae''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5vdn]] – GS – ''Yersinia pestis''<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Glutathione reductase complex | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2gh5]] - hGR + suicide substrate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1bwc]], [[1dnc]], [[1gsn]], [[1k4q]], [[1xan]], [[2aaq]] - hGR + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1gra]], [[1gre]] - hGR + glutathione<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4gr1]] - hGR + glutathione analog<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1grf]] - hGR + acetamide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3sqp]] - hGR + pyocyanin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1grh]] - hGR + nitrosourea drug<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2hqm]] – GR + glutathione – yeast<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6zzx]], [[6zzy]] – GR in photosystem I – alga – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
Glutathione reductase, also known as GSH reductase, is found in the human cells and converts oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to two molecules of reduced gluthatione (GSH) [1]. EC:1.8.1.7. For more details see Molecular Playground/Glutathione Reductase.
| |||||||||||
3D structures of glutathione reductase
Updated on 17-July-2025
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Berkholz DS, Faber HR, Savvides SN, Karplus PA. Catalytic cycle of human glutathione reductase near 1 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 3;382(2):371-84. Epub 2008 Jul 7. PMID:18638483 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.083
- ↑ Holleschau AM, Rathbun WB. Thermal inactivation study of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase activities in lenses of primates and non-primates. Curr Eye Res. 1991 Mar;10(3):221-9. PMID:2044390
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kelner MJ, Montoya MA. Structural organization of the human glutathione reductase gene: determination of correct cDNA sequence and identification of a mitochondrial leader sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Mar 16;269(2):366-8. PMID:10708558 doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2267
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Dym O, Eisenberg D. Sequence-structure analysis of FAD-containing proteins. Protein Sci. 2001 Sep;10(9):1712-28. PMID:11514662 doi:10.1110/ps.12801
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Masella R, Di Benedetto R, Vari R, Filesi C, Giovannini C. Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J Nutr Biochem. 2005 Oct;16(10):577-86. PMID:16111877 doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.013
- ↑ Pastore A, Federici G, Bertini E, Piemonte F. Analysis of glutathione: implication in redox and detoxification. Clin Chim Acta. 2003 Jul 1;333(1):19-39. PMID:12809732
- ↑ Masella R, Di Benedetto R, Vari R, Filesi C, Giovannini C. Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J Nutr Biochem. 2005 Oct;16(10):577-86. PMID:16111877 doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.013
- ↑ Voehringer DW, Hirschberg DL, Xiao J, Lu Q, Roederer M, Lock CB, Herzenberg LA, Steinman L, Herzenberg LA. Gene microarray identification of redox and mitochondrial elements that control resistance or sensitivity to apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 14;97(6):2680-5. PMID:10716996
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 Kamerbeek NM, van Zwieten R, de Boer M, Morren G, Vuil H, Bannink N, Lincke C, Dolman KM, Becker K, Schirmer RH, Gromer S, Roos D. Molecular basis of glutathione reductase deficiency in human blood cells. Blood. 2007 Apr 15;109(8):3560-6. Epub 2006 Dec 21. PMID:17185460 doi:10.1182/blood-2006-08-042531