Colicin M
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
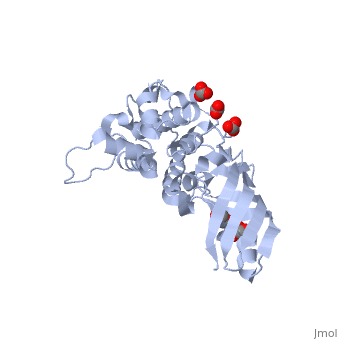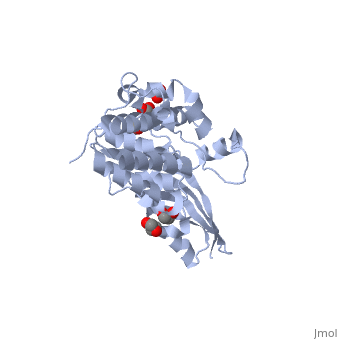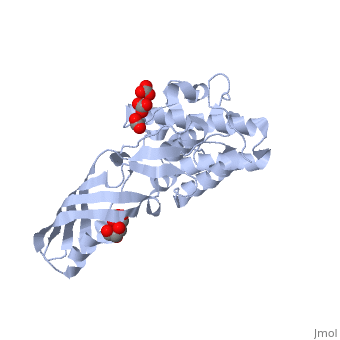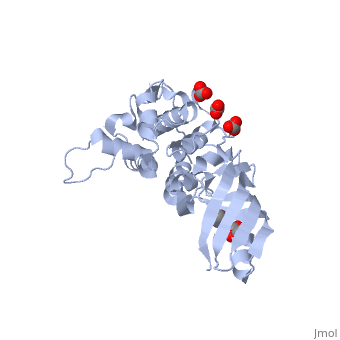
| - | + | <StructureSection load='2xmx' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of E. coli colicin M complex with glycerol and carbonate (PDB entry [[2xmx]])' scene=''> | |
| - | Colicin M is a type of [[Colicin]], a bacteriocin made by ''E. coli'' which acts against other nearby ''E. coli'' to kill them by inhibiting synthesis of peptidoglycan - murein, preventing synthesis of the cell wall and ultimately leading to cell lysis. | + | '''Colicin M''' is a type of [[Colicin]], a bacteriocin made by ''E. coli'' which acts against other nearby ''E. coli'' to kill them by inhibiting synthesis of peptidoglycan - murein, preventing synthesis of the cell wall and ultimately leading to cell lysis. <scene name='Colicin_M/Colmsingle/1'>Monomer</scene> of Colicin M. |
==Synthesis and release== | ==Synthesis and release== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The operon for colicin M is encoded on a plasmid in the cytoplasm of the E. coli. This operon also encodes its [[Colicin Immunity Protein]], [[Cmi]], to protect the membrane of the cell from the activity of the cytotoxic domain, alongside a protein to aid the release of the colicin outside the cell. When produced, the immunity protein binds to and inhibits the enzymatic cytotoxic domain. | ||
==Mechanism of uptake== | ==Mechanism of uptake== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The receptor binding domain of the colicin binds to the outer membrane receptor FhuA on the target cell; it is a constitutively expressed protein parasitised by the colicin. The translocation domain then recruits proteins from the [[Ton]] system to translocate the protein across the membrane and into the cytoplasm. | ||
==Killing Activities== | ==Killing Activities== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||