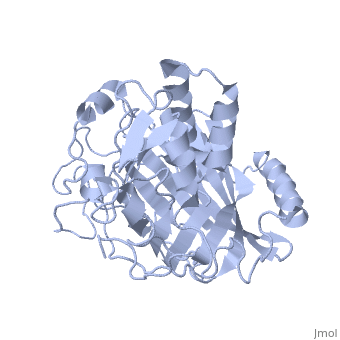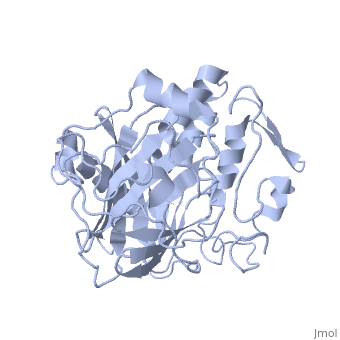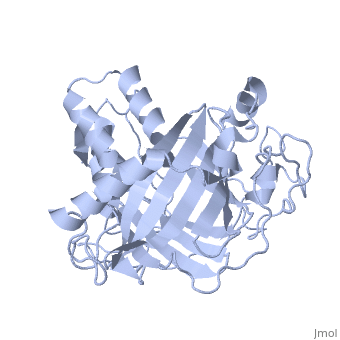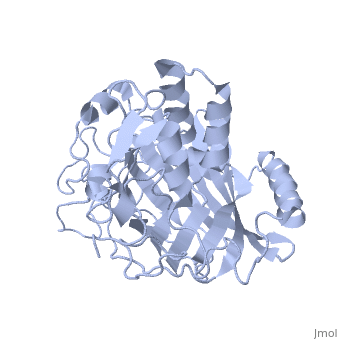
Dinoflagellate luciferase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
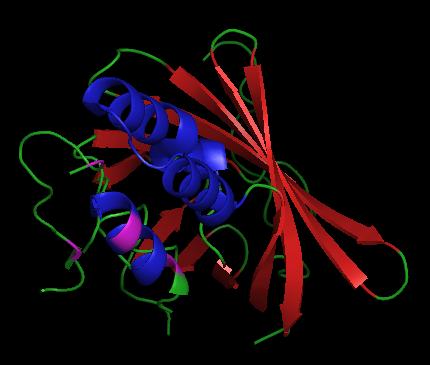
| - | + | <StructureSection load='1vpr' size='300' side='right' scene='' caption='Luciferase domain from a Dinoflagellate. Selenomethionines shown as space-filling objects [[1vpr]]'> | |
| - | + | == Introduction == | |
| - | |||
| - | == Introduction == | ||
| - | pineapples | ||
''Lingulodinium polyedrum'', a marine dinoflagellate often responsible for red tide, possesses a unique [[luciferase]] enyzme. When mechanically stimulated, the organism uses this enzyme to produce a blue light, likely for use in quorum sensing. Other luciferase enzymes typically produce green-yellow to red light. Also, while all luciferase enzymes produce light through oxidation of luciferin, the biochemical mechanism by which this is achieved varies. This means that while the result is the same, there is low similarity to bacterial or firefly luciferases. | ''Lingulodinium polyedrum'', a marine dinoflagellate often responsible for red tide, possesses a unique [[luciferase]] enyzme. When mechanically stimulated, the organism uses this enzyme to produce a blue light, likely for use in quorum sensing. Other luciferase enzymes typically produce green-yellow to red light. Also, while all luciferase enzymes produce light through oxidation of luciferin, the biochemical mechanism by which this is achieved varies. This means that while the result is the same, there is low similarity to bacterial or firefly luciferases. | ||
In ''L. polyedrum'', the luciferase enzyme is a single polypeptide chain folded into 3 similar domains. Interestingly, all three domains appear to be distinct luciferase centres with their own catalytic activities <ref name="main">PMID:15665092</ref> | In ''L. polyedrum'', the luciferase enzyme is a single polypeptide chain folded into 3 similar domains. Interestingly, all three domains appear to be distinct luciferase centres with their own catalytic activities <ref name="main">PMID:15665092</ref> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 21: | ||
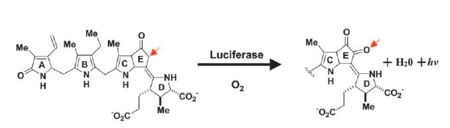
| - | [[Image:Luciferase_reaction.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Luciferase_reaction.jpg|left|thumb|450px]] |
''Image courtesy of L. Wayne Schultz.'' | ''Image courtesy of L. Wayne Schultz.'' | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | ==Content Donors== | ||
| + | |||
| + | All the initial portions of this page were created by [[User:James Jones|James Jones]] and were moved because it deserved its own separate page distinct from the associated PDB entry. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ==3D structures of luciferase== | ||
| - | == Related Links == | ||
[[Luciferase]] | [[Luciferase]] | ||
| - | [[1vpr]] is the structure used on this page. | + | ==See Also== |
| + | *[[1vpr]] is the structure used on this page. | ||
| + | *[[Colored & Bioluminescent Proteins]] | ||
| + | * [[PyMOL]] | ||
| - | [http://www.pymol.org/ Pymol molecular viewer] | ||
| - | + | == External Resources == | |
| - | [http://www. | + | *[http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1VPR Protein Data Bank file on 1VPR] |
| - | [http:// | + | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/ABO61076.1?ordinalpos=1&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Sequence.Sequence_ResultsPanel.Sequence_RVDocSum NCBI protein entry on ''P. lunula'' luciferase] |
| - | + | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2006_6 PDB molecule of the month feature on luciferases] | |
| - | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of luciferase
See Also
- 1vpr is the structure used on this page.
- Colored & Bioluminescent Proteins
- PyMOL
External Resources
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Wayne Decatur, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, James Jones, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner