Group:MUZIC:Myozenin
From Proteopedia

(→Introduction) |
|||
| (53 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction== | == Introduction== | ||
| - | The '''f'''ilamin-C α-'''a'''ctinin '''t'''elethonin '''Z'''-disc binding protein ('''FATZ''') is a protein family of three | + | The '''f'''ilamin-C α-'''a'''ctinin '''t'''elethonin '''Z'''-disc binding protein ('''FATZ''') is a protein family of three members: FATZ-1, FATZ-2, FATZ-3, which are expressed in muscle cells<ref name="r1">PMID: 10984498</ref> This protein family also known as '''Myozenin''' or '''Calsarcin''', is mainly localized in the Z-disc, although recently it has been described that FATZ-2 appears in cardiac nuclei<ref>PMID: 20170660</ref>. The expression of all three proteins has been shown to be fibre type specific. For instance, FATZ-1 and FATZ-3 are exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle fast-twitch fibres while FATZ-2 is expressed in cardiac and slow-twitch fibres<ref name="r3">PMID: 11114196</ref><ref name="r4">PMID: 11842093</ref>. FATZ proteins have multiple binding partners in the Z-disc, which involve them in different functions like the Z-disc formation and maintenance or in signaling pathways like the calcineurin/NFAT<ref name="r5">PMID: 15543153</ref>. Therefore, the FATZ protein family could be seen as one example of Z-disc proteins where signalling and structural support converge. |
| - | + | ||
==Sequence Annotation== | ==Sequence Annotation== | ||
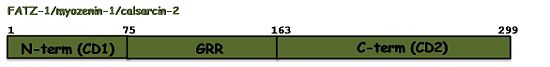
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:FATZ1_v2.jpg|550px|left|thumb|The sequence annotation of FATZ-1 shows the sequence conservation profile among the three isoforms]] The sequence annotation of FATZ-1 is related to the sequence conservation profile among the three isoforms, which share well conserved N-terminal and C-terminal regions. Therefore, the N-terminal of FATZ-1 was named '''c'''onserved '''d'''omain 1 (CD1, 1-75aa) and its C-terminal '''c'''onserved '''d'''omain 2 (CD2, 163-299aa). Both regions are connected by a stretch of amino acids with a 39.5% of glycine. Consequently, this region was named as '''g'''lycine '''r'''ich '''r'''egion (GRR, 75-162aa)<ref name="r2">PMID: 11171996</ref> [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NP98 Q9NP98]. Although the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the other two proteins could be also named CD1 and CD2 no such sequence annotations exist in their UniProtKB entries [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NPC6 Q9NPC6], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8TDC0 Q8TDC0]. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Function and Interactions== | == Function and Interactions== | ||
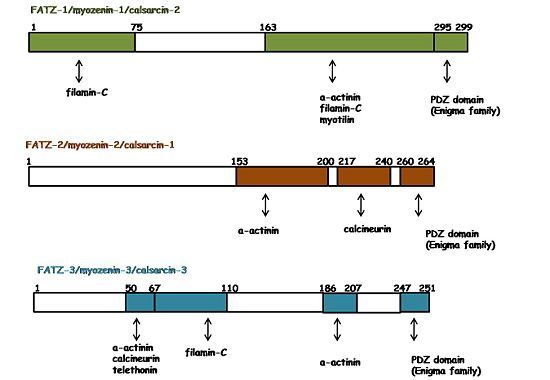
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:FATZ_binding_map.jpg|550px|left|thumb|Binding regions on FATZ proteins]]The three protein members of the FATZ family have a plethora of interacting partners which are additionally shared by all of them. As shown by the figure on the right, they interact with several Z-disc proteins. For instance: α-actinin-2, filamin-C, myotilin, telethonin, calcineurin and ZASP/Cypher (in general the Enigma protein family, [[http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Group:MUZIC:Enigma_Family]]) <ref name="r2">PMID: 11171996</ref><ref name="r4">PMID: 11842093</ref><ref>PMID: 19047374</ref><ref>PMID: 16076904</ref><ref name="r3">PMID: 11114196</ref><ref name="r1">PMID: 10984498</ref>. In general, those interactions and their binding regions were found by yeast two-hybrid assays, co-immunoprecipitation, and pull down assays. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | The interaction of FATZ-1 with α-actinin-2 has been reported on the CD2 domain of all FATZ proteins<ref name="r1">PMID: 10984498</ref><ref name="r2">PMID: 11171996 </ref><ref name="r4">PMID: 11842093</ref>. The data suggest a binding interface on α-actinin-2 spanning the spectrin repeat domains SR2,SR3 and SR4. FATZ-1, α-actinin-2 and myotilin appear in premyofibrils, when there is no Z-disc but a small structure called Z-body. In addition, the complexes FATZ-1::α-actinin-2, FATZ-1::myotilin and myotilin::α-actinin-2 are observed in that early stages. In contrast, telethonin localized to the Z-disc in later stages and the complex FATZ-1::telethonin was only observed in mature myofibrils. These findings suggest that the interactions of FATZ-1 with α-actinin-2 and myotilin are very important for the initiation of the Z-disc assembly. Besides, it is hypothesized that FATZ-1 should undergone conformational changes during myofibrilogenesis to interact with telethonin. Thus, telethonin incorporation to the the Z-disc depends to FATZ-1 viability <ref> PMID: 15810059 </ref> . It is suggested that FATZ-1 performs other functions, like bridging filamin-C and α-actinin-2. However, a competitive binding assay showed that α-actinin-2 displaces filamin-C from FATZ-1. Therefore, it still remains an open question whether a ternary complex could exist and what its physiological role would be <ref name="r2">PMID: 11171996</ref>. | |
| - | + | ||
| + | Both proteins, FATZ-1 and FATZ-2 are negative regulators of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway in striated muscle. The activation of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway determines the switch to slow-twitch fiber phenotype in skeletal muscle, and also the hypertrophic response to pressure overload in cardiac muscle. The isoform FATZ-1 is a negative regulator of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway in fast-twitch fibers. In absence of FATZ-1 the activity of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway increases, consequently, there are a major number of oxidative fibers, and less fatigue of FATZ-1 knockdown compared to FATZ-1 wild type mice subjected to long endurance exercise <ref>PMID: 18846255 </ref>. FATZ-2 is a negative regulator of Calcineurin in cardiomyocytes, where the absence of FATZ-2 leads to hypertrophy in response to pressure overload and hypertrophic agonists <ref>PMID: 15543153</ref>. | ||
== Pathology== | == Pathology== | ||
| - | + | FATZ-2 knockdown mouse hearts, subjected to pressure overload, over-activated the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway. Consequently, they showed hypertrophic hearts and developed cardiomyopathy. The transgenic over-expression of FATZ-2 rescued the mouse hearts from the disease, even when treated with hypertrophic agonists, suggesting that FATZ-2 could be an affected gene in patients with the same condition <ref name="r5">PMID: 15543153</ref>. Later on, the investigation of two families with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM) found that two mutations in FATZ-2: S48P and I246M, could be responsible for the disease <ref>PMID: 17347475 </ref>. However, a study on 438 patients concluded that those mutations in FATZ-2 were rare causes of familial HCM <ref>PMID: 18591919</ref>. | |
| + | |||
| + | A recent study of the mutants S48P and I246M in mouse models showed that the animals develop the clinical symptoms of HCM, myofibrillar disarray and Z-disc structural abnormalities. In contrast, it was not observed any over-activity of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway, revealing that HCM caused by those mutations is not associated with the negative regulation of FATZ-2 over Calcineurin <ref>PMID: 22987565</ref>. These findings suggest that FATZ-2 might modulate the activity of other proteins, also involved in pathways controlling the hypertrophy response to pressure overload. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category: Z-disk]] | ||
Current revision
Contents |
Introduction
The filamin-C α-actinin telethonin Z-disc binding protein (FATZ) is a protein family of three members: FATZ-1, FATZ-2, FATZ-3, which are expressed in muscle cells[1] This protein family also known as Myozenin or Calsarcin, is mainly localized in the Z-disc, although recently it has been described that FATZ-2 appears in cardiac nuclei[2]. The expression of all three proteins has been shown to be fibre type specific. For instance, FATZ-1 and FATZ-3 are exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle fast-twitch fibres while FATZ-2 is expressed in cardiac and slow-twitch fibres[3][4]. FATZ proteins have multiple binding partners in the Z-disc, which involve them in different functions like the Z-disc formation and maintenance or in signaling pathways like the calcineurin/NFAT[5]. Therefore, the FATZ protein family could be seen as one example of Z-disc proteins where signalling and structural support converge.
Sequence Annotation
The sequence annotation of FATZ-1 is related to the sequence conservation profile among the three isoforms, which share well conserved N-terminal and C-terminal regions. Therefore, the N-terminal of FATZ-1 was named conserved domain 1 (CD1, 1-75aa) and its C-terminal conserved domain 2 (CD2, 163-299aa). Both regions are connected by a stretch of amino acids with a 39.5% of glycine. Consequently, this region was named as glycine rich region (GRR, 75-162aa)[6] Q9NP98. Although the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the other two proteins could be also named CD1 and CD2 no such sequence annotations exist in their UniProtKB entries Q9NPC6, Q8TDC0.Function and Interactions
The three protein members of the FATZ family have a plethora of interacting partners which are additionally shared by all of them. As shown by the figure on the right, they interact with several Z-disc proteins. For instance: α-actinin-2, filamin-C, myotilin, telethonin, calcineurin and ZASP/Cypher (in general the Enigma protein family, [[1]]) [6][4][7][8][3][1]. In general, those interactions and their binding regions were found by yeast two-hybrid assays, co-immunoprecipitation, and pull down assays.The interaction of FATZ-1 with α-actinin-2 has been reported on the CD2 domain of all FATZ proteins[1][6][4]. The data suggest a binding interface on α-actinin-2 spanning the spectrin repeat domains SR2,SR3 and SR4. FATZ-1, α-actinin-2 and myotilin appear in premyofibrils, when there is no Z-disc but a small structure called Z-body. In addition, the complexes FATZ-1::α-actinin-2, FATZ-1::myotilin and myotilin::α-actinin-2 are observed in that early stages. In contrast, telethonin localized to the Z-disc in later stages and the complex FATZ-1::telethonin was only observed in mature myofibrils. These findings suggest that the interactions of FATZ-1 with α-actinin-2 and myotilin are very important for the initiation of the Z-disc assembly. Besides, it is hypothesized that FATZ-1 should undergone conformational changes during myofibrilogenesis to interact with telethonin. Thus, telethonin incorporation to the the Z-disc depends to FATZ-1 viability [9] . It is suggested that FATZ-1 performs other functions, like bridging filamin-C and α-actinin-2. However, a competitive binding assay showed that α-actinin-2 displaces filamin-C from FATZ-1. Therefore, it still remains an open question whether a ternary complex could exist and what its physiological role would be [6].
Both proteins, FATZ-1 and FATZ-2 are negative regulators of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway in striated muscle. The activation of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway determines the switch to slow-twitch fiber phenotype in skeletal muscle, and also the hypertrophic response to pressure overload in cardiac muscle. The isoform FATZ-1 is a negative regulator of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway in fast-twitch fibers. In absence of FATZ-1 the activity of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway increases, consequently, there are a major number of oxidative fibers, and less fatigue of FATZ-1 knockdown compared to FATZ-1 wild type mice subjected to long endurance exercise [10]. FATZ-2 is a negative regulator of Calcineurin in cardiomyocytes, where the absence of FATZ-2 leads to hypertrophy in response to pressure overload and hypertrophic agonists [11].
Pathology
FATZ-2 knockdown mouse hearts, subjected to pressure overload, over-activated the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway. Consequently, they showed hypertrophic hearts and developed cardiomyopathy. The transgenic over-expression of FATZ-2 rescued the mouse hearts from the disease, even when treated with hypertrophic agonists, suggesting that FATZ-2 could be an affected gene in patients with the same condition [5]. Later on, the investigation of two families with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM) found that two mutations in FATZ-2: S48P and I246M, could be responsible for the disease [12]. However, a study on 438 patients concluded that those mutations in FATZ-2 were rare causes of familial HCM [13].
A recent study of the mutants S48P and I246M in mouse models showed that the animals develop the clinical symptoms of HCM, myofibrillar disarray and Z-disc structural abnormalities. In contrast, it was not observed any over-activity of the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway, revealing that HCM caused by those mutations is not associated with the negative regulation of FATZ-2 over Calcineurin [14]. These findings suggest that FATZ-2 might modulate the activity of other proteins, also involved in pathways controlling the hypertrophy response to pressure overload.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Faulkner G, Pallavicini A, Comelli A, Salamon M, Bortoletto G, Ievolella C, Trevisan S, Kojic' S, Dalla Vecchia F, Laveder P, Valle G, Lanfranchi G. FATZ, a filamin-, actinin-, and telethonin-binding protein of the Z-disc of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):41234-42. PMID:10984498 doi:10.1074/jbc.M007493200
- ↑ Paulsson AK, Franklin S, Mitchell-Jordan SA, Ren S, Wang Y, Vondriska TM. Post-translational regulation of calsarcin-1 during pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1206-14. Epub 2010 Feb 17. PMID:20170660 doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.02.009
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Frey N, Richardson JA, Olson EN. Calsarcins, a novel family of sarcomeric calcineurin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14632-7. PMID:11114196 doi:10.1073/pnas.260501097
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Frey N, Olson EN. Calsarcin-3, a novel skeletal muscle-specific member of the calsarcin family, interacts with multiple Z-disc proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13998-4004. Epub 2002 Feb 12. PMID:11842093 doi:10.1074/jbc.M200712200
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Frey N, Barrientos T, Shelton JM, Frank D, Rutten H, Gehring D, Kuhn C, Lutz M, Rothermel B, Bassel-Duby R, Richardson JA, Katus HA, Hill JA, Olson EN. Mice lacking calsarcin-1 are sensitized to calcineurin signaling and show accelerated cardiomyopathy in response to pathological biomechanical stress. Nat Med. 2004 Dec;10(12):1336-43. Epub 2004 Nov 14. PMID:15543153 doi:nm1132
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Takada F, Vander Woude DL, Tong HQ, Thompson TG, Watkins SC, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH. Myozenin: an alpha-actinin- and gamma-filamin-binding protein of skeletal muscle Z lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1595-600. Epub 2001 Feb 6. PMID:11171996 doi:10.1073/pnas.041609698
- ↑ von Nandelstadh P, Ismail M, Gardin C, Suila H, Zara I, Belgrano A, Valle G, Carpen O, Faulkner G. A class III PDZ binding motif in the myotilin and FATZ families binds enigma family proteins: a common link for Z-disc myopathies. Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;29(3):822-34. Epub 2008 Dec 1. PMID:19047374 doi:10.1128/MCB.01454-08
- ↑ Gontier Y, Taivainen A, Fontao L, Sonnenberg A, van der Flier A, Carpen O, Faulkner G, Borradori L. The Z-disc proteins myotilin and FATZ-1 interact with each other and are connected to the sarcolemma via muscle-specific filamins. J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3739-49. Epub 2005 Aug 2. PMID:16076904 doi:10.1242/jcs.02484
- ↑ Wang J, Shaner N, Mittal B, Zhou Q, Chen J, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Dynamics of Z-band based proteins in developing skeletal muscle cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005 May;61(1):34-48. PMID:15810059 doi:10.1002/cm.20063
- ↑ Frey N, Frank D, Lippl S, Kuhn C, Kogler H, Barrientos T, Rohr C, Will R, Muller OJ, Weiler H, Bassel-Duby R, Katus HA, Olson EN. Calsarcin-2 deficiency increases exercise capacity in mice through calcineurin/NFAT activation. J Clin Invest. 2008 Nov;118(11):3598-608. doi: 10.1172/JCI36277. Epub 2008 Oct 9. PMID:18846255 doi:10.1172/JCI36277
- ↑ Frey N, Barrientos T, Shelton JM, Frank D, Rutten H, Gehring D, Kuhn C, Lutz M, Rothermel B, Bassel-Duby R, Richardson JA, Katus HA, Hill JA, Olson EN. Mice lacking calsarcin-1 are sensitized to calcineurin signaling and show accelerated cardiomyopathy in response to pathological biomechanical stress. Nat Med. 2004 Dec;10(12):1336-43. Epub 2004 Nov 14. PMID:15543153 doi:nm1132
- ↑ Osio A, Tan L, Chen SN, Lombardi R, Nagueh SF, Shete S, Roberts R, Willerson JT, Marian AJ. Myozenin 2 is a novel gene for human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2007 Mar 30;100(6):766-8. Epub 2007 Mar 8. PMID:17347475 doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000263008.66799.aa
- ↑ Posch MG, Thiemann L, Tomasov P, Veselka J, Cardim N, Garcia-Castro M, Coto E, Perrot A, Geier C, Dietz R, Haverkamp W, Ozcelik C. Sequence analysis of myozenin 2 in 438 European patients with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Med Sci Monit. 2008 Jul;14(7):CR372-4. PMID:18591919
- ↑ Ruggiero A, Chen SN, Lombardi R, Rodriguez G, Marian AJ. Pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by myozenin 2 mutations is independent of calcineurin activity. Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Oct 19. PMID:22987565 doi:10.1093/cvr/cvs294