We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Simvastatin Synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (22 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:svs.jpg|300px|left|thumb|]] | + | <StructureSection load='3hle' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Structure of Simvastatin Synthase complex with monacolin J acid and dithiothreitol [[3hle]]'> |
| - | + | [[Image:svs.jpg|300px|left|thumb|]] | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
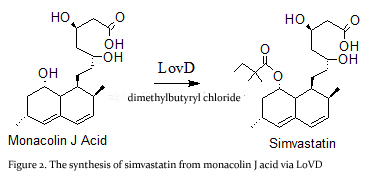
| - | This enzyme is isolated from the natural product biosynthetic pathways of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspergillus_terreus ''Aspergillus terreus''], specifically the polyketide biosynthetic pathway. Simvastatin Synthase converts the inactive monacolin J acid (MJA) by dimethylbutyryl chloride to yield the protected form of simvastatin (Figure 2), which subsequently undergoes lactonization to yield [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simvastatin ''simvastatin'']<ref name="paper5">PMID:19875080</ref>. | ||
| - | [[Image:Sim_mja.jpg]] | ||
| - | LovD can also synthesize the blockbuster drug simvastatin using MJA and a synthetic α-dimethylbutyryl thioester<ref name="paper1">PMID:17277201</ref>. | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| + | ==Function== | ||
| + | '''Simvastatin synthase''' or '''transesterase''' (LovD) is a 46 kDa acyltransferase found in the lovastatin biosynthetic pathway and catalyzes the final step of [[Lovastatin]] biosynthesis<ref name="paper4">PMID:17113998</ref>. Pictured here is the generated double mutant C40A/C60N (G0), from wild type LovD (Figure 1).This enzyme is isolated from the natural product biosynthetic pathways of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspergillus_terreus ''Aspergillus terreus''], specifically the polyketide biosynthetic pathway. Simvastatin Synthase converts the inactive monacolin J acid (MJA) by dimethylbutyryl chloride to yield the protected form of simvastatin (Figure 2), which subsequently undergoes lactonization to yield [[Simvastatin]]<ref name="paper5">PMID:19875080</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Sim_mja.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | LovD can also synthesize the blockbuster drug simvastatin using MJA and a synthetic α-dimethylbutyryl thioester<ref name="paper1">PMID:17277201</ref>. | ||
==Exploring the structure== | ==Exploring the structure== | ||
| - | + | ||
LovD is a 413-amino acid protein predicted to have an α/β hydrolase fold based on primary sequence analysis<ref name="paper2">PMID:10334994</ref>. | LovD is a 413-amino acid protein predicted to have an α/β hydrolase fold based on primary sequence analysis<ref name="paper2">PMID:10334994</ref>. | ||
LovD has of two domains. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Firsstdomain/1'>first domain</scene>, which consists of residues 1–92 and 204–413, is a central seven-stranded antiparallel β-sheet flanked by α-helices on either face<ref name="paper1">PMID:17277201</ref>. The | LovD has of two domains. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Firsstdomain/1'>first domain</scene>, which consists of residues 1–92 and 204–413, is a central seven-stranded antiparallel β-sheet flanked by α-helices on either face<ref name="paper1">PMID:17277201</ref>. The | ||
| Line 17: | Line 42: | ||
LovD has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Cysteines/2'>nine cysteines</scene> at the following positions: C40, C49, C60, C72, C89, C216, C266, C380, and C395<ref name="paper3">PMID:18988191</ref>. | LovD has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Cysteines/2'>nine cysteines</scene> at the following positions: C40, C49, C60, C72, C89, C216, C266, C380, and C395<ref name="paper3">PMID:18988191</ref>. | ||
| - | |||
==Additional Information== | ==Additional Information== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1CI8' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='' scene='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Estb/1'/> | ||
As simvastatin is an active pharmaceutical ingredient in the cholesterol-lowering drug Zocor®, its efficient synthesis from lovastatin, via LovD is intensely pursued <ref name="paper4">PMID:19875080</ref>. | As simvastatin is an active pharmaceutical ingredient in the cholesterol-lowering drug Zocor®, its efficient synthesis from lovastatin, via LovD is intensely pursued <ref name="paper4">PMID:19875080</ref>. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 50: | ||
Among enzymes that of known structures, <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Estb/1'>EstB</scene> (cephalosporin esterase), is homologous to LovD: 26% sequence identity <ref name="paper6">PMID: | Among enzymes that of known structures, <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_316/Estb/1'>EstB</scene> (cephalosporin esterase), is homologous to LovD: 26% sequence identity <ref name="paper6">PMID: | ||
11847270</ref>. | 11847270</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of simvastatin synthase== | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[3hl9]], [[3hlb]], [[3hlc]], [[4lcl]], [[4lcm]] – AtLovD (mutant) – ''Aspergillus terreus'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[3hld]], [[3hle]] – AtLovD (mutant) + monacolin J acid | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[3hlf]] – AtLovD (mutant) + simvastatin | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[3hlg]] – AtLovD (mutant) + lovastatin | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Eric Ginter, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky