User:Brian Hernandez/DOPA Decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
< User:Brian Hernandez(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
==='''The Active Site'''=== | ==='''The Active Site'''=== | ||
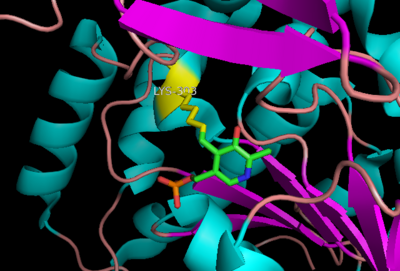
| - | DDC's active site is located in a <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Dimer_interface/2'>cleft</scene> between the two monomer subunits, but is composed mainly of residues from one monomer.The <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> is composed of several key residues, including Lys-303, Asp-271, His-192, Thr-82, Ile-101, and Phe-103. In the ligand free form, PLP binds to Lys 303 via a '''Schiff base linkage'''. A [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_(protein) salt bridge] forms between the carboxylate group of Asp 271 and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP yielding a strong '''electron sink''' capable of stabilizing the carbanionic intermediates. The only two active site residues from the adjacent monomer, Ile-101 and Phe-103, are part of the substrate binding pocket. | + | DDC's active site is located in a <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Dimer_interface/2'>cleft</scene> between the two monomer subunits, but is composed mainly of residues from one monomer.The <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> is composed of several key residues, including Lys-303, Asp-271, His-192, Thr-82, Ile-101, and Phe-103. In the ligand free form, PLP binds to Lys 303 via a '''Schiff base linkage'''. A [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_(protein) salt bridge] forms between the carboxylate group of Asp 271 and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP yielding a strong '''electron sink''' capable of stabilizing the carbanionic intermediates. The only two active site residues from the adjacent monomer, Ile-101 and Phe-103, are part of the substrate binding pocket that stabilizes the substrate via <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Vanderwaals/1'>van der waals forces</scene>. |
[[image:plp bound.png|thumb|center|400px|'''Schiff base linkage of PLP to Lys303 in the active site''']] | [[image:plp bound.png|thumb|center|400px|'''Schiff base linkage of PLP to Lys303 in the active site''']] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==='''Inhibitor Binding'''=== | ==='''Inhibitor Binding'''=== | ||
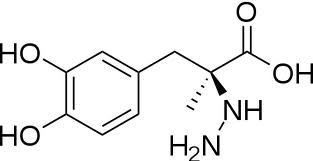
The inhibitor <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Carbidopa/1'>carbiDOPA</scene> binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with the PLP cofactor through its hydrazine moiety <ref name=Burkhard>PMID: 11685243 </ref>. | The inhibitor <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Carbidopa/1'>carbiDOPA</scene> binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with the PLP cofactor through its hydrazine moiety <ref name=Burkhard>PMID: 11685243 </ref>. | ||
| - | [[Image:carbidopa.jpeg|thumb|right|400px|'''carbiDOPA''']] The catechol ring buries itself deep within the active site cleft, with the 4' hydroxyl of the catechol ring hydrogen bonded to the hydroxyl group of Thr 82. Additionally, the highly conserved His 192 residue forms a hydrogen bond to the carboxylate group of carbiDOPA (with the carboxylate group of L-DOPA being even closer in binding range). Thus, His 192 is most likely a key residue in the enzyme's catalytic activity because a H192A mutation can cause complete loss of activity. | + | [[Image:carbidopa.jpeg|thumb|right|400px|'''carbiDOPA''']] The catechol ring buries itself deep within the active site cleft, with the 4' hydroxyl of the catechol ring hydrogen bonded to the hydroxyl group of Thr 82. Additionally, the highly conserved His 192 residue forms a hydrogen bond to the carboxylate group of carbiDOPA (with the carboxylate group of L-DOPA being even closer in binding range). Thus, His 192 is most likely a key residue in the enzyme's catalytic activity because a H192A mutation can cause complete loss of activity<ref name=Burkhard>PMID: 11685243 </ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase
| |||||||||
| 1js3, resolution 2.25Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase, with EC number 4.1.1.28 | ||||||||
| Related: | 1js6 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
3k40 – DDC – Drosophila melanogaster
1js3 – pDDC + inhibitor – pig
1js6 - pDDC
3rbf, 3rbl – hDDC – human
3rch – hDDC + vitamin B6 phosphate + pyridoxal phosphate
References
- ↑ Christenson JG, Dairman W, Udenfriend S. On the identity of DOPA decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase (immunological titration-aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-serotonin-dopamine-norepinephrine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):343-7. PMID:4536745
- ↑ Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Ishii S, Mizuguchi H, Nishino J, Hayashi H, Kagamiyama H. Functionally important residues of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase probed by sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1996 Aug;120(2):369-76. PMID:8889823