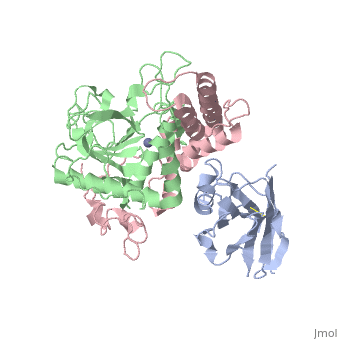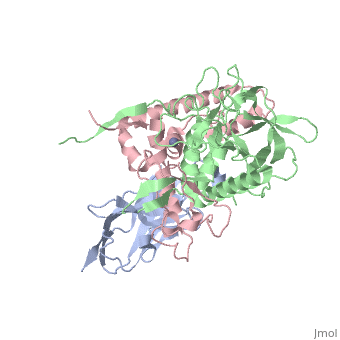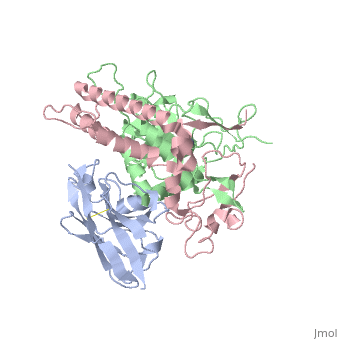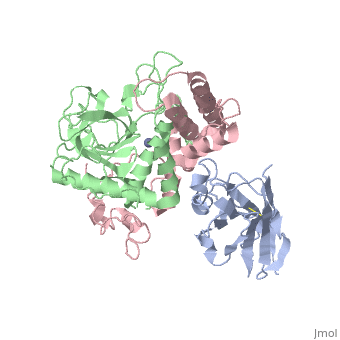Llama Antibody Inhibits Botulinum Neruotoxin
From Proteopedia
| (15 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==''[http:// | + | ==''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clostridium_botulinum Clostridium Botulinum]''== |
[[Image:toxins_l.gif|right|180px|alt Clostridium botulinum bacteria up close. Image courtesy of CDC.]] | [[Image:toxins_l.gif|right|180px|alt Clostridium botulinum bacteria up close. Image courtesy of CDC.]] | ||
C. botulinum bacteria, which are commonly found in soil, can form spores that allow them to survive in a dormant state until they're exposed to conditions that support their growth. Infant botulism, the most common type of botulism, occurs when infants consume these spores, which then grow in their intestines and release toxin. In adults, most outbreaks are caused by contaminated home-canned foods. You can also get botulism through contaminated wounds. | C. botulinum bacteria, which are commonly found in soil, can form spores that allow them to survive in a dormant state until they're exposed to conditions that support their growth. Infant botulism, the most common type of botulism, occurs when infants consume these spores, which then grow in their intestines and release toxin. In adults, most outbreaks are caused by contaminated home-canned foods. You can also get botulism through contaminated wounds. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Botulinum Toxin== | ==Botulinum Toxin== | ||
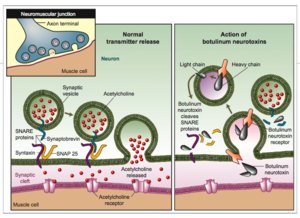
[[Image:Figure1.png|left|300px]] | [[Image:Figure1.png|left|300px]] | ||
| - | Botulinum Toxin is very deadly in a sense that it prevents muscle contraction. Botulinum toxin prevents the release of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholine#Function Acetylcholine]into the synaptic cleft to relay the signaling to another neuron. Acetylcholine has functions both in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and in the central nervous system (CNS) as a neuromodulator.In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine activates muscles, and is a major neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system.In the central nervous system, acetylcholine and the associated neurons form a neurotransmitter system, the cholinergic system, which tends to cause anti-excitatory actions. [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6n3rrjbweO8 Mechanism of Botulinum Toxin] | + | Botulinum Toxin is very deadly in a sense that it prevents muscle contraction. [[Botulinum neurotoxin|Botulinum toxin]] prevents the release of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholine#Function Acetylcholine]into the synaptic cleft to relay the signaling to another neuron. Acetylcholine has functions both in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and in the central nervous system (CNS) as a neuromodulator.In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine activates muscles, and is a major neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system.In the central nervous system, acetylcholine and the associated neurons form a neurotransmitter system, the cholinergic system, which tends to cause anti-excitatory actions. [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6n3rrjbweO8 Mechanism of Botulinum Toxin] |
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| - | ==[http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/01/100120211009.htm | + | ==[http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/01/100120211009.htm Llama Antibody] Inhibits Botulinum Neruotoxin== |
| - | + | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='3k3q' size='400' side='right' caption='Botulinium neurotoxin N-terminal (green) and C-terminal (pink) bound to Llama antibody (grey) (PDB entry [[3k3q]])'> | ||
'''[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3K3Q PubMed Abstract]:''' | '''[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3K3Q PubMed Abstract]:''' | ||
| - | Ingestion or inhalation of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) results in botulism, a severe and frequently fatal disease. Current treatments rely on antitoxins, which, while effective, cannot reverse symptoms once BoNT has entered the neuron. For treatments that can reverse intoxication, interest... [ Read More & Search PubMed Abstracts ] | ||
Ingestion or inhalation of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) results in botulism, a severe and frequently fatal disease. Current treatments rely on antitoxins, which, while effective, cannot reverse symptoms once BoNT has entered the neuron. For treatments that can reverse intoxication, interest has focused on developing inhibitors of the enzymatic BoNT light chain (BoNT Lc). Such inhibitors typically mimic substrate and bind in or around the substrate cleavage pocket. To explore the full range of binding sites for serotype A light chain (BoNT/A Lc) inhibitors, we created a library of non-immune llama single-domain VHH (camelid heavy-chain variable region derived from heavy-chain-only antibody) antibodies displayed on the surface of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Library selection on BoNT/A Lc yielded 15 yeast-displayed VHH with equilibrium dissociation constants (K(d)) from 230 to 0.03 nM measured by flow cytometry. Eight of 15 VHH inhibited the cleavage of substrate SNAP25 (synaptosome-associated protein of 25,000 Da) by BoNT/A Lc. The most potent VHH (Aa1) had a solution K(d) for BoNT/A Lc of 1.47 x 10(-)(10) M and an IC(50) (50% inhibitory concentration) of 4.7 x 10(-)(10) M and was resistant to heat denaturation and reducing conditions. To understand the mechanism by which Aa1 inhibited catalysis, we solved the X-ray crystal structure of the BoNT/A Lc-Aa1 VHH complex at 2.6 A resolution. The structure reveals that the Aa1 VHH binds in the alpha-exosite of the BoNT/A Lc, far from the active site for catalysis. The study validates the utility of non-immune llama VHH libraries as a source of enzyme inhibitors and identifies the BoNT/A Lc alpha-exosite as a target for inhibitor development. | Ingestion or inhalation of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) results in botulism, a severe and frequently fatal disease. Current treatments rely on antitoxins, which, while effective, cannot reverse symptoms once BoNT has entered the neuron. For treatments that can reverse intoxication, interest has focused on developing inhibitors of the enzymatic BoNT light chain (BoNT Lc). Such inhibitors typically mimic substrate and bind in or around the substrate cleavage pocket. To explore the full range of binding sites for serotype A light chain (BoNT/A Lc) inhibitors, we created a library of non-immune llama single-domain VHH (camelid heavy-chain variable region derived from heavy-chain-only antibody) antibodies displayed on the surface of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Library selection on BoNT/A Lc yielded 15 yeast-displayed VHH with equilibrium dissociation constants (K(d)) from 230 to 0.03 nM measured by flow cytometry. Eight of 15 VHH inhibited the cleavage of substrate SNAP25 (synaptosome-associated protein of 25,000 Da) by BoNT/A Lc. The most potent VHH (Aa1) had a solution K(d) for BoNT/A Lc of 1.47 x 10(-)(10) M and an IC(50) (50% inhibitory concentration) of 4.7 x 10(-)(10) M and was resistant to heat denaturation and reducing conditions. To understand the mechanism by which Aa1 inhibited catalysis, we solved the X-ray crystal structure of the BoNT/A Lc-Aa1 VHH complex at 2.6 A resolution. The structure reveals that the Aa1 VHH binds in the alpha-exosite of the BoNT/A Lc, far from the active site for catalysis. The study validates the utility of non-immune llama VHH libraries as a source of enzyme inhibitors and identifies the BoNT/A Lc alpha-exosite as a target for inhibitor development. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===The New!=== | ===The New!=== | ||
The crystal structure of the substrate SNAP25 complexed to the BoNT/A Lc showed the extended nature of ligand recognition and identified potential exosites that are away from the catalytic active site. To display the range of bidning sites for potential BoNT/A Lc inhibitors, the authors of the paper generated and selected a non-immune camelid(llama) library of single-domain VHH antibodies for binding to the BoNT/A Lc. This single-domain antibody has been postulated to be more able to bind into enzymatic cavities. Furthermore VHH is able to withstand intracellular reducing environment. | The crystal structure of the substrate SNAP25 complexed to the BoNT/A Lc showed the extended nature of ligand recognition and identified potential exosites that are away from the catalytic active site. To display the range of bidning sites for potential BoNT/A Lc inhibitors, the authors of the paper generated and selected a non-immune camelid(llama) library of single-domain VHH antibodies for binding to the BoNT/A Lc. This single-domain antibody has been postulated to be more able to bind into enzymatic cavities. Furthermore VHH is able to withstand intracellular reducing environment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Uses of Botulinum Toxin== | ==Uses of Botulinum Toxin== | ||
| + | ===Cosmetic=== | ||
[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dkpohXE06pg&feature=related BOTOX®] | [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dkpohXE06pg&feature=related BOTOX®] | ||
| - | [[Image:Hilary.jpg|left]][[Image:Cox.jpg| | + | |
| + | [[Image:Hilary.jpg|left]][[Image:Cox.jpg|190px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Botox Medicinal/Therapeutic]=== | ||
| + | -Muscle Spasms,Upper motor neuron syndrome,Sweating, Cervical Dystonia, Migraines | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
J Mol Biol. 2010 Apr 9;397(4):1106-18. Epub 2010 Feb 6. | J Mol Biol. 2010 Apr 9;397(4):1106-18. Epub 2010 Feb 6. | ||
Current revision
Clostridium Botulinum
C. botulinum bacteria, which are commonly found in soil, can form spores that allow them to survive in a dormant state until they're exposed to conditions that support their growth. Infant botulism, the most common type of botulism, occurs when infants consume these spores, which then grow in their intestines and release toxin. In adults, most outbreaks are caused by contaminated home-canned foods. You can also get botulism through contaminated wounds.
If diagnosed early, botulism can be treated with an antitoxin, which blocks the action of the toxin in the blood. But recovery still takes many months. The antitoxin can also cause serious side effects, has only a very short window of application and is expensive to produce in large enough quantities to combat a bioterrorism attack.
Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum Toxin is very deadly in a sense that it prevents muscle contraction. Botulinum toxin prevents the release of Acetylcholineinto the synaptic cleft to relay the signaling to another neuron. Acetylcholine has functions both in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and in the central nervous system (CNS) as a neuromodulator.In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine activates muscles, and is a major neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system.In the central nervous system, acetylcholine and the associated neurons form a neurotransmitter system, the cholinergic system, which tends to cause anti-excitatory actions. Mechanism of Botulinum Toxin
Llama Antibody Inhibits Botulinum Neruotoxin
| |||||||||||