T-box proteins
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(Restoring references - don't know how to do them properly) |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
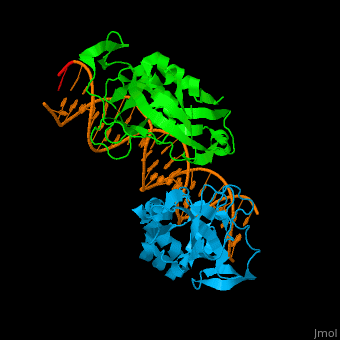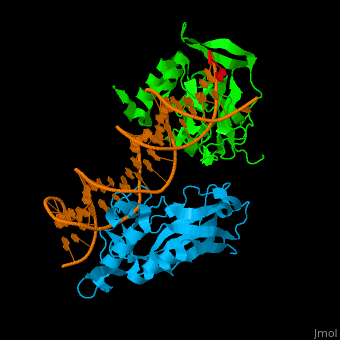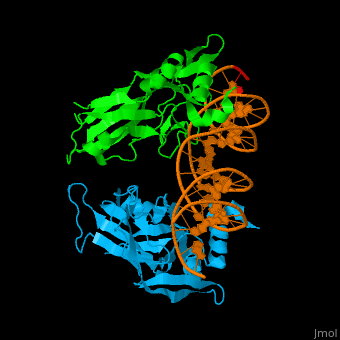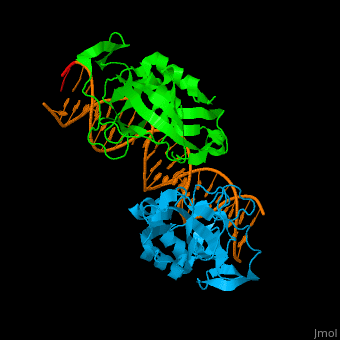
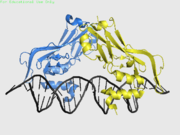
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' scene='40/408030/Cv/1' caption='Human TBX1 complex with DNA, [[4a04]]' > | |
| + | [[Image:TBX3.png|thumb|left|alt=TBX3 dimer on DNA|TBX3, a T-box protein, binds to palindromic DNA as a dimer.]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| - | The family of T-box proteins are transcription factors with a transcriptional activator or repressor domain and a DNA-binding T-box domain. The first two proteins discovered were Brachyury and Omb, which were found to have a new distinct domain unlike any other, designated the T-box domain. Other homologous proteins have been discovered in both invertebrate and vertebrate organisms but not in some organisms such as ''Aribidopsis thaliana''. This family has ~20 members in ''Homo sapiens''. | + | The family of '''T-box proteins''' are transcription factors with a transcriptional activator or repressor domain and a DNA-binding T-box domain. The first two proteins discovered were Brachyury and Omb, which were found to have a new distinct domain unlike any other, designated the T-box domain. Other homologous proteins have been discovered in both invertebrate and vertebrate organisms but not in some organisms such as ''Aribidopsis thaliana''. This family has ~20 members in ''Homo sapiens''. For details on individual T-box proteins see<br /> |
| + | * [[TBX1]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[TBX3]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[TBX5]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[TBX15]]<br /> | ||
| + | * '''TBX21''' regulates type-1-like immunity<ref>PMID:16696895</ref>. | ||
| + | * [[Transcription and RNA Processing]]. | ||
=Gene loci and structure= | =Gene loci and structure= | ||
| - | The loci of these genes are dispersed throughout the genomes of relevant oragnisms, though a few select cases of clustering exist. Tight linkages include Tbx8 and Tbx9 in ''C. elegans'', and in mice: Tbx2 and Tbx4 on chromosome 11; and | + | The loci of these genes are dispersed throughout the genomes of relevant oragnisms, though a few select cases of clustering exist. Tight linkages include Tbx8 and Tbx9 in ''C. elegans'', and in mice: Tbx2 and Tbx4 on chromosome 11; and [[TBX3]] and [[TBX5]] on chromosome 5. Similar linkages are present in humans. These genes include multiple exons, typically 8 (as in Tbx5). There are a few cases of alternative splicing, such as VegT in ''Xenopus'' and [[TBX1]] in humans. |
=Protein structure= | =Protein structure= | ||
A T-box protein is typically 50 - 78 kDa, within which the T-box domain is typically 17 - 26 kDa. T-box proteins have folds characteristic of the immunoglobin fold. The T-box domains of most family members bind to the consensus sequence TCACACCT. Some residues are conserved through particular subfamilies, such as Lys149 of the Xbra family, and others throughout the entire T-box family. However, differences lie in the binding topology of multiple recognised sequence motifs. For example, Xbra binds two head-to-head sequence motifs, and cannot bind them tail-to-tail; VegT can bind tail-to-tail and not head-to-head. It has been suggested that other functions may lie within the T-box such as mediating protein-protein interactions. The transcription-mediating domain can either be activating or repressing and bears less to no sequence homology. | A T-box protein is typically 50 - 78 kDa, within which the T-box domain is typically 17 - 26 kDa. T-box proteins have folds characteristic of the immunoglobin fold. The T-box domains of most family members bind to the consensus sequence TCACACCT. Some residues are conserved through particular subfamilies, such as Lys149 of the Xbra family, and others throughout the entire T-box family. However, differences lie in the binding topology of multiple recognised sequence motifs. For example, Xbra binds two head-to-head sequence motifs, and cannot bind them tail-to-tail; VegT can bind tail-to-tail and not head-to-head. It has been suggested that other functions may lie within the T-box such as mediating protein-protein interactions. The transcription-mediating domain can either be activating or repressing and bears less to no sequence homology. | ||
| + | *<scene name='40/408030/Cv/5'>Human TBX1 dimer complex with DNA</scene> ([[4a04]]). | ||
=Function and implications in development= | =Function and implications in development= | ||
T-box proteins are expressed in specific organs or in only particular cell types, and are involved in decisions about early cell fate. Mutant alleles typically show haploinsufficiency (T-box proteins tend to be dosage-specific). When mutations occur, developmental disorders arise such as the ulnar-mammary syndrome caused by mutations in TBX3, and some aspects of DiGeorge syndrome implicated by mutations in TBX1. | T-box proteins are expressed in specific organs or in only particular cell types, and are involved in decisions about early cell fate. Mutant alleles typically show haploinsufficiency (T-box proteins tend to be dosage-specific). When mutations occur, developmental disorders arise such as the ulnar-mammary syndrome caused by mutations in TBX3, and some aspects of DiGeorge syndrome implicated by mutations in TBX1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: [[T]], TBX2, [[TBX3]], [[TBX5]], [[TBX15]] and TBX18. | Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: [[T]], TBX2, [[TBX3]], [[TBX5]], [[TBX15]] and TBX18. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 56: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[TBX1]] | | [[TBX1]] | ||
| - | | Crystal structure solved | + | | Crystal structure solved ([[4a04]]) |
| DiGeorge syndrome | | DiGeorge syndrome | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 88: | Line 100: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[TBX5]] | | [[TBX5]] | ||
| - | | | + | | Crystal structure solved |
| Holt-Oram syndrome | | Holt-Oram syndrome | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 125: | Line 137: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =3D structures of T-box protein= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[4a04]] – hTBX1 T-box domain + DNA - human<br /> | ||
| + | [[1h6f]] - hTBX3 T-box domain + DNA <br /> | ||
| + | [[2x6u]], [[5bqd]] – hTBX5 T-box domain<br /> | ||
| + | [[2x6v]] – hTBX5 T-box domain + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | [[4s0h]], [[5flv]] - hTBX5 T-box domain + homebox protein + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | [[5t1j]] – TBX21 T-box domain + DNA - mouse<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Additional Resources= | ||
| + | For additional information, see: [[Transcription and RNA Processing]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| Line 132: | Line 157: | ||
* American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 140A:1407–1413 (2006); | * American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 140A:1407–1413 (2006); | ||
* Genome Biology 2002, 3(6):reviews3008.1–3008.7; | * Genome Biology 2002, 3(6):reviews3008.1–3008.7; | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: T, TBX2, TBX3, TBX5, TBX15 and TBX18.
Contents |
T-box family members in Homo sapiens
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| T | Crystal structure solved | |
| TBX19 |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX1 | Crystal structure solved (4a04) | DiGeorge syndrome |
| TBX10 | ||
| TBX15 | Cousin syndrome | |
| TBX18 | ||
| TBX20 | ||
| TBX22 | Truncated T-box domain predicted not to bind DNA | Cleft palate with ankyloglossia |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX2 | Mutation of Arg122 destroys DNA binding. Acts as a repressor. TRP-1 promoter is a possible binding site. | Amplified in certain types of breast cancer. |
| TBX3 | Crystal structure solved | Ulnar-mammary syndrome |
| TBX4 | Small patella syndrome | |
| TBX5 | Crystal structure solved | Holt-Oram syndrome |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX6 | ||
| MGA | Also contains leucine zipper domain |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBR1 | ||
| EOMES | ||
| TBX21 |
3D structures of T-box protein
4a04 – hTBX1 T-box domain + DNA - human
1h6f - hTBX3 T-box domain + DNA
2x6u, 5bqd – hTBX5 T-box domain
2x6v – hTBX5 T-box domain + DNA
4s0h, 5flv - hTBX5 T-box domain + homebox protein + DNA
5t1j – TBX21 T-box domain + DNA - mouse
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Transcription and RNA Processing
References
- Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 1997, 7:474-480;
- Gene 258 (2000) 15–29;
- American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 140A:1407–1413 (2006);
- Genome Biology 2002, 3(6):reviews3008.1–3008.7;
- ↑ Peng SL. The T-box transcription factor T-bet in immunity and autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2006 Apr;3(2):87-95 PMID:16696895
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Helen Ginn, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman