User:Joel L. Sussman/Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
(New page: This guide to the contents of Proteopedia is maintained manually (not automatically generated) and so is inevitably incomplete. Please be sure to use the [[Help:Searching|search slots at t...) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | [[Image:HuBChE.png|left|250px]] | |
| + | |||
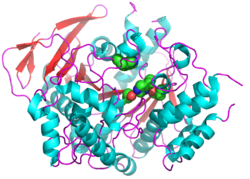
| + | Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) is an enzyme widely distributed throughout the body in humans, but particularly prevalent in serum, where it occurs as a tetramer of catalytic subunits. It is distinguished from the homologous enzyme, acetylcholinesterase, by its ability to hydrolyze the non-natural substrate butyrylcholine as well as the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. Its biological role remains obscure, but mutations in the human BCHE gene result in prolonged post-surgical apnea due to the inability of the mutant BChEs to hydrolyse the local anaesthetic, succinylcholine. BChE finds medical use as a bioscavenger for overcoming organophosphate (OP) nerve agent and insecticide intoxication by interacting rapidly with the toxic agents. Crystal structures of both the native enzyme and of its conjugates with nerve agents are available.<br /> | ||
<big> | <big> | ||
{{#tree:id=siteTree|openlevels=1|close=top|open=top| | {{#tree:id=siteTree|openlevels=1|close=top|open=top| | ||
| + | * hBChE - Apo human | ||
| + | ** [[2pm8]] | ||
| + | ** [[1p0i]] | ||
| - | * | + | * BChE+OP irreversible inhibitors, including nerve agents and insecticides |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | *** [[ | + | ** [[3djy]], [[3dkk]] - hBChE+tabun |
| - | ** | + | ** [[2wid]], [[2wif]] - hBChE+Tabun analogue TA1 |
| + | ** [[2wsl]], [[2wig]] – hBChE+Tabun analogue TA4 | ||
| + | ** [[2wil]], [[2wij]] - hBChE+Tabun analogue TA5 | ||
| + | ** [[2wik]] - hBChE+Tabun analogue TA6 | ||
| + | ** [[1xlw]] - hBChE+echothiophate | ||
| + | ** [[1p0q]] - hBChE+soman | ||
| + | ** [[1xlu]] - hBChE+Di-Isopropyl-Phosphoro-Fluoridate (DFP) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * BChE+inhibitor binding at surface of the protein (far from the active site) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** [[2j4c]] – hBChE+ HgCl2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * BChE+substrate analogues mimicking BCh (so as to study the enzyme/substrate complex) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** [[1p0m]] - hBChE+choline | ||
| + | ** [[1p0p]] - hBChE+butyrylthiocholine | ||
| - | *** [[Amino Acids]] | ||
| - | *** [[Cation-pi interactions]] | ||
| - | *** [[Hydrogen bond]] | ||
| - | *** [[Hydrogen in macromolecular models|Hydrogen in Macromolecular Models]] | ||
| - | *** [[Isoelectric point]] | ||
| - | *** [[Salt bridges]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
</big> | </big> | ||
Current revision
Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) is an enzyme widely distributed throughout the body in humans, but particularly prevalent in serum, where it occurs as a tetramer of catalytic subunits. It is distinguished from the homologous enzyme, acetylcholinesterase, by its ability to hydrolyze the non-natural substrate butyrylcholine as well as the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. Its biological role remains obscure, but mutations in the human BCHE gene result in prolonged post-surgical apnea due to the inability of the mutant BChEs to hydrolyse the local anaesthetic, succinylcholine. BChE finds medical use as a bioscavenger for overcoming organophosphate (OP) nerve agent and insecticide intoxication by interacting rapidly with the toxic agents. Crystal structures of both the native enzyme and of its conjugates with nerve agents are available.