Joel L. Sussman Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(→'''Butyrylcholinesterase - BuChE''') |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | [[Image:1p0i.png|left|200px]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Butyrylcholinesterase, also known as pseudocholinesterase, BCHE or | Butyrylcholinesterase, also known as pseudocholinesterase, BCHE or | ||
| Line 24: | Line 19: | ||
Proteopedia examples on these experiments and related publications are | Proteopedia examples on these experiments and related publications are | ||
| - | BChE | + | =Butyrylcholinesterase - BChE= |
| - | == | + | == hBChE - Apo human: [[2pm8]], [[1p0i]] == |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | Gallivan and Dougherty conclude "When a cationic sidechain is near an aromatic sidechain, the geometry is biased toward one that would experience a favorable cation-pi interaction", and "cation-pi interactions should be considered alongside the more conventional hydrogen bonds, salt bridges, and hydrophobic effects in any analysis of protein structure". They provide a [http://capture.caltech.edu/a server that lists text results from their program CaPTURE]. | ||
| - | Zacharias and Dougherty (2002)<ref>PMID: 12084634</ref> reviewed cation-pi interactions in the binding of ligands to proteins. Cation-pi interactions are usually energetically important when the ligand has either positive charge or an aromatic ring, and are involved in control of ion channels, G-protein-coupled receptors, transporters, and enzymatic catalysis. An example is [[1l8b]], <scene name='Cation-pi_interactions/1l8b_pi5/1'>a portion of a eukaryotic translation initiation factor that recognizes N7-methylated guanosine on the 5'-end of mRNAs. The ligand's heterocyclic base (cationic) is sandwiched between Trp56 and Trp102</scene>. | ||
| - | == | + | == BChE+organophosphate inhibitors causing irreversible inhibition == |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | *[[1gai]]: <scene name='Cation-pi_interactions/1gai_pi4/1'>a 472-amino acid chain (glucoamylase) with a spectacular cluster of four aromatic rings (two Trp's, two Tyr's) around a single Lys108</scene>. | ||
| - | + | [[2wsl]], [[2wig]] – hBChE+TA4 | |
| + | [[2wil]], [[2wij]] - hBChE+TA5 | ||
| + | [[2wid]], [[2wif]] - hBChE+TA1 | ||
| + | [[2wik]] - hBChE+TA6 | ||
| + | [[3djy]], [[3dkk]] - hBChE+tabun | ||
| + | [[1xlu]] - hBChE+DFP | ||
| + | [[1xlw]] - hBChE+echothiophate | ||
| + | [[1p0q]] - hBChE+soman | ||
| - | *[[2wea]]: the longest single chain (323 residues) with no energetically significant cation-pi interactions from the original set of 593 proteins originally analyzed. | ||
| - | + | == BChE+inhibitor binding at surface of the protein == | |
| - | *[[1axi]] (human growth hormone): Chain B contains an unusual string of three aromatic sidechains separated by, and capped at the ends with, 4 cationic sidechains. (Using "c" for cation and "p" for pi, the chain is "cpcpcpc".) Only the one of these six interactions is deemed energetically insignificant by CaPTURE (Lys at one end). See image [http://www.umass.edu/microbio/chime/pe_beta/pe/protexpl/cp-1axi.gif here]. | ||
| - | *[[1bl8]] <scene name='Cation-pi_interactions/1bl8_pi2/3'>(bacterial potassium channel): There is a single interchain cation-pi pair for each contact between chains of this homotetramer, but no intrachain cation-pi interactions.</scene> | ||
| - | *[[2vab]] (peptide bound to class I histocompatibility protein): The N-terminal Phe of the nonapeptide stacks with Trp 167 of the protein. On either side of the stacked rings are cations (Arg 170, Lys 66), forming the unusual cppc chain RWFK. See image [http://www.umass.edu/microbio/chime/pe_beta/pe/protexpl/cp-2vab.gif here]. | ||
| - | *[[1rog]] (peptide bound to class I histocompatibility protein): Three (of the four) cations in the 9-residue peptide interact with aromatic sidechains in the protein groove. This is a theoretical model. | ||
| - | *[[1dlh]] (peptide bound to class II histocompatibility protein): There are no cation-pi interactions for the 13-residue peptide, despite its containing three lysines and one tyrosine. A number of nearby sidechains that potentially could interact appear to be blocked by other noncovalent bonding interactions, and the peptide lysine sidechains are generally pointing away from the protein. | ||
| - | + | [[2j4c]] – hBChE+ HgCl2 | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ==Literature References== | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
| - | == | + | == BChE+ substrate analogues mimicking the binding of the substrate butyrylcholine == |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ==Content Attribution== | ||
| - | The initial content of this page was adapted, with the permission of [[User:Eric Martz|Eric Martz]], from the [http://proteinexplorer.org/igloss.htm Glossary] and [http://proteinexplorer.org/cationpi.htm Introduction, Gallery & Tutorial for Cation-Pi Interactions] that accompanies [[Protein Explorer]]. | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[1p0m]] - hBChE+choline |
| - | [[ | + | [[1p0p]] - hBChE+butyrylthiocholine |
| - | + | ||
Current revision
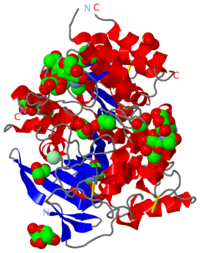
Butyrylcholinesterase, also known as pseudocholinesterase, BCHE or BuChE, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the BCHE gene. Butyrylcholinesterase is also called serum cholinesterase. It is very similar to the neuronal acetylcholinesterase, and is a non-specific cholinesterase found in the blood plasma, which hydrolyses many different choline esters. Butyrylcholine is a synthetic compound and does not occur in the body naturally. It is used as a tool to distinguish between acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase. The structure for this protein is available in its unmodified form (2pm8 and 1p0i)
One of the main functions of butyrylcholinesterase is its ability to remove and clean away organophosphorus nerve agents. This function and its inhibitors has been intensibely studied by solving protein structure of BChE in combination with organophosphate inhibitors and substrate inhibitors.
Proteopedia examples on these experiments and related publications are
Contents |
Butyrylcholinesterase - BChE
hBChE - Apo human: 2pm8, 1p0i
BChE+organophosphate inhibitors causing irreversible inhibition
2wsl, 2wig – hBChE+TA4 2wil, 2wij - hBChE+TA5 2wid, 2wif - hBChE+TA1 2wik - hBChE+TA6 3djy, 3dkk - hBChE+tabun 1xlu - hBChE+DFP 1xlw - hBChE+echothiophate 1p0q - hBChE+soman
BChE+inhibitor binding at surface of the protein
2j4c – hBChE+ HgCl2