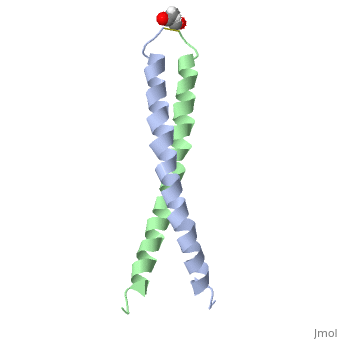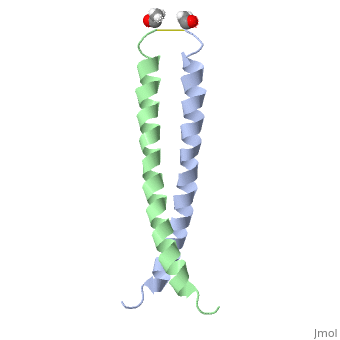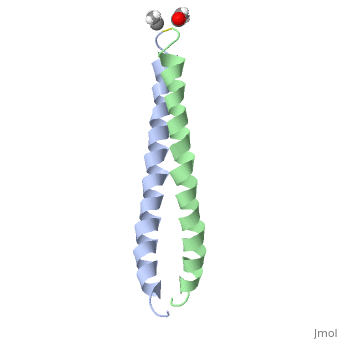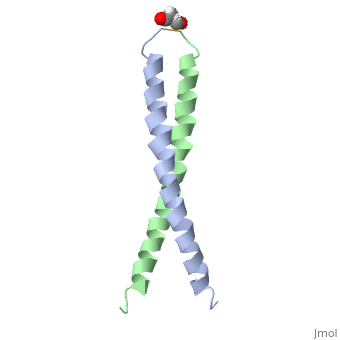
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
C-JUN
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (15 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='1jun' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human C-Jun homodimer leucine zipper domain complex with acetyl (PDB code [[1jun]])'> |
| + | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | The c-Jun protein is a member of transcription factors which consist of a basic region leucine zipper region <ref name="one"> PMID:8662824 </ref>. Originally identified by its homology to v-jun, the oncogene from the avian sarcomoa virus <ref name="four"> Bossy-Wetzel, E., Bakiri, L., Yaniv, M. (1997). Induction of apoptosis by the transcription factor c-Jun. EMO Journal. Vol.16;7. 1695-1709 </ref>. All these leucine zipper factors bind to DNA in one of two states: homo or heterodimers <ref name="two"> PMID:8662824 </ref>. In conjunction with the c-Fos protein these two proteins bind to specific regions of DNA strands. Together these two proteins form the c-fos/c-jun complex which help regulate cell growth and differentiation <ref name="one" />. The members of the jun and fos families include three Jun proteins and four Fos proteins (c-Jun, JunB, JunD,c-Fos, Fos-B, Fra1, and Fra2) <ref name="one" />. Regulation of the complex iteslf is done by interactions between the protein and DNA in addition to the protein-protein interactions between each of the leucine zipper domains <ref name="one" />. | + | The '''c-Jun''' protein is a member of transcription factors which consist of a basic region leucine zipper region <ref name="one"> PMID:8662824 </ref>. Originally identified by its homology to v-jun, the oncogene from the avian sarcomoa virus <ref name="four"> Bossy-Wetzel, E., Bakiri, L., Yaniv, M. (1997). Induction of apoptosis by the transcription factor c-Jun. EMO Journal. Vol.16;7. 1695-1709 </ref>. All these leucine zipper factors bind to DNA in one of two states: homo or heterodimers <ref name="two"> PMID:8662824 </ref>. In conjunction with the c-Fos protein these two proteins bind to specific regions of DNA strands. Together these two proteins form the c-fos/c-jun complex which help regulate cell growth and differentiation <ref name="one" />. The members of the jun and fos families include three Jun proteins and four Fos proteins (c-Jun, JunB, JunD,c-Fos, Fos-B, Fra1, and Fra2) <ref name="one" />. Regulation of the complex iteslf is done by interactions between the protein and DNA in addition to the protein-protein interactions between each of the leucine zipper domains <ref name="one" />. See [[Transcription and RNA Processing]]. |
== Structure Overview == | == Structure Overview == | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:1jun.png|left|thumb|''Figure 1.'' A 3-D representation of the two alpha helices which form a coiled coil [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/jmol.do?structureId=1JUN] ]] | ||
The structure of c-Jun is comprised of a leucine zipper as previously stated. This dimerization motif may be in one of two classes, both of which are required for DNA-binding transcription factors; the basic-domain leucine zipper proteins (bZIP) and the basic helix loop-helix-leucine zipper proteins(bHLH-ZIP) <ref name="two"> A Junius, F.K., Mackay, J.P., Bubb, W.A., Jensen, S.A., Weiss, A.S., King, G.F. 2006. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization of the Jun Leucine Zipper Domain: Unusual Properties of Coiled-Coil Interfacial Polar Residues?</ref>. The strand becomes an elongated coiled coil. This is formed by residues at the a and d positions in each of the two monomers, whereby they create hydrophobic centers which conform to the "knobs into holes" model by Crick. <ref name="two" />. Amino acids at these a and d positions are each surrounded by 4 additional residues from adjacent a-helix monomer <ref name="two" />. | The structure of c-Jun is comprised of a leucine zipper as previously stated. This dimerization motif may be in one of two classes, both of which are required for DNA-binding transcription factors; the basic-domain leucine zipper proteins (bZIP) and the basic helix loop-helix-leucine zipper proteins(bHLH-ZIP) <ref name="two"> A Junius, F.K., Mackay, J.P., Bubb, W.A., Jensen, S.A., Weiss, A.S., King, G.F. 2006. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization of the Jun Leucine Zipper Domain: Unusual Properties of Coiled-Coil Interfacial Polar Residues?</ref>. The strand becomes an elongated coiled coil. This is formed by residues at the a and d positions in each of the two monomers, whereby they create hydrophobic centers which conform to the "knobs into holes" model by Crick. <ref name="two" />. Amino acids at these a and d positions are each surrounded by 4 additional residues from adjacent a-helix monomer <ref name="two" />. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
It was found that the N-terminus contains both calcium and stress-regulated transcriptional activation domains <ref name="five" />. According to the study,distinct mechanisms of c-Jun control function by calcium and stress signals <ref name="five" />. | It was found that the N-terminus contains both calcium and stress-regulated transcriptional activation domains <ref name="five" />. According to the study,distinct mechanisms of c-Jun control function by calcium and stress signals <ref name="five" />. | ||
| + | ==Additional Resources== | ||
| + | To See Additional information, see: [[Transcription and RNA Processing]] <br /> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ==3D structure of C-JUN== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1jun]] – hCJUN leucine zipper domain – human – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[1jnm]] - hCJUN leucine zipper domain + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | [[1fos]] – hCJUN + p55 c-Fos + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | [[5fv8]] – hCJUN + FOSW<br /> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structure of C-JUN
Updated on 11-April-2018
1jun – hCJUN leucine zipper domain – human – NMR
1jnm - hCJUN leucine zipper domain + DNA
1fos – hCJUN + p55 c-Fos + DNA
5fv8 – hCJUN + FOSW
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Junius FK, O'Donoghue SI, Nilges M, Weiss AS, King GF. High resolution NMR solution structure of the leucine zipper domain of the c-Jun homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 7;271(23):13663-7. PMID:8662824
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Bossy-Wetzel, E., Bakiri, L., Yaniv, M. (1997). Induction of apoptosis by the transcription factor c-Jun. EMO Journal. Vol.16;7. 1695-1709
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Junius FK, O'Donoghue SI, Nilges M, Weiss AS, King GF. High resolution NMR solution structure of the leucine zipper domain of the c-Jun homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 7;271(23):13663-7. PMID:8662824
- ↑ Mechta-Grigoriou F, Giudicelli F, Pujades C, Charnay P, Yaniv M. c-jun regulation and function in the developing hindbrain. Dev Biol. 2003 Jun 15;258(2):419-31. PMID:12798298
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Hoeffler WK, Levinson AD, Bauer EA. Activation of c-Jun transcription factor by substitution of a charged residue in its N-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1305-12. PMID:8165146
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Cruzalegui FH, Hardingham GE, Bading H. c-Jun functions as a calcium-regulated transcriptional activator in the absence of JNK/SAPK1 activation. EMBO J. 1999 Mar 1;18(5):1335-44. PMID:10064599 doi:10.1093/emboj/18.5.1335
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Andrew Rebeyka, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Andrea Gorrell