|
|
| (83 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| - | [[Image:SSU front and LSU front side by side white backgroundSMALL.jpg|middle|500px]]<br>
| + | <StructureSection load='4v42' size='450' side='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/SandboxRibosome/Bothmodels6/1' caption='The Ribosome ([[4v42]])'> |
| - | | + | __TOC__ |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[Image:Screen capture of 70S white background spacefill tRNAS.jpg|left|300px]]<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''The Ribosome'''<br> | + | |
| - | '''The protein synthesis machine of cells''' <br> | + | |
| - | '''shown with the 3 transfer RNAs and messenger RNA bound.'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | | + | |
| | ==Introduction== | | ==Introduction== |
| - | <table width='550' align='right' cellpadding='5'><tr><td rowspan='2'> </td><td bgcolor='#eeeeee'><applet load='1jgo1giy.gz.pdb' size='540' frame='true' align='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/SandboxRibosome/Bothmodels6/1' /></td></tr><tr><td bgcolor='#eeeeee'><center>'''The Ribosome''' ([[1jgo]] and [[1giy]]), resolution 5.5Å (<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/SandboxRibosome/Bothmodels6/1'>initial scene</scene>). <br> | |
| - | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribotRNAs}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribomRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriborRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboProtein}} ··<br> | |
| - | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboAsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboPsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboEsitetRNA}} ·· <br> | |
| - | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboLSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboSSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle BlackWhiteBackground}} ·· <br></center></td></tr></table> | |
| | The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ribosome ribosome] is a complex composed of RNA and protein that adds up to several million daltons in size and plays a critical role in the process of decoding the genetic information stored in the genome into protein as outlined in what is now known as [http://sandwalk.blogspot.com/2009/10/ribosome-and-central-dogma-of-molecular.html the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology]. Specifically, the ribosome carries out the process of translation, decoding the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA, one amino acid at a time, into newly synthesized polypeptide chains. | | The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ribosome ribosome] is a complex composed of RNA and protein that adds up to several million daltons in size and plays a critical role in the process of decoding the genetic information stored in the genome into protein as outlined in what is now known as [http://sandwalk.blogspot.com/2009/10/ribosome-and-central-dogma-of-molecular.html the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology]. Specifically, the ribosome carries out the process of translation, decoding the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA, one amino acid at a time, into newly synthesized polypeptide chains. |
| | + | *'''30S ribosome''' - prokaryote small subunit |
| | + | *'''40S ribosome''' - eukaryote small subunit |
| | + | *'''pre-40S ribosome''' - eukaryote small subunit with associated assembly factors |
| | + | *'''43S ribosome''' - eukaryote preinitiation small subunit containing eIF3, eIF1 and eIF1A |
| | + | *'''48S ribosome''' - eukaryote small subunit initiation complex containing Met-tRNA |
| | + | *'''50S ribosome''' - prokaryote large subunit |
| | + | *'''60S ribosome''' - eukaryote large subunit |
| | + | *'''pre-60S ribosome''' - eukaryote nucleolar large subunit with associated assembly factors |
| | + | *'''70S ribosome''' - prokaryote full ribosome containing small and large subunits |
| | + | *'''80S ribosome''' - eukaryote full ribosome containing small and large subunits |
| | + | *'''90S pre-ribosome''' - eukaryote an early biogenesis ribosome intermediate containing assembly factors and small nucleolar RNAs. |
| | + | *'''100S ribosome''' - a dimer of prokaryote full ribosomes |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | ==Nobel Prize Winners and Other Contributors== | | ==Nobel Prize Winners and Other Contributors== |
| Line 31: |
Line 28: |
| | | | |
| | ==Ribosome Components== | | ==Ribosome Components== |
| | + | <br> |
| | + | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribotRNAs}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribomRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriborRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboProtein}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboAsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboPsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboEsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboLSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboSSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle BlackWhiteBackground}} ·· |
| | + | |
| | The small subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 30S<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Svedberg Svedberg unit] in Wikipedia</ref>. It is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,500 bases long (~500 kDa), plus about 20 protein chains. The proteins in the first small subunit determined range from about 3 kDa to 29 kDa. | | The small subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 30S<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Svedberg Svedberg unit] in Wikipedia</ref>. It is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,500 bases long (~500 kDa), plus about 20 protein chains. The proteins in the first small subunit determined range from about 3 kDa to 29 kDa. |
| | | | |
| - | The large subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 50S. It is composed of two chains of RNA, a 23S chain (~3000 bases long, 946 kDa) and a 5S chain (~120 bases long, 39 kDa). Assembled with the RNA are about 30 protein chains. The proteins in the first large subunit determined range from 6 kDa to 37 kDa. | + | The large subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 50S. It is composed of two chains of RNA, a 23S chain (~3000 bases long, 946 kDa) and a 5S chain (~120 bases long, 39 kDa). Assembled with the RNA are about 30 protein chains. The proteins in the first large subunit determined range from 6 kDa to 37 kDa. See also [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula]]. The large subunit contains several [[Kink-turn motif]]s. |
| | + | |
| | + | The ''mitochindrial ribosome'' or '''mitoribosome''' is smaller than the the cytoplasmic ribosome with a small subunit which sediments at 28S and a large subunit which sediments at 39S. The whole mitoribosome sediments at 55S. |
| | | | |
| | Other macromolecules in a functioning ribosome include three transfer RNA molecules, messenger RNA, and the nascent protein chain. | | Other macromolecules in a functioning ribosome include three transfer RNA molecules, messenger RNA, and the nascent protein chain. |
| Line 44: |
Line 46: |
| | The small subunit of the ribosome is the main site of decoding, directing the interaction of the messenger RNA codon with the anticodon stem-loops of the proper transfer RNA. The formation of peptide bonds occurs in the large subunit where the acceptor-stems of the tRNAs are docked. However, it is important to keep in mind that in the active ribosome the two subunits are in contact via bridges, and the actions in one subunit affect the other as the process of translation advances through the stages of initiation, elongation, and termination. | | The small subunit of the ribosome is the main site of decoding, directing the interaction of the messenger RNA codon with the anticodon stem-loops of the proper transfer RNA. The formation of peptide bonds occurs in the large subunit where the acceptor-stems of the tRNAs are docked. However, it is important to keep in mind that in the active ribosome the two subunits are in contact via bridges, and the actions in one subunit affect the other as the process of translation advances through the stages of initiation, elongation, and termination. |
| | | | |
| - | The initial determination of the atomic resolution structures of the subunits '''surprisingly revealed that RNA, but not protein, contributes directly to forming the site of both decoding and catalysis of peptide bond synthesis, with the ribosomal proteins only acting in an ancillary role'''. (Examine the structural data concerning peptide bond synthesis [[User:Wayne Decatur/Haloarcula Large Ribosomal Subunit#The ribosome is a ribozyme - protein DOES NOT participate directly in the chemistry of peptide bond synthesis:|here]].) During the elongation stage of translation, new peptides are added to the carboxy-terminus of the growing nascent chain that is linked to the acceptor-end of the tRNA in the peptidyl or P site. As the nascent chain grows, it advances into a tunnel that passes through the large subunit, called the polypeptide exit tunnel. Several factors can interact at the site of extrusion of the nascent polypeptide chain to ensure proper folding or transport across a membrane. Additionally, during protein synthesis, many additional factors such as elongation factors (EF-Tu and EF-G) interact with the ribosome to elicit decoding and peptide bond synthesis accurately and efficiently. Structures of several of these factors in complex with the ribosome, as well as intermediate states in the process, are being observed now, building upon the first atomic structures. | + | The initial determination of the atomic resolution structures of the subunits '''surprisingly revealed that RNA, but not protein, contributes directly to forming the site of both decoding and catalysis of peptide bond synthesis, with the ribosomal proteins only acting in an ancillary role''', see [[ribozyme]]. (Examine the structural data concerning peptide bond synthesis [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula#The ribosome is a ribozyme - protein DOES NOT participate directly in the chemistry of peptide bond synthesis:|here]].) During the elongation stage of translation, new peptides are added to the carboxy-terminus of the growing nascent chain that is linked to the acceptor-end of the tRNA in the peptidyl or P site. As the nascent chain grows, it advances into a tunnel that passes through the large subunit, called the polypeptide exit tunnel. Several factors can interact at the site of extrusion of the nascent polypeptide chain to ensure proper folding or transport across a membrane. Additionally, during protein synthesis, many additional factors such as elongation factors (EF-Tu and EF-G) interact with the ribosome to elicit decoding and peptide bond synthesis accurately and efficiently. Structures of several of these factors in complex with the ribosome, as well as intermediate states in the process, are being observed now, building upon the first atomic structures. |
| | | | |
| | ==First Atomic-Resolution Ribosome Structures== | | ==First Atomic-Resolution Ribosome Structures== |
| Line 51: |
Line 53: |
| | *<b>Yonath lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11007480</ref><ref>PMID: 11733066</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit - [[1fka]], improved in [[1i94]], [[1i95]], [[1i96]], and [[1i97]]. <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> is a [[Extremophiles|thermophilic]] eubacteria. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> large ribosomal subunit - [[1nkw]], later refined to give [[2zjr]]. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> is a mesophilic eubacteria.<br> | | *<b>Yonath lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11007480</ref><ref>PMID: 11733066</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit - [[1fka]], improved in [[1i94]], [[1i95]], [[1i96]], and [[1i97]]. <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> is a [[Extremophiles|thermophilic]] eubacteria. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> large ribosomal subunit - [[1nkw]], later refined to give [[2zjr]]. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> is a mesophilic eubacteria.<br> |
| | | | |
| - | *<b>Ramakrishnan lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11014182</ref><ref>PMID: 11014183</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit -[[1fjf]] which was later refined to [[1j5e]]. Related: in complex with the antibiotics streptomycin, spectinomycin, and paromomycin in [[1fjg]]; in complex with tetracycline in [[1hnw]], pactamycin in [[1hnx]], hygromycin B in [[1hnz]]. | + | *<b>Ramakrishnan lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11014182</ref><ref>PMID: 11014183</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit in [[1j5e]]. Related: in complex with the antibiotics streptomycin, spectinomycin, and paromomycin in [[1fjg]]; in complex with tetracycline in [[1hnw]], pactamycin in [[1hnx]], hygromycin B in [[1hnz]]. |
| | The <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,522 bases long (494 kDa), plus 20 protein chains (S2-S20, THX). The protein chains range from 26 (THX, 3 kDa) to 256 amino acids (S2, 29 kDa). | | The <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,522 bases long (494 kDa), plus 20 protein chains (S2-S20, THX). The protein chains range from 26 (THX, 3 kDa) to 256 amino acids (S2, 29 kDa). |
| | | | |
| - | *<b>Steitz and Moore labs original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID:10937989</ref><ref>PMID: 10937990</ref>: <em>Haloarcula marismortui</em> large ribosomal subunit - [[1ffk]] and later refined to give [[1jj2]], and then refined to give [[1s72]]. Related: [[1ffz]], [[1fg0]]. <em>Haloracula</em> is a [[Extremophiles|halophilic]] archaea. Assembled with the ribosomal RNAs (2,922 and 122 nucleotides long) in the structure are 27 protein chains (of a total of 31 known), varying in length from 49 (L39E, 6 kDa) to 337 amino acids (L3, 37 kDa).<ref>PMID:10937989</ref> | + | *<b>Steitz and Moore labs original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID:10937989</ref><ref>PMID: 10937990</ref>: <em>Haloarcula marismortui</em> large ribosomal subunit - [[1ffk]] and later refined to give [[1jj2]], and then refined to give [[1s72]], and later [[3cc2]]<ref>PMID:18455733</ref>. Related: [[1ffz]], [[1fg0]]. <em>Haloracula</em> is a [[Extremophiles|halophilic]] archaea. Assembled with the ribosomal RNAs (2,922 and 122 nucleotides long) in the structure are 27 protein chains (of a total of 31 known), varying in length from 49 (L39E, 6 kDa) to 337 amino acids (L3, 37 kDa).<ref>PMID:10937989</ref> |
| | | | |
| | ==Proteopedia Topic Pages Covering the Ribosome and Subunits== | | ==Proteopedia Topic Pages Covering the Ribosome and Subunits== |
| | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]] as solved by the Steitz & Moore labs.<br> | | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]] as solved by the Steitz & Moore labs.<br> |
| | *[[User:Wayne Decatur/Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome|Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome]]<br> | | *[[User:Wayne Decatur/Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome|Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome]]<br> |
| | + | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula]]<br /> |
| | *[[User:Wayne_Decatur/Haloarcula Large Ribosomal Subunit With Azithromycin|Azithromycin bound to the Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula marismortui]]<br> | | *[[User:Wayne_Decatur/Haloarcula Large Ribosomal Subunit With Azithromycin|Azithromycin bound to the Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula marismortui]]<br> |
| | + | *[[Azithromycin]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Clarithromycin]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Doxycycline]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[40S rRNA and proteins and P/E tRNA for eukaryotic ribosome]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Ribosomal A Site Binding Paromomycin: A Morph]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Ribosome structure]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Ribosome structure (Spanish)]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[Ribosome (Czech)]]<br /> |
| | | | |
| - | ==Additional Ribosome Structures== | + | ==Ribosome 3D structures== |
| - | <b>Several other ribosome structures have now been published, and here are just a few of these entries in Proteopedia (with apologies to the authors of those not yet listed):<br></b>
| + | |
| - | *[[2j00]] and [[2j01]] are the subunits of the 70S ribosome structure from the Ramakrishnan lab; the aminoglycoside antibiotic paromomycin is present as well. [[2j02]] and [[2j02]] form another molecule described in the accompanying report.<br>
| + | [[Ribosome 3D structures]] |
| - | *[[1gix]] and [[1giy]] are the subunits of the 70S ribosome structure determined by the Noller lab, the first for the 70S at near-atomic resolution; more of the mRNA chain is seen in [[1jgo]].<br>
| + | |
| - | *[[2i2u]] and [[2i2v]] are the subunits of the <em>E. coli</em> ribosome at 3.2 Å as solved by the Cate lab. [[2i2t]] and [[2i2p]] are related structures.<br>
| + | |
| - | *[[2gya]] and [[2gy9]] are the subunits of a complete <em>E. coli</em> ribosome as determined by cryo-EM by Joachim Frank's lab.<br>
| + | |
| - | *[[1ibk]] is paromomycin bound to the small subunit.<br>
| + | |
| - | *[[1ibm]] is the small subunit with an mRNA analog bound and an anticodon stem loop bound to the A site.<br>
| + | |
| - | *Small subunit bound to near-cognate tRNA anticodon stem-loop: [[1n32]], [[1n33]], [[1n34]], [[1n36]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *[[2ow8]] and [[1vsa]] are the subunits of a 70S-tRNA-mRNA complex from the Noller lab.<br>
| + | |
| - | *Macrolide, lincosamide, streptogramin B, and ketolide antibiotics bound to the large subunit, which impacts mechanisms of drug resistance:[[1yi2]], [[1yj2]], [[1yit]], [[1yhq]], [[1yjn]], [[1yij]], and [[1yj9]] <br>
| + | |
| - | *Chloramphenicol bound to the ''H. marimortui'' 50S ribosomal subunit: [[1nji]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *Chloramphenicol bound to the ''D. radiodurans'' 50S ribosomal subunit: [[1k01]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *The antibiotic linezolid (example of the first new class of antibiotics to enter into clinical usage within the past 30 years) bound to the large ribosomal subunit of ''D. radiodurans'': [[3dll]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *Thiopeptide antibiotics bound to the large ribosomal subunit of ''D. radiodurans'': [[2zjp]], [[2zjq]],and [[3cf5]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *Macrolide antibiotics bound to the large ribosomal subunit of ''D. radiodurans'': [[2o43]], [[2o44]], and [[2o45]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *Ribosome Binding Domain of the Trigger Factor in complex with the large ribosomal subunit of ''D. radiodurans'': [[2d3o]] and [[2aar]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *Initiation factor 1 bound to the small subunit: [[1hr0]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *70S interaction with the Shine-Dalgarno sequence: [[2qnh]] and [[1vsp]].<br>
| + | |
| - | *Ribosome Recycling Factor bound to the 70S Ribosome: [[2v46]], [[2v47]], [[2v48]], and [[2v49]] <br>
| + | |
| - | *[[2e5l]] shows the small subunit with an mRNA mimic bound and the Shine-Dalgarno and anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequences interacting.<br>
| + | |
| - | *70S ribosome in complex with release factors RF1 and RF2 bound to a cognate stop codon: [[2b64]] and [[2b66]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *Structures of the 30S bound with anticodon stem-loops from tRNAs that facilitate frame-shifting: [[2uxb]], [[2uxc]], and [[2uxd]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *70S Ribosome in complex with mRNA, paromomycin, acylated A- And P-Site tRNAs, and E-Site tRNA: [[2wdg]], [[2wdh]], [[2wdi]], [[2wdj]], [[2wdk]], [[2wdl]], [[2wdm]], and [[2wdn]]<br>
| + | |
| - | * ''E. coli'' 70S ribosome in complex with paramomycin and ribosome recycling factor: [[2qal]], [[2qam]], [[2qan]], [[2qao]], [[2qb9]], [[2qba]], [[2qbb]], [[2qbc]], [[2qbd]], [[2qbe]], [[2qbf]], [[2qbg]], [[2qbh]], [[2qbi]], [[2qbj]], [[2qbk]], [[2z4k]], [[2z4l]], [[2z4m]], and [[2z4n]].<br>
| + | |
| - | *''E. coli'' 70S ribosome intermediates in a key conformational change: [[3i1m]], [[3i1n]], [[3i1o]], [[3i1p]], [[3i1q]], [[3i1r]],[[3i1s]],[[3i1t]],[[3i1z]], [[3i20]], [[3i21]], and [[3i22]].<br>
| + | |
| - | *''E. coli'' ribosome in complex with the atypical aminoglycoside antibiotic hygromycin B: [[3df1]], [[3df2]],[[3df3]], and [[3df4]].<br>
| + | |
| - | *Structural basis of a mechanism of hydrolytic release of the newly formed polypeptide by the large subunit that may be analogous to that used by release factors:[[3cma]] and [[3cme]]
| + | |
| - | *Elongation factor P bound to the 70S ribosome: [[3huw]], [[3hux]], [[3huy]], and [[3huz]].<br>
| + | |
| - | *70S ribosome in complex with Ef-Tu and and aminoacyl-tRNA (P- and E- site tRNAs are also present): [[2wrn]], [[2wro]], [[2wrq]], and [[2wrr]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *70S ribosome in complex with EF-G (P- and E- site tRNAs are also present): [[2wri]] , [[2wrj]], [[2wrk]], and [[2wrl]]<br>
| + | |
| - | *The eukaryotic (''S. cerevisiae'') ribosome at atomic resolution using cryo-EM reconstruction and protein [[Theoretical models#Homology Models|homology modeling]]: [[3jyx]], [[3jyw]], and [[3jyv]] <br>
| + | |
| | | | |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| | + | |
| | * [[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]] | | * [[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]] |
| | + | * [[Highest impact structures]] of all time |
| | + | * [[Translation]] |
| | + | * [[DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation]] |
| | + | * [[tRNA]] |
| | + | * [[LepA|Escherichia coli LepA, the ribosomal back translocase]] |
| | * [[Extremophiles]] | | * [[Extremophiles]] |
| - | * [[Highest_impact_structures]] of all time | + | * [[RNA]] |
| | + | * [[Ribozyme]] |
| | + | * For Spanish see [[Ribosoma 70S]] |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |
| Line 103: |
Line 94: |
| | | | |
| | ==Additional Literature and Resources== | | ==Additional Literature and Resources== |
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID:19222865</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19838167</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 11297922</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19962317</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19938030</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 18547810</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 17764954</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 18292779</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19089882</ref><references group="xtra"/> | + | <ref group="xtra">PMID:19222865</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19838167</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 11297922</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19962317</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19938030</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 18547810</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 17764954</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 18292779</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 19089882</ref><ref group="xtra">PMID: 23771137</ref><references group="xtra"/> |
| | + | *[http://apollo.chemistry.gatech.edu/RiboVision/ RiboVision] - a nice way to explore the representative structures with the secondary structures of the RNA side-by-side with the 3D structure, from from Georgia Institute of Technology and NASA. |
| | + | *The people behind [http://apollo.chemistry.gatech.edu/RiboVision/ RiboVision] have determined a [http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/41/15/7522.short?rss=1 revised secondary structure for two of the rRNAs] based on the 3D structures and it is described in [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23771137?dopt=Abstract their paper]<ref group="xtra">PMID: 23771137</ref>. |
| | *[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=general_information/news_publications/news/news_2009.html#20091013 RCSB Protein Data Bank coverage of the 2009 Nobel Prizes in Chemistry] | | *[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=general_information/news_publications/news/news_2009.html#20091013 RCSB Protein Data Bank coverage of the 2009 Nobel Prizes in Chemistry] |
| | *[http://www.pdb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb121_1.html 70S Ribosome: January 2010 Molecule of the Month] as part of the series of tutorials that are at [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do the RCSB Protein Data Bank] and written by [[User:David_S._Goodsell|David Goodsell]] | | *[http://www.pdb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb121_1.html 70S Ribosome: January 2010 Molecule of the Month] as part of the series of tutorials that are at [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do the RCSB Protein Data Bank] and written by [[User:David_S._Goodsell|David Goodsell]] |
| | *[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb10_1.html Ribosome: October 2000 Molecule of the Month] as part of the series of tutorials that are at [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do the RCSB Protein Data Bank] and written by [[User:David_S._Goodsell|David Goodsell]] | | *[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb10_1.html Ribosome: October 2000 Molecule of the Month] as part of the series of tutorials that are at [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do the RCSB Protein Data Bank] and written by [[User:David_S._Goodsell|David Goodsell]] |
| | + | |
| | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
| | + | [[Category:Translation]] |
| | + | [[Category:Ribosome]] |
| | + | [[Category: BioMolViz]] |
| | + | [[Category: Macromolecular Assemblies]] |
|
Introduction
The ribosome is a complex composed of RNA and protein that adds up to several million daltons in size and plays a critical role in the process of decoding the genetic information stored in the genome into protein as outlined in what is now known as the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. Specifically, the ribosome carries out the process of translation, decoding the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA, one amino acid at a time, into newly synthesized polypeptide chains.
- 30S ribosome - prokaryote small subunit
- 40S ribosome - eukaryote small subunit
- pre-40S ribosome - eukaryote small subunit with associated assembly factors
- 43S ribosome - eukaryote preinitiation small subunit containing eIF3, eIF1 and eIF1A
- 48S ribosome - eukaryote small subunit initiation complex containing Met-tRNA
- 50S ribosome - prokaryote large subunit
- 60S ribosome - eukaryote large subunit
- pre-60S ribosome - eukaryote nucleolar large subunit with associated assembly factors
- 70S ribosome - prokaryote full ribosome containing small and large subunits
- 80S ribosome - eukaryote full ribosome containing small and large subunits
- 90S pre-ribosome - eukaryote an early biogenesis ribosome intermediate containing assembly factors and small nucleolar RNAs.
- 100S ribosome - a dimer of prokaryote full ribosomes
Nobel Prize Winners and Other Contributors
Venkatraman Ramakrishnan of the M.R.C. Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England; Thomas A. Steitz of Yale University; and Ada E. Yonath of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel have been awarded the the 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry[1] for their landmark work revealing the atomic details of the molecular machine that make proteins in all cells, the ribosome. Their findings are the gloriously enlightening culmination of years of work[2], first heralded by Ada Yonath's report of crystals in 1980[3]. Others made significant contributions to the detailed structure of this machine, as poignantly summarized by Jeremy Berg, current Director of National Institute of General Medical Sciences, in his announcement
The Nobel committee has the daunting challenge of limiting itself to up to three laureates for each prize. Several other long-time NIGMS grantees who also contributed greatly to our understanding of the structure and function of the ribosome include Peter Moore, Harry Noller and Joachim Frank.
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology posted an announcement of the prize echoing this sentiment as well.
Impact of Ribosome Structure
The ribosome ranks among the known structures with highest impact. Imagine the wonder and thrill at suddenly knowing how tens of proteins and large and small RNAs fit together into the elegant machines that serve as the protein factories in every cell and organelle of every organism on the planet. The immense size of the ribosome and each of the two individual ribosomal subunits that come together to form the complete ribosome that is active in translation made for a daunting task in structure determination. These structures were at the time they were first determined, and remain (in 2009), the largest asymmetric molecules solved crystallographically. In addition to providing us immense insight into the general molecular and atomic details of protein synthesis in every organism on earth, the development of new antibiotics are likely to rely on this ground-breaking work.
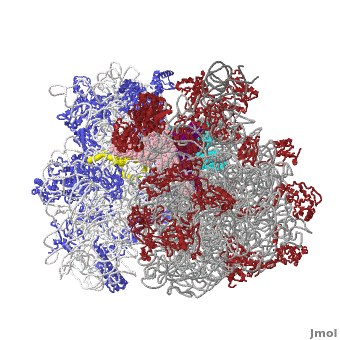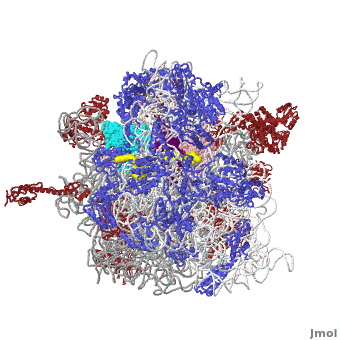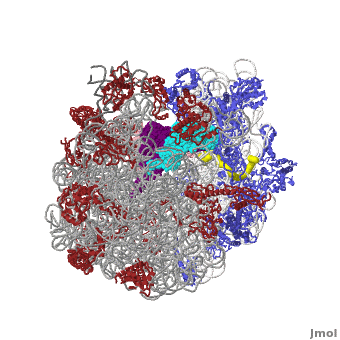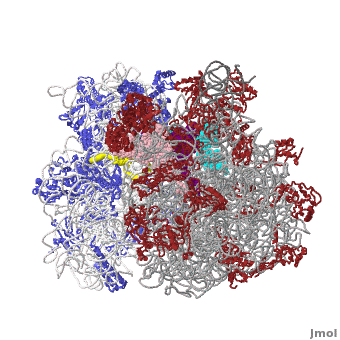
Ribosome Components
·· ·· ·· ·· ·· ·· ·· ·· ·· ·· ··
The small subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 30S[4]. It is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,500 bases long (~500 kDa), plus about 20 protein chains. The proteins in the first small subunit determined range from about 3 kDa to 29 kDa.
The large subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 50S. It is composed of two chains of RNA, a 23S chain (~3000 bases long, 946 kDa) and a 5S chain (~120 bases long, 39 kDa). Assembled with the RNA are about 30 protein chains. The proteins in the first large subunit determined range from 6 kDa to 37 kDa. See also Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula. The large subunit contains several Kink-turn motifs.
The mitochindrial ribosome or mitoribosome is smaller than the the cytoplasmic ribosome with a small subunit which sediments at 28S and a large subunit which sediments at 39S. The whole mitoribosome sediments at 55S.
Other macromolecules in a functioning ribosome include three transfer RNA molecules, messenger RNA, and the nascent protein chain.
Thus, a complete functioning prokaryotic ribosome contains 7 RNA chains (including three tRNA's and one mRNA), 47 ribosomal protein chains, and one nascent protein chain. The total molecular mass is several million daltons.
The cytoplasmic ribosomes of eukaryotes are larger with more RNA and proteins. Eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes also have an additional RNA in the large subunit, the 5.8S rRNA, that is about 150 nts and related to the 5' end of prokaryotic rRNA. In regards to the size, the ribosomal subunits of budding yeast and humans sediment at 40S and 60S; the complete ribosome sediments at 80S and it is generally about another million daltons larger than the prokaryotic one.
The Peptidyl Transferase Is A Ribozyme
The small subunit of the ribosome is the main site of decoding, directing the interaction of the messenger RNA codon with the anticodon stem-loops of the proper transfer RNA. The formation of peptide bonds occurs in the large subunit where the acceptor-stems of the tRNAs are docked. However, it is important to keep in mind that in the active ribosome the two subunits are in contact via bridges, and the actions in one subunit affect the other as the process of translation advances through the stages of initiation, elongation, and termination.
The initial determination of the atomic resolution structures of the subunits surprisingly revealed that RNA, but not protein, contributes directly to forming the site of both decoding and catalysis of peptide bond synthesis, with the ribosomal proteins only acting in an ancillary role, see ribozyme. (Examine the structural data concerning peptide bond synthesis here.) During the elongation stage of translation, new peptides are added to the carboxy-terminus of the growing nascent chain that is linked to the acceptor-end of the tRNA in the peptidyl or P site. As the nascent chain grows, it advances into a tunnel that passes through the large subunit, called the polypeptide exit tunnel. Several factors can interact at the site of extrusion of the nascent polypeptide chain to ensure proper folding or transport across a membrane. Additionally, during protein synthesis, many additional factors such as elongation factors (EF-Tu and EF-G) interact with the ribosome to elicit decoding and peptide bond synthesis accurately and efficiently. Structures of several of these factors in complex with the ribosome, as well as intermediate states in the process, are being observed now, building upon the first atomic structures.
First Atomic-Resolution Ribosome Structures
The particular structures for which the Nobel prize was awarded were published in 2000 and were subsequently refined or improved upon. All these structures were determined using proteins from extremophiles. Here are the links to the Proteopedia entries:
- Yonath lab original atomic-resolution structures[5][6]: Thermus thermophilus small ribosomal subunit - 1fka, improved in 1i94, 1i95, 1i96, and 1i97. Thermus thermophilus is a thermophilic eubacteria. Deinococcus radiodurans large ribosomal subunit - 1nkw, later refined to give 2zjr. Deinococcus radiodurans is a mesophilic eubacteria.
- Ramakrishnan lab original atomic-resolution structures[7][8]: Thermus thermophilus small ribosomal subunit in 1j5e. Related: in complex with the antibiotics streptomycin, spectinomycin, and paromomycin in 1fjg; in complex with tetracycline in 1hnw, pactamycin in 1hnx, hygromycin B in 1hnz.
The Thermus thermophilus small ribosomal subunit is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,522 bases long (494 kDa), plus 20 protein chains (S2-S20, THX). The protein chains range from 26 (THX, 3 kDa) to 256 amino acids (S2, 29 kDa).
- Steitz and Moore labs original atomic-resolution structures[9][10]: Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit - 1ffk and later refined to give 1jj2, and then refined to give 1s72, and later 3cc2[11]. Related: 1ffz, 1fg0. Haloracula is a halophilic archaea. Assembled with the ribosomal RNAs (2,922 and 122 nucleotides long) in the structure are 27 protein chains (of a total of 31 known), varying in length from 49 (L39E, 6 kDa) to 337 amino acids (L3, 37 kDa).[12]
Proteopedia Topic Pages Covering the Ribosome and Subunits
Ribosome 3D structures
Ribosome 3D structures
See Also
References
- ↑ Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure.
- ↑ Service RF. Chemistry Nobel. Honors to researchers who probed atomic structure of ribosomes. Science. 2009 Oct 16;326(5951):346-7. PMID:19833925 doi:326/5951/346
- ↑ Yonath A, Mussig J, Tesche B, Lorenz S, Erdmann VA, Wittmann HG. Crystallization of the large ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem. Internat. 1980 1:428-435.
- ↑ Svedberg unit in Wikipedia
- ↑ Schluenzen F, Tocilj A, Zarivach R, Harms J, Gluehmann M, Janell D, Bashan A, Bartels H, Agmon I, Franceschi F, Yonath A. Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution. Cell. 2000 Sep 1;102(5):615-23. PMID:11007480
- ↑ Harms J, Schluenzen F, Zarivach R, Bashan A, Gat S, Agmon I, Bartels H, Franceschi F, Yonath A. High resolution structure of the large ribosomal subunit from a mesophilic eubacterium. Cell. 2001 Nov 30;107(5):679-88. PMID:11733066
- ↑ Wimberly BT, Brodersen DE, Clemons WM Jr, Morgan-Warren RJ, Carter AP, Vonrhein C, Hartsch T, Ramakrishnan V. Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature. 2000 Sep 21;407(6802):327-39. PMID:11014182 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35030006
- ↑ Carter AP, Clemons WM, Brodersen DE, Morgan-Warren RJ, Wimberly BT, Ramakrishnan V. Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature. 2000 Sep 21;407(6802):340-8. PMID:11014183 doi:10.1038/35030019
- ↑ Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution. Science. 2000 Aug 11;289(5481):905-20. PMID:10937989
- ↑ Nissen P, Hansen J, Ban N, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The structural basis of ribosome activity in peptide bond synthesis. Science. 2000 Aug 11;289(5481):920-30. PMID:10937990
- ↑ Blaha G, Gurel G, Schroeder SJ, Moore PB, Steitz TA. Mutations outside the anisomycin-binding site can make ribosomes drug-resistant. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 6;379(3):505-19. Epub 2008 Apr 8. PMID:18455733 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.075
- ↑ Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution. Science. 2000 Aug 11;289(5481):905-20. PMID:10937989
Additional Literature and Resources
- Moore PB. The ribosome returned. J Biol. 2009;8(1):8. Epub 2009 Jan 26. PMID:19222865 doi:10.1186/jbiol103
- Schmeing TM, Ramakrishnan V. What recent ribosome structures have revealed about the mechanism of translation. Nature. 2009 Oct 29;461(7268):1234-42. Epub 2009 Oct 18. PMID:19838167 doi:10.1038/nature08403
- Ramakrishnan V, Moore PB. Atomic structures at last: the ribosome in 2000. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Apr;11(2):144-54. PMID:11297922
- Rodnina MV, Wintermeyer W. The ribosome goes Nobel. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010 Jan;35(1):1-5. Epub 2009 Dec 2. PMID:19962317 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2009.11.003
- Sprinzl M, Erdmann VA. Protein biosynthesis on ribosomes in molecular resolution: Nobel Prize for chemistry 2009 goes to three chemical biologists. Chembiochem. 2009 Dec 14;10(18):2851-3. PMID:19938030 doi:10.1002/cbic.200900652
- Bashan A, Yonath A. Correlating ribosome function with high-resolution structures. Trends Microbiol. 2008 Jul;16(7):326-35. Epub 2008 Jun 9. PMID:18547810 doi:10.1016/j.tim.2008.05.001
- Korostelev A, Noller HF. The ribosome in focus: new structures bring new insights. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007 Sep;32(9):434-41. Epub 2007 Aug 30. PMID:17764954 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2007.08.002
- Steitz TA. A structural understanding of the dynamic ribosome machine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;9(3):242-53. PMID:18292779 doi:10.1038/nrm2352
- Zimmerman E, Yonath A. Biological implications of the ribosome's stunning stereochemistry. Chembiochem. 2009 Jan 5;10(1):63-72. PMID:19089882 doi:10.1002/cbic.200800554
- Petrov AS, Bernier CR, Hershkovits E, Xue Y, Waterbury CC, Hsiao C, Stepanov VG, Gaucher EA, Grover MA, Harvey SC, Hud NV, Wartell RM, Fox GE, Williams LD. Secondary structure and domain architecture of the 23S and 5S rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jun 14. PMID:23771137 doi:10.1093/nar/gkt513
|