Beta-lactamase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (62 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
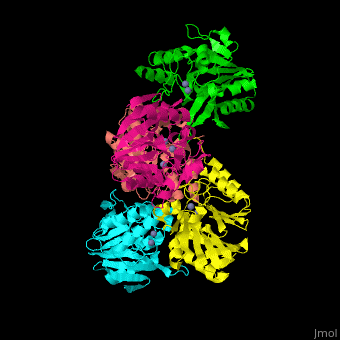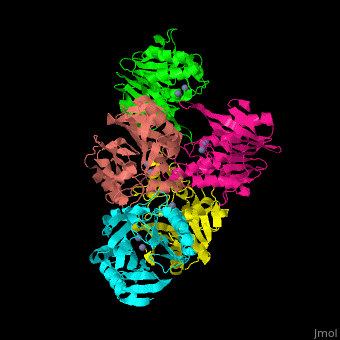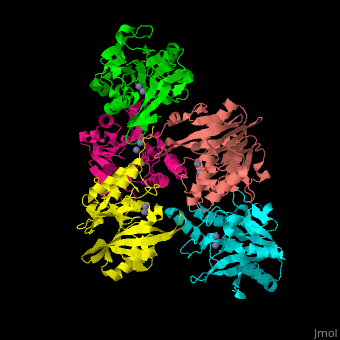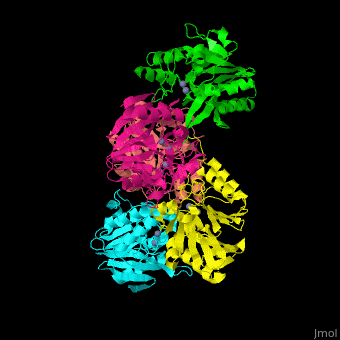
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='45/453531/Cv/1' caption='Class B β-lactamase Ndm-1 complex with Zn+2 (grey) (PDB code [[3spu]])'> | |
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
| + | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Beta-lactamase''' (Blac) are enzymes which make bacteria | + | '''Beta-lactamase''' (Blac) are enzymes which make bacteria resistant to β-lactam antibiotics by breaking their β-lactam ring. Blac are classified according to their resistance targets.<br /> |
| - | + | *'''Class A''' are broad-spectrum. See also [[TEM1 Class Antibiotic Resistance Proteins]].<br /> | |
| - | + | *'''Class B''' are metalloenzymes. See also [[New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase 1]].<br /> | |
| - | + | *'''Class C''' are cephalosporinases. See also [[Class C beta-lactamase]].<br /> | |
| - | + | *'''Class D''' are cloxacilanases<br /> | |
| + | *'''Carbapenemase''' (Car) are Blac with wide hydrolytic capacities. Car can hydrolyze penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams and carbapenems. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''Extended-spectrum Blac''' class A (ESBL) hydrolyze penicillins but not cephalosporins.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Serine beta-lactamase''' (ClbP) has a serine-active site. | ||
| + | *'''AmpC beta-lactamase''' (ClbP) mediate resistance to cephalosphin, cefazolin,cefoxitin and most penicillins<ref>PMID:19136439</ref>. | ||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | Blac makes some bacteria resistant to antibiotics like penicillin, cephamycin and carbapenems. | ||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The <scene name='45/453531/Cv/3'>active site of class B Blac contains 2 Zn+2 ions</scene>.<ref>PMID:21774017</ref> | ||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | [[Journal:Structure:1]] | ||
== 3D Structures of Beta-lactamase == | == 3D Structures of Beta-lactamase == | ||
| + | [[Beta-lactamase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Jacoby GA. AmpC beta-lactamases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009 Jan;22(1):161-82, Table of Contents. PMID:19136439 doi:10.1128/CMR.00036-08
- ↑ King D, Strynadka N. Crystal structure of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase reveals molecular basis for antibiotic resistance. Protein Sci. 2011 Sep;20(9):1484-91. doi: 10.1002/pro.697. Epub 2011 Aug, 2. PMID:21774017 doi:10.1002/pro.697
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman