Rohan Patil/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(New page: ==This is a placeholder== This is a placeholder text to help you get started in placing a Jmol applet on your page. At any time, click "Show Preview" at the bottom of this page to see how...) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
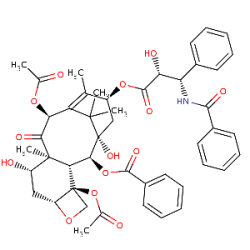
| - | + | [[Image:taxol.png|frame|Paclitaxel (Taxol)]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | A [[CBI Molecule]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | |
| - | and display | + | |
| - | + | Paclitaxel, also called as Taxol, is a plant derived anticancer drug. It was first isolated from the bark of Pacific yew tree, ''Taxus brevifolia''. It has been FDA approved for the treatment of ovarian, breast and non-small cell lung cancer. Taxol binds to the ends of microtubules and inhibits further microtubule elongation. This prevents the cell from dividing and causes the cell to die. Because cancer cells divide much quicker than normal cells, taxol predominantly attacks tumors. | |
| + | |||
| + | Presently, taxol supply is made available either through a semi-synthetic route using precursors isolated from needles of yew species or through ''Taxus'' cell suspension cultures. ''Taxus'' cell suspension culture is an alternative to stripping bark from ''Taxus'' trees and extracting precursors from needles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Link to Roberts Lab: http://robertsgroup.ecs.umass.edu/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <applet size='[450,338]' frame='true' align='right' | ||
| + | caption='Paclitaxel (also known as Taxol)' /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='Rohan_Patil/Sandbox1/Taxol/6'>Paclitaxel [Molecular formula :C47H51NO14] </scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Molecular Playground Banner : "Paclitaxel (Taxol), a natural product with anti-cancer activity" | ||
Current revision
A CBI Molecule being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
Paclitaxel, also called as Taxol, is a plant derived anticancer drug. It was first isolated from the bark of Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia. It has been FDA approved for the treatment of ovarian, breast and non-small cell lung cancer. Taxol binds to the ends of microtubules and inhibits further microtubule elongation. This prevents the cell from dividing and causes the cell to die. Because cancer cells divide much quicker than normal cells, taxol predominantly attacks tumors.
Presently, taxol supply is made available either through a semi-synthetic route using precursors isolated from needles of yew species or through Taxus cell suspension cultures. Taxus cell suspension culture is an alternative to stripping bark from Taxus trees and extracting precursors from needles.
Link to Roberts Lab: http://robertsgroup.ecs.umass.edu/
|
Molecular Playground Banner : "Paclitaxel (Taxol), a natural product with anti-cancer activity"