This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Prp24
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (Sandbox Reserved 340 moved to Prp24: Publishing the Sandbox to an official page) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='2ghp' size='450' side='right' scene='Sandbox_Reserved_340/2ghp/1' caption='Yeast N-terminal 3 RNA binding domains of splicing factor Prp24 (PDB code [[2ghp]]).'> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | {{STRUCTURE_2ghp| PDB=2ghp | SCENE=Sandbox_Reserved_340/2ghp/1 }} | ||
'''Prp24''' ('''Pr'''e-mRNA splicing '''P'''rotein '''24''') is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''] yeast protein that functions in the formation of base pair interactions between the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U6_spliceosomal_RNA U6] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U4_spliceosomal_RNA U4] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SnRNP snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins)] to form the U4/U6 di-snRNP during the assembly of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spliceosome spliceosome] <ref name="Bae">PMID:17320109</ref>. This protein contains four RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) that function in the binding of Prp24 to U6 snRNA <ref name="Bae"/>. These RRM domains are conserved in structure and sequence in proteins orthologous to Prp24 in ''Homo sapiens'' and ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', as well as in other proteins containing RRMs <ref name="Rader">PMID:12458792</ref>. | '''Prp24''' ('''Pr'''e-mRNA splicing '''P'''rotein '''24''') is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''] yeast protein that functions in the formation of base pair interactions between the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U6_spliceosomal_RNA U6] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U4_spliceosomal_RNA U4] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SnRNP snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins)] to form the U4/U6 di-snRNP during the assembly of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spliceosome spliceosome] <ref name="Bae">PMID:17320109</ref>. This protein contains four RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) that function in the binding of Prp24 to U6 snRNA <ref name="Bae"/>. These RRM domains are conserved in structure and sequence in proteins orthologous to Prp24 in ''Homo sapiens'' and ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', as well as in other proteins containing RRMs <ref name="Rader">PMID:12458792</ref>. | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
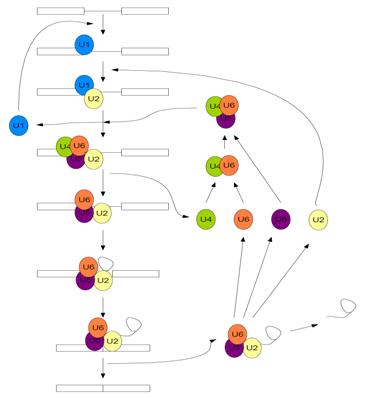
| - | + | [[Image:Spliceosome.jpg |frame|left| Figure 1. Assembly and disassembly of the spliceosome in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' (after Staley and Guthrie 1998 <ref name="Staley"/>)]] | |
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
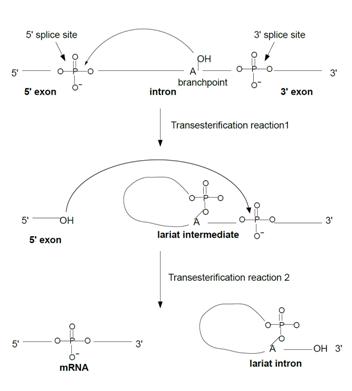
[[Image:Transester.jpg |frame|left| Figure 2. The transesterificiation reactions of pre-mRNA splicing (after Brow 2002<ref name="Brow review"/>) ]] | [[Image:Transester.jpg |frame|left| Figure 2. The transesterificiation reactions of pre-mRNA splicing (after Brow 2002<ref name="Brow review"/>) ]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
=== Pre-mRNA Splicing === | === Pre-mRNA Splicing === | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | <Structure load='2ghp' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='' scene='Sandbox_Reserved_340/2ghp/3'/> | ||
The key structural elements of Prp24 are the conserved RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). These motifs are found in many proteins with RNA binding properties and contain conserved RNP elements that are recognizable by their primary sequence <ref name="Shannon"/>. For several years, Prp24 was thought to contain three RRMs, termed RRM 1, RRM 2, and RRM 3 <ref name="Shannon"/>. However, analysis of homologs of Prp24 from several different species allowed the identification of a fourth RRM in Prp24 of ''S. cerevisiae'', albeit one that was much less highly conserved and not easily recognizable by its RNP-consensus domain <ref name="Rader"/>. | The key structural elements of Prp24 are the conserved RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). These motifs are found in many proteins with RNA binding properties and contain conserved RNP elements that are recognizable by their primary sequence <ref name="Shannon"/>. For several years, Prp24 was thought to contain three RRMs, termed RRM 1, RRM 2, and RRM 3 <ref name="Shannon"/>. However, analysis of homologs of Prp24 from several different species allowed the identification of a fourth RRM in Prp24 of ''S. cerevisiae'', albeit one that was much less highly conserved and not easily recognizable by its RNP-consensus domain <ref name="Rader"/>. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 51: | ||
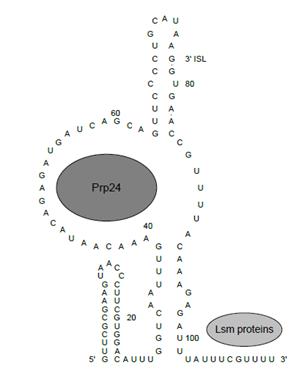
Prp24 co-immunoprecipitates with free U6 and U4/U6 di-snRNP, indicating that it is closely associated with these particles <ref name="Shannon"/><ref name="Ghetti">PMID:7585243</ref>. Initial investigation of the structure showed that Prp24 very likely binds directly to the 40-43 nucleotides of U6 based on chemical modification of naked U6 snRNA compared to free U6 snRNP<ref name="Jandrositz"/>. Further investigation suggested that Prp24 binds within the 30-56 nucleotide region of free U6, as well as to stem II of U4/U6 in the 39-56 and 67-70 nucleotide regions of U6 <ref name="Ghetti"/>. | Prp24 co-immunoprecipitates with free U6 and U4/U6 di-snRNP, indicating that it is closely associated with these particles <ref name="Shannon"/><ref name="Ghetti">PMID:7585243</ref>. Initial investigation of the structure showed that Prp24 very likely binds directly to the 40-43 nucleotides of U6 based on chemical modification of naked U6 snRNA compared to free U6 snRNP<ref name="Jandrositz"/>. Further investigation suggested that Prp24 binds within the 30-56 nucleotide region of free U6, as well as to stem II of U4/U6 in the 39-56 and 67-70 nucleotide regions of U6 <ref name="Ghetti"/>. | ||
| - | + | ||
The main function of Prp24 seems to be directly related to formation of the U4/U6 complex, particularly based on the evidence that Prp24 is present in U6 and U4/U6, but not U4/U6.U5 <ref name="Shannon"/><ref name="Ghetti"/><ref name="Jandrositz"/>. Prp24 greatly increases the rate and efficiency of U4/U6 annealing <ref name="Raghunathan">PMID:9452384</ref> and mutations in Prp24 have been shown to prevent the formation of the U4/U6 di-snRNP <ref name="Lygerou">PMID:10022888</ref>. Although the exact mechanism by which Prp24 promotes annealing of U4 and U6 is not known, it has been suggested that Prp24 may stabilize the secondary structure of U6 to allow it to interact with U4 in order to allow formation of U4/U6 <ref name="Vidaver"/>. | The main function of Prp24 seems to be directly related to formation of the U4/U6 complex, particularly based on the evidence that Prp24 is present in U6 and U4/U6, but not U4/U6.U5 <ref name="Shannon"/><ref name="Ghetti"/><ref name="Jandrositz"/>. Prp24 greatly increases the rate and efficiency of U4/U6 annealing <ref name="Raghunathan">PMID:9452384</ref> and mutations in Prp24 have been shown to prevent the formation of the U4/U6 di-snRNP <ref name="Lygerou">PMID:10022888</ref>. Although the exact mechanism by which Prp24 promotes annealing of U4 and U6 is not known, it has been suggested that Prp24 may stabilize the secondary structure of U6 to allow it to interact with U4 in order to allow formation of U4/U6 <ref name="Vidaver"/>. | ||
| Line 71: | Line 69: | ||
Several additional roles for Prp24 have been suggested in spliceosome assembly/disassembly, although nothing has been sufficiently supported. A genetic interaction in which Prp24 mutation suppressed a Prp21 (a component of the U2 snRNP) mutation suggested that the two proteins may interact during the base pairing of U2 and U6 at the 5' splice site; however, further investigation failed to produce evidence of a definite interaction between the two proteins, although the authors maintained that a transient interaction between Prp24 and Prp21 may exist in an intermediate form of the assembling spliceosome <ref name="Vaidya"/>. It has also been suggested that Prp24 may also assist in the formation of U4/U5.U6 <ref name="Ryan">PMID:12212846</ref> or in the destabilization of U6 from U2 upon completion of splicing to release free U6 snRNP,<ref name="Vidaver"/>, but there is insufficient evidence to conclusively support these functions of Prp24. | Several additional roles for Prp24 have been suggested in spliceosome assembly/disassembly, although nothing has been sufficiently supported. A genetic interaction in which Prp24 mutation suppressed a Prp21 (a component of the U2 snRNP) mutation suggested that the two proteins may interact during the base pairing of U2 and U6 at the 5' splice site; however, further investigation failed to produce evidence of a definite interaction between the two proteins, although the authors maintained that a transient interaction between Prp24 and Prp21 may exist in an intermediate form of the assembling spliceosome <ref name="Vaidya"/>. It has also been suggested that Prp24 may also assist in the formation of U4/U5.U6 <ref name="Ryan">PMID:12212846</ref> or in the destabilization of U6 from U2 upon completion of splicing to release free U6 snRNP,<ref name="Vidaver"/>, but there is insufficient evidence to conclusively support these functions of Prp24. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of pre-mRNA-splicing factors== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[pre-mRNA-splicing factor]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of pre-mRNA-splicing factors
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Bae E, Reiter NJ, Bingman CA, Kwan SS, Lee D, Phillips GN Jr, Butcher SE, Brow DA. Structure and interactions of the first three RNA recognition motifs of splicing factor prp24. J Mol Biol. 2007 Apr 13;367(5):1447-58. Epub 2007 Feb 7. PMID:17320109 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.01.078
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Rader SD, Guthrie C. A conserved Lsm-interaction motif in Prp24 required for efficient U4/U6 di-snRNP formation. RNA. 2002 Nov;8(11):1378-92. PMID:12458792
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Staley JP, Guthrie C. Mechanical devices of the spliceosome: motors, clocks, springs, and things. Cell. 1998 Feb 6;92(3):315-26. PMID:9476892
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Brow DA. Allosteric cascade of spliceosome activation. Annu Rev Genet. 2002;36:333-60. Epub 2002 Jun 11. PMID:12429696 doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.36.043002.091635
- ↑ Fortner DM, Troy RG, Brow DA. A stem/loop in U6 RNA defines a conformational switch required for pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(2):221-33. PMID:8299941
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Jandrositz A, Guthrie C. Evidence for a Prp24 binding site in U6 snRNA and in a putative intermediate in the annealing of U6 and U4 snRNAs. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):820-32. PMID:7882985
- ↑ Dunn EA, Rader SD. Secondary structure of U6 small nuclear RNA: implications for spliceosome assembly. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1099-104. PMID:20659011 doi:10.1042/BST0381099
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Karaduman R, Dube P, Stark H, Fabrizio P, Kastner B, Luhrmann R. Structure of yeast U6 snRNPs: arrangement of Prp24p and the LSm complex as revealed by electron microscopy. RNA. 2008 Dec;14(12):2528-37. Epub 2008 Oct 29. PMID:18971323 doi:10.1261/rna.1369808
- ↑ Madhani HD, Bordonne R, Guthrie C. Multiple roles for U6 snRNA in the splicing pathway. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2264-77. PMID:2149118
- ↑ Vijayraghavan U, Company M, Abelson J. Isolation and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1206-16. PMID:2676722
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 Shannon KW, Guthrie C. Suppressors of a U4 snRNA mutation define a novel U6 snRNP protein with RNA-binding motifs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):773-85. PMID:1827420
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 Vidaver RM, Fortner DM, Loos-Austin LS, Brow DA. Multiple functions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae splicing protein Prp24 in U6 RNA structural rearrangements. Genetics. 1999 Nov;153(3):1205-18. PMID:10545453
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Vaidya V, Vijayraghavan U. Prp21, a U2-snRNP-associated protein, and Prp24, a U6-snRNP-associated protein, functionally interact during spliceosome assembly. J Genet. 1998 Dec; 77(3):85-94
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Maris C, Dominguez C, Allain FH. The RNA recognition motif, a plastic RNA-binding platform to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression. FEBS J. 2005 May;272(9):2118-31. PMID:15853797 doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04653.x
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Kwan SS, Brow DA. The N- and C-terminal RNA recognition motifs of splicing factor Prp24 have distinct functions in U6 RNA binding. RNA. 2005 May;11(5):808-20. Epub 2005 Apr 5. PMID:15811912 doi:10.1261/rna.2010905
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Karaduman R, Fabrizio P, Hartmuth K, Urlaub H, Luhrmann R. RNA structure and RNA-protein interactions in purified yeast U6 snRNPs. J Mol Biol. 2006 Mar 10;356(5):1248-62. Epub 2005 Dec 20. PMID:16410014 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.013
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Ghetti A, Company M, Abelson J. Specificity of Prp24 binding to RNA: a role for Prp24 in the dynamic interaction of U4 and U6 snRNAs. RNA. 1995 Apr;1(2):132-45. PMID:7585243
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Raghunathan PL, Guthrie C. A spliceosomal recycling factor that reanneals U4 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Science. 1998 Feb 6;279(5352):857-60. PMID:9452384
- ↑ Lygerou Z, Christophides G, Seraphin B. A novel genetic screen for snRNP assembly factors in yeast identifies a conserved protein, Sad1p, also required for pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):2008-20. PMID:10022888
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Martin-Tumasz S, Reiter NJ, Brow DA, Butcher SE. Structure and functional implications of a complex containing a segment of U6 RNA bound by a domain of Prp24. RNA. 2010 Apr;16(4):792-804. Epub 2010 Feb 24. PMID:20181740 doi:10.1261/rna.1913310
- ↑ Mayes AE, Verdone L, Legrain P, Beggs JD. Characterization of Sm-like proteins in yeast and their association with U6 snRNA. EMBO J. 1999 Aug 2;18(15):4321-31. PMID:10428970 doi:10.1093/emboj/18.15.4321
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Vidal VP, Verdone L, Mayes AE, Beggs JD. Characterization of U6 snRNA-protein interactions. RNA. 1999 Nov;5(11):1470-81. PMID:10580475
- ↑ Fromont-Racine M, Mayes AE, Brunet-Simon A, Rain JC, Colley A, Dix I, Decourty L, Joly N, Ricard F, Beggs JD, Legrain P. Genome-wide protein interaction screens reveal functional networks involving Sm-like proteins. Yeast. 2000 Jun 30;17(2):95-110. PMID:10900456 doi:<95::AID-YEA16>3.0.CO;2-H 10.1002/1097-0061(20000630)17:2<95::AID-YEA16>3.0.CO;2-H
- ↑ Verdone L, Galardi S, Page D, Beggs JD. Lsm proteins promote regeneration of pre-mRNA splicing activity. Curr Biol. 2004 Aug 24;14(16):1487-91. PMID:15324666 doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.08.032
- ↑ Ryan DE, Stevens SW, Abelson J. The 5' and 3' domains of yeast U6 snRNA: Lsm proteins facilitate binding of Prp24 protein to the U6 telestem region. RNA. 2002 Aug;8(8):1011-33. PMID:12212846