This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
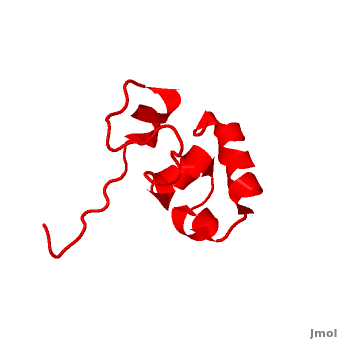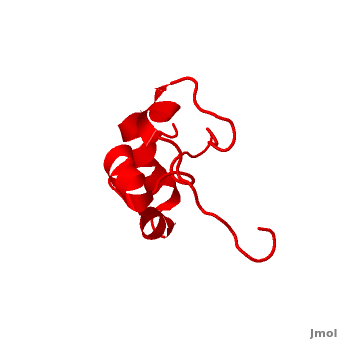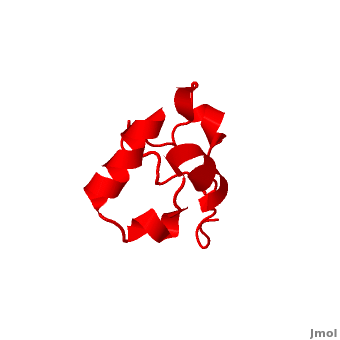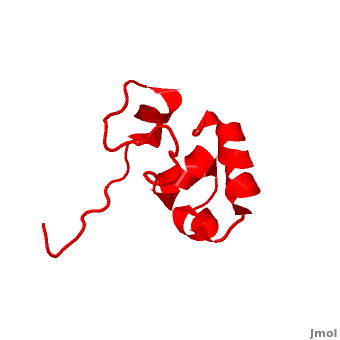
Villin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (42 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[ | + | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human supervillin headpiece, [[2k6n]]' scene='Villin/Cv/1' > |
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | * [[Villin]] (VIL) is an actin-binding protein. It contains gelsolin-like domains in its N-terminal and a helical headpiece which binds actin<ref>PMID:10480879</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Supervillin (SVIL)''' contains numerous gelsolin-like domains in its C-terminal and interacts with actin<ref>PMID:20309963</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Advillin (AVIL)''' is another actin-binding protein in the [[gelsolin]] superfamily which is expressed in the peripheral sensory neurons.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Cytovillin (CVIL) or ezrin or villin-2''' serves as intermediate between plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton<ref>PMID:8089177</ref>. | ||
| - | + | == Relevance == | |
| + | VIL immunohisochemistry is a reliable method for diagnosing microvillus inclusion disease (MVID)<ref>PMID:25517957</ref>. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | == 3D Structures of Villin == | ||
| - | + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |
| - | + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | * Supervillin | |
| + | **[[2k6m]], [[2k6n]] – hSVIL headpiece– human – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | + | * Villin | |
| + | **[[3fg7]] – hVIL-1 gelsolin domains 4-6<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1unc]] – hVIL-1 headpiece<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3iur]] - hVIL headpiece H2H3 helices + prolyl endopeptidase <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1yu5]], [[1qqv]] - cVIL headpiece - chicken<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2rjw]], [[2rjx]], [[2rjv]], [[2rjy]], [[1yu7]], [[1yu8]], [[3myc]], [[3mye]], [[3nkj]], [[3mya]], [[3tjw]], [[3trv]], [[3trw]], [[3try]] - cVIL-1 headpiece (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2llf]] - cVIL-1 gelsolin-like domain 6 - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5i1n]], [[5i1o]], [[5i1p]], [[5i1s]] – cVIL-1 + cVIL headpiece<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1vii]], [[2vik]], [[2vil]], [[4cz3]], [[4cz4]] - cVIL-14T headpiece - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2ppz]], [[2jm0]] - VIL-1 headpiece (mutant) – synthetic – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2f4k]], [[1wy3]], [[1wy4]], [[1yrf]], [[1yri]] - VIL-1 fragment (mutant) – synthetic<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5vnt]] - VIL-4 C-terminal headpiece - ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | + | * Advillin | |
| + | **[[1und]] – hAVIL headpiece<br /> | ||
| - | + | *Cytovillin or ezrin | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[1ni2]] – hCVIL N terminal<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4rm8]], [[4rm9]] – hCVIL <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4rma]] – hCVIL FERM domain<br /> | ||
| - | + | }} | |
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Villin
Updated on 11-January-2021
References
- ↑ Friederich E, Vancompernolle K, Louvard D, Vandekerckhove J. Villin function in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Correlation of in vivo effects to its biochemical activities in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):26751-60. PMID:10480879
- ↑ Smith TC, Fang Z, Luna EJ. Novel interactors and a role for supervillin in early cytokinesis. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010 Jun;67(6):346-64. doi: 10.1002/cm.20449. PMID:20309963 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cm.20449
- ↑ Turunen O, Wahlstrom T, Vaheri A. Ezrin has a COOH-terminal actin-binding site that is conserved in the ezrin protein family. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1445-53. PMID:8089177
- ↑ Shillingford NM, Calicchio ML, Teot LA, Boyd T, Kurek KC, Goldsmith JD, Bousvaros A, Perez-Atayde AR, Kozakewich HP. Villin immunohistochemistry is a reliable method for diagnosing microvillus inclusion disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015 Feb;39(2):245-50. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000355. PMID:25517957 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000355
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman