|
|
| (55 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| - | [[Image: VEGFR Opening.png|250px|left|thumb| VEGFR Kinase Domain. Two Major Segments in Orange and Blue. Phosphorylated Tyrosines in Green, [[3c7q]]]]
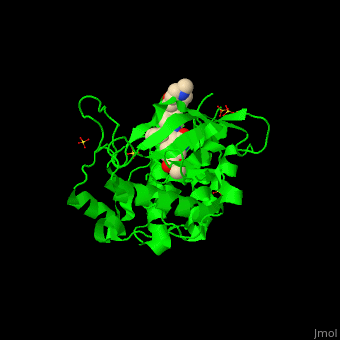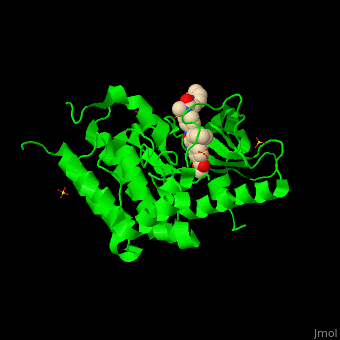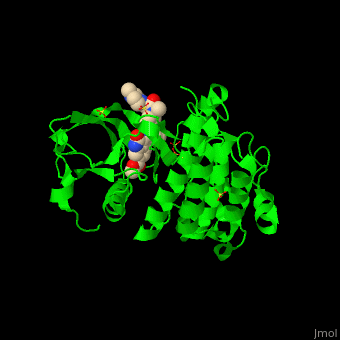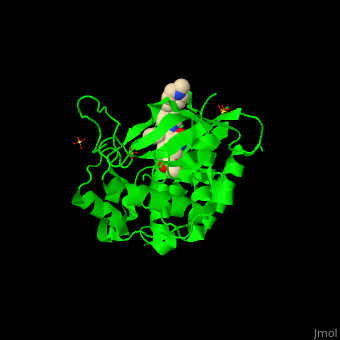
| + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='41/411436/Cv/1' caption='Human VEGFR kinase domain complex with anti-tumor inhibitor and sulfate (PDB code [[3c7q]])'> |
| - | {{STRUCTURE_3ewh| right| PDB=3ewh | SCENE=Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_opening_scene/1|CAPTION= Crystal structure of the VEGFR2 kinase domain in complex with a pyridyl-pyrimidine benzimidazole inhibitor, [[3ewh]] }}
| + | ==Introduction== |
| - | [[Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor]]s (VEGFRs) are tyrosine kinase receptors responsible for binding with [[VEGF]] to initiate signal cascades that stimulate angiogenesis among other effects. VEGFRs convey signals to other signal transduction effectors via autophosphorylation of specific residues in its structure. Because VEGFRs are up-regulated in cancerous tumors which have a high metabolic need for oxygen, VEGFRs are an important target for [[pharmaceutical drugs]] treating [[cancer]]. VEGFR subtypes are numbered 1,2,3. | + | [[Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor]]s (VEGFRs) are [[tyrosine kinase receptors]] responsible for binding with [[VEGF]] to initiate signal cascades that stimulate angiogenesis among other effects<ref>PMID:22130231</ref>. VEGFRs convey signals to other signal transduction effectors via autophosphorylation of specific residues in its structure. Because VEGFRs are up-regulated in cancerous tumors which have a high metabolic need for oxygen, VEGFRs are an important target for [[pharmaceutical drugs]] treating [[cancer]]. VEGFR subtypes are numbered 1,2,3. |
| | + | *'''VEGFR-1''' regulates angiogenesis and has no kinase activity while '''VEGFR-2''' also regulates angiogenesis and has kinase activity<ref>PMID:16146773</ref>. |
| | + | *'''VEGFR-3''' regulates lymphangiogenesis and has a role in blood vessel angiogenesis<ref>PMID:11745682</ref>. |
| | [[Image: VEGF_receptors.png|250px|left|thumb| Interaction of VEGFs with VEGFRs. Colored arrows indicate major pathway. Black arrows indicate minor pathway.]] | | [[Image: VEGF_receptors.png|250px|left|thumb| Interaction of VEGFs with VEGFRs. Colored arrows indicate major pathway. Black arrows indicate minor pathway.]] |
| - | <br />
| + | {{Clear}} |
| | | | |
| - | ==Biological Function: ==
| + | See also [[Kinase-linked, enzyme-linked and related receptors]]. |
| | | | |
| - | The VEGFRs are a family of tyrosine kinase receptors on the surface of different cells depending on family identity. VEGFR-1 is expressed on haematopoietic stem cells, monocytes, and vascular endothelial cells. VEGFR-2 is expressed on vascular endothelial cells and lymphatic endothelial cells, while VEGFR-3 is only expressed on lymphatic endothelial cells.<ref>PMID:16633338</ref> | + | ==Biological Function == |
| | + | |
| | + | The VEGFRs are a family of tyrosine kinase receptors on the surface of different cells depending on family identity. VEGFR-1 is expressed on haematopoietic stem cells, monocytes, and vascular endothelial cells. VEGFR-2 is expressed on vascular endothelial cells and lymphatic endothelial cells, while VEGFR-3 is only expressed on lymphatic endothelial cells<ref>PMID:16633338</ref>. |
| | | | |
| | In terms of function, VEGFR-1 is required for the recruitment of haematopoietic stem cells as well as the migration of monocytes and macrophages while VEGFR-2 regulates vascular endothelial function and VEGFR-3 regulates lymphatic endothelial cell function.<ref>PMID: 17658244</ref> VEGFR-2 has been the focus of the most research as it is the major signal transducer of both physioligcal, and perhaps more importantly, pathological angiogenesis, especially in cancerous tumors. VEGFR-2 is of critical importance to the body as exemplified by Shalaby ''et al.'' who demonstrated that VEGFR-2 gene knockout mice die at E8-8.5 due to lack of vasculogenesis.<ref>PMID:7596453</ref> The signal cascade initiated by binding VEGF to VEGFR is dependent upon specific sites of phosphorylation in the VEGFR structure and the interaction between these phosphorylated sites and other signaling molecules. | | In terms of function, VEGFR-1 is required for the recruitment of haematopoietic stem cells as well as the migration of monocytes and macrophages while VEGFR-2 regulates vascular endothelial function and VEGFR-3 regulates lymphatic endothelial cell function.<ref>PMID: 17658244</ref> VEGFR-2 has been the focus of the most research as it is the major signal transducer of both physioligcal, and perhaps more importantly, pathological angiogenesis, especially in cancerous tumors. VEGFR-2 is of critical importance to the body as exemplified by Shalaby ''et al.'' who demonstrated that VEGFR-2 gene knockout mice die at E8-8.5 due to lack of vasculogenesis.<ref>PMID:7596453</ref> The signal cascade initiated by binding VEGF to VEGFR is dependent upon specific sites of phosphorylation in the VEGFR structure and the interaction between these phosphorylated sites and other signaling molecules. |
| - | {{STRUCTURE_3c7q| right| PDB=3c7q | SCENE=Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_number_2_opening/2 |CAPTION= Structure of VEGFR2 kinase domain in complex with BIBF1120, [[3c7q]] }}
| + | |
| - | ==Structure of VEGFR-2 and Biology:== | + | ==Structure of VEGFR-2 and Biology== |
| - | The structure of VEGFR-2 can been seen at the right. VEGF-A binds to the second and third extracellular Ig-like domains of VEGFR-2 with a 10-fold lower affinity than it does to the second Ig-like domain of VEGFR-1, despite the fact that VEGFR-2 is the principal mediator of several physiological effects on endothelial cells including proliferation, migration, and survival.<ref> PMID:9813036</ref> Binding of VEGF to the domains 2 and 3 of a VEGFR-2 monomer increases the probability that an additional VEGFR-2 binds the tethered ligand to form a dimmer. Once the two receptors are cross-linked, interactions between their membrane-proximal domain 7s stabilize the dimmer significantly. This dimerization and stabilization allows for precise positioning of the intracellular kinase domains, resulting in autophosphorylation and subsequent activation of the classical extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) pathway.<ref>PMID:17293873</ref> | + | The structure of VEGFR-2 can been seen at the right. VEGF-A binds to the second and third extracellular Ig-like domains of VEGFR-2 with a 10-fold lower affinity than it does to the second Ig-like domain of VEGFR-1, despite the fact that VEGFR-2 is the principal mediator of several physiological effects on endothelial cells including proliferation, migration, and survival.<ref> PMID:9813036</ref> Binding of VEGF to the domains 2 and 3 of a VEGFR-2 monomer increases the probability that an additional VEGFR-2 binds the tethered ligand to form a dimmer. Once the two receptors are cross-linked, interactions between their membrane-proximal domain 7s stabilize the dimmer significantly. This dimerization and stabilization allows for precise positioning of the intracellular kinase domains, resulting in autophosphorylation and subsequent activation of the classical extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) pathway.<ref>PMID:17293873</ref>. |
| | | | |
| - | The tyrosine kinase domain of VEGFR-2 is separated into two segments with a 70 amino acid long kinase insert region. Upon binding VEGFA and subsequent dimerization, VEGFR-2 is autophosphoryalted at the carboxy terminal tail and kinase insert region. Several tyrosine residues such as residues,<scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_num939-1000/1'> 951</scene>, <scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_num1050-1060/1'>1054, 1059</scene>, <scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_num1160-1180/1'>1175</scene>, and 1214 are phosphorylated.<ref>PMID:2158038</ref> Unfotunately, due to the flexible nature of these residues, they are very difficult to crystallize. Of <scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_3_binding_sites/1'>these sites</scene>, 1175-Tyr-P is the binding site for the SH2 domain of Phospholipase-Cγ (PLCγ). PLCγ is then phosphorylated and activates the downstream PKC map-kinase pathway, resulting in angiogenesis. The importance of this pathway is highlighted by research on PLCγ knockout mice which die as embryos at approximately E9.0 with greatly diminished vasculature.<ref>pmid:9096335</ref> The enzyme Shb is also able to bind to the phosphorylated Y1175 resulting in its autophosphorylation and subsequently bind to focal adhesion kinase, an enzyme that is critical for cellular migration.<ref>PMID:9484780</ref> Phosphorylation of Y951 and <scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Recptor/Vegfr-2_phosphorylated_tyr/1'>Y1059</scene> was shown to activate a T-Cell specific adapter, resulting in stimulation of the endothelial cell migration and vascular formation. The role of phosphorylated 1054 is currently unknown, but might play a role in migration as well.<ref>PMID:11435426</ref> Phosphorylation of Y1214 creates a binding site for the adaptor protein NcK which is involved in transducing signals from receptor tyrosine kinases to downstream signal ERK pathway recipients such as [[Ras|RAS]].<ref>PMID:9737977</ref> | + | The tyrosine kinase domain of VEGFR-2 is separated into two segments with a 70 amino acid long kinase insert region. Upon binding VEGFA and subsequent dimerization, VEGFR-2 is autophosphoryalted at the carboxy terminal tail and kinase insert region. Six tyrosine residues of VEGFR2 are autophosphorylated (see Fig.1<ref>PMID:15962004</ref>). <scene name='41/411436/Cv/2'>Auto-phosphorylation of residues1054 and 1059</scene> within the activation loop of VEGFR2 leads to increased kinase activity<ref>PMID:10037737</ref>.<br /> |
| - | <br /> | + | |
| | | | |
| - | ==Medical== | + | ==Medical significance== |
| | [[Image: Sorafenib.png|300px|left|thumb| [[Sorafenib]], anti VEGFR drug targeting the MAP Kinase pathway, marketed by Bayer for Renal and Liver [[Cancer]].]] | | [[Image: Sorafenib.png|300px|left|thumb| [[Sorafenib]], anti VEGFR drug targeting the MAP Kinase pathway, marketed by Bayer for Renal and Liver [[Cancer]].]] |
| | + | {{Clear}} |
| | + | VEGFRs play a critical role in a number of signal transduction pathways essential for angiogenesis and cell migration. VEGFR is a particularly attractive target because they are expressed almost exclusively in endothelial cells and are highly upregulated in many tumor endothelium types.<ref>PMID:12360282</ref> In fact, work by Plate ''et al.'' revealed that VEGFR-2 expression is 5 fold higher in the tumor vasculature than in normal vasculature. This increased VEGFR-2 expression is due to a cancer cells high metabolic demand for oxygen and other nutrients to continue growing, thus requiring a vast vasculature. VEGFR signaling has also been implicated in diabetic reinopathy and the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis.<ref>PMID:17826917</ref> |
| | | | |
| - | VEGFRs play a critical role in a number of signal transduction pathways essential for angiogenesis and cell migration. VEGFR is a particularly attractive target because they are expressed almost exclusively in endothelial cells and are highly upregulated in many tumor endothelium types.<ref>PMID:12360282</ref> In fact, work by Plate ''et al.'' revealed that VEGFR-2 expression is 5 fold higher in the tumor vasculature than in normal vasculature. This increased VEGFR-2 expression is due to a cancer cells high metabolic demand for oxygen and other nutrients to continue growing, thus requiring a vast vasculature. VEGFR signaling has also been implicated in diabetic reinopathy and the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis.<ref>PMID:17826917 </ref>
| + | Bevacizumab ([[Avastin]]) is a recombinant [[monoclonal antibody]] marketed by the pharmaceutical company Roche. It earned over $5 billion dollars in 2009 treating a number of cancers. It’s principal mechanism of action is as an anti-VEGF antibody that favors antiangiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment while effecting the rest of the body to a lesser extent. It has been found to decrease tumor vascular permeability subsequently reducing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells when used in combination with chemotherapy.<ref>PMID:11533692 </ref> Other drugs target VEGFR such as [[Sorafenib]] ([[Nexavar]]), [[Sunitinib]] ([[Sutent]]) and Vandetanib, binding to various parts of the receptor, either preventing interaction with [[VEGF]] or with other downstream signaling molecules. |
| | | | |
| - | Bevacizumab ([[Avastin]]) is a recombinant [[monoclonal antibody]] marketed by the pharmaceutical company Roche. It earned over $5 billion dollars in 2009 treating a number of cancers. It’s principal mechanism of action is as an anti-VEGF antibody that favors antiangiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment while effecting the rest of the body to a lesser extent. It has been found to decrease tumor vascular permeability subsequently reducing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells when used in combination with chemotherapy.<ref>PMID:11533692 </ref> Other drugs target VEGFR such as Sorafenib ([[Nexavar]]), Sunitinib ([[Sutent]]) and Vandetanib, binding to various parts of the receptor, either preventing interaction with [[VEGF]] or with other downstream signaling molecules.<ref>PMID:17826917 </ref>
| + | *<scene name='41/411436/Cv/4'>Anti-tumor inhibitor binding site</scene> (PDB code [[3c7q]]). |
| | <br /> | | <br /> |
| - | | + | ==[[3D structures of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor]]== |
| - | == 3D Structures of VEGFR== | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ''Update December 2011''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===VEGFR-1===
| + | |
| - | [[1rv6]] - hVEGFR-1 domain 2 + PlGF - human <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2xac]] – hVEGFR-1D2 + hVEGF-B<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3hng]] - hVEGFR-1 kinase domain + N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzamid <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===VEGFR-2:=== | + | |
| - | [[3kvq]] - hVEGFR-2 extracellular domain 7<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2x1w]], [[2x1x]] – hVEGFR-2 IG-like domains 2 & 3 +hVEGF-C<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3efl]] – hVEGFR-2 kinase domain (mutant)+ motesanib <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3ewh]], [[3cjf]], [[3cjg]], [[3vhe]] - hVEGFR-2 kinase domain + pyrimidine derivative<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3c7q]] - hVEGFR-2 kinase domain + BIBF1120<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3dtw]] - hVEGFR-2 kinase domain + benzisoxazole <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3cp9]], [[3cpb]], [[3cpc]], [[3be2]], [[3b8q]], [[3b8r]], [[2qu5]], [[2qu6]], [[2p2h]], [[2p2i]], [[1ywn]], [[1y6a]], [[1y6b]] - hVEGFR-2 kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2oh4]], [[2rl5]], [[2xir]] - hVEGFR-2 kinase domain (mutant)+ inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3s35]], [[3s36]], [[3s37]] - hVEGFR-2 extracellular domain 3 + Fab heavy+light chains
| + | |
| | | | |
| | ==Additional Resources== | | ==Additional Resources== |
| - | For additional information, see: [[Cancer]] | + | For additional information, see: |
| - | <br />
| + | * [[Cancer]] |
| | + | * [[Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor]] |
| | + | * [[Hormone]] |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |
| | <references /> | | <references /> |
| | + | </StructureSection> |
| | __NOEDITSECTION__ | | __NOEDITSECTION__ |
| - | __NOTOC__ | |
| | | | |
| | [[Category:Topic Page]] | | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
|
Introduction
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors (VEGFRs) are tyrosine kinase receptors responsible for binding with VEGF to initiate signal cascades that stimulate angiogenesis among other effects[1]. VEGFRs convey signals to other signal transduction effectors via autophosphorylation of specific residues in its structure. Because VEGFRs are up-regulated in cancerous tumors which have a high metabolic need for oxygen, VEGFRs are an important target for pharmaceutical drugs treating cancer. VEGFR subtypes are numbered 1,2,3.
- VEGFR-1 regulates angiogenesis and has no kinase activity while VEGFR-2 also regulates angiogenesis and has kinase activity[2].
- VEGFR-3 regulates lymphangiogenesis and has a role in blood vessel angiogenesis[3].
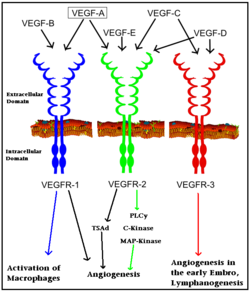 Interaction of VEGFs with VEGFRs. Colored arrows indicate major pathway. Black arrows indicate minor pathway. See also Kinase-linked, enzyme-linked and related receptors.
Biological Function
The VEGFRs are a family of tyrosine kinase receptors on the surface of different cells depending on family identity. VEGFR-1 is expressed on haematopoietic stem cells, monocytes, and vascular endothelial cells. VEGFR-2 is expressed on vascular endothelial cells and lymphatic endothelial cells, while VEGFR-3 is only expressed on lymphatic endothelial cells[4].
In terms of function, VEGFR-1 is required for the recruitment of haematopoietic stem cells as well as the migration of monocytes and macrophages while VEGFR-2 regulates vascular endothelial function and VEGFR-3 regulates lymphatic endothelial cell function.[5] VEGFR-2 has been the focus of the most research as it is the major signal transducer of both physioligcal, and perhaps more importantly, pathological angiogenesis, especially in cancerous tumors. VEGFR-2 is of critical importance to the body as exemplified by Shalaby et al. who demonstrated that VEGFR-2 gene knockout mice die at E8-8.5 due to lack of vasculogenesis.[6] The signal cascade initiated by binding VEGF to VEGFR is dependent upon specific sites of phosphorylation in the VEGFR structure and the interaction between these phosphorylated sites and other signaling molecules.
Structure of VEGFR-2 and Biology
The structure of VEGFR-2 can been seen at the right. VEGF-A binds to the second and third extracellular Ig-like domains of VEGFR-2 with a 10-fold lower affinity than it does to the second Ig-like domain of VEGFR-1, despite the fact that VEGFR-2 is the principal mediator of several physiological effects on endothelial cells including proliferation, migration, and survival.[7] Binding of VEGF to the domains 2 and 3 of a VEGFR-2 monomer increases the probability that an additional VEGFR-2 binds the tethered ligand to form a dimmer. Once the two receptors are cross-linked, interactions between their membrane-proximal domain 7s stabilize the dimmer significantly. This dimerization and stabilization allows for precise positioning of the intracellular kinase domains, resulting in autophosphorylation and subsequent activation of the classical extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) pathway.[8].
The tyrosine kinase domain of VEGFR-2 is separated into two segments with a 70 amino acid long kinase insert region. Upon binding VEGFA and subsequent dimerization, VEGFR-2 is autophosphoryalted at the carboxy terminal tail and kinase insert region. Six tyrosine residues of VEGFR2 are autophosphorylated (see Fig.1[9]). within the activation loop of VEGFR2 leads to increased kinase activity[10].
Medical significance
 Sorafenib, anti VEGFR drug targeting the MAP Kinase pathway, marketed by Bayer for Renal and Liver Cancer. VEGFRs play a critical role in a number of signal transduction pathways essential for angiogenesis and cell migration. VEGFR is a particularly attractive target because they are expressed almost exclusively in endothelial cells and are highly upregulated in many tumor endothelium types.[11] In fact, work by Plate et al. revealed that VEGFR-2 expression is 5 fold higher in the tumor vasculature than in normal vasculature. This increased VEGFR-2 expression is due to a cancer cells high metabolic demand for oxygen and other nutrients to continue growing, thus requiring a vast vasculature. VEGFR signaling has also been implicated in diabetic reinopathy and the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis.[12]
Bevacizumab (Avastin) is a recombinant monoclonal antibody marketed by the pharmaceutical company Roche. It earned over $5 billion dollars in 2009 treating a number of cancers. It’s principal mechanism of action is as an anti-VEGF antibody that favors antiangiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment while effecting the rest of the body to a lesser extent. It has been found to decrease tumor vascular permeability subsequently reducing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells when used in combination with chemotherapy.[13] Other drugs target VEGFR such as Sorafenib (Nexavar), Sunitinib (Sutent) and Vandetanib, binding to various parts of the receptor, either preventing interaction with VEGF or with other downstream signaling molecules.
Additional Resources
For additional information, see:
References
- ↑ Takahashi S. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for antiangiogenic tumor therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(12):1785-8. PMID:22130231
- ↑ Rahimi N. VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2: two non-identical twins with a unique physiognomy. Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:818-29. PMID:16146773 doi:10.2741/1839
- ↑ Witmer AN, van Blijswijk BC, Dai J, Hofman P, Partanen TA, Vrensen GF, Schlingemann RO. VEGFR-3 in adult angiogenesis. J Pathol. 2001 Nov;195(4):490-7. PMID:11745682 doi:10.1002/path.969
- ↑ Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006 May;7(5):359-71. PMID:16633338 doi:10.1038/nrm1911
- ↑ Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM, Cross MJ. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: structure, function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell Signal. 2007 Oct;19(10):2003-12. Epub 2007 Jun 12. PMID:17658244 doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.013
- ↑ Gallina P, Nohra G, Cioloca C, Meder JF, Roux FX. [Multiple cavernoma of delayed appearance] Neurochirurgie. 1994;40(5):322-5. PMID:7596453
- ↑ Shinkai A, Ito M, Anazawa H, Yamaguchi S, Shitara K, Shibuya M. Mapping of the sites involved in ligand association and dissociation at the extracellular domain of the kinase insert domain-containing receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1998 Nov 20;273(47):31283-8. PMID:9813036
- ↑ Ruch C, Skiniotis G, Steinmetz MO, Walz T, Ballmer-Hofer K. Structure of a VEGF-VEGF receptor complex determined by electron microscopy. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;14(3):249-50. Epub 2007 Feb 11. PMID:17293873 doi:10.1038/nsmb1202
- ↑ Matsumoto T, Bohman S, Dixelius J, Berge T, Dimberg A, Magnusson P, Wang L, Wikner C, Qi JH, Wernstedt C, Wu J, Bruheim S, Mugishima H, Mukhopadhyay D, Spurkland A, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor-2 Y951 signaling and a role for the adapter molecule TSAd in tumor angiogenesis. EMBO J. 2005 Jul 6;24(13):2342-53. Epub 2005 Jun 16. PMID:15962004 doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600709
- ↑ Kendall RL, Rutledge RZ, Mao X, Tebben AJ, Hungate RW, Thomas KA. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor KDR tyrosine kinase activity is increased by autophosphorylation of two activation loop tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 5;274(10):6453-60. PMID:10037737
- ↑ Ferrara N. VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002 Oct;2(10):795-803. PMID:12360282 doi:10.1038/nrc909
- ↑ Rosa DD, Ismael G, Lago LD, Awada A. Molecular-targeted therapies: lessons from years of clinical development. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008 Feb;34(1):61-80. Epub 2007 Sep 10. PMID:17826917 doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.07.019
- ↑ Jain RK. Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med. 2001 Sep;7(9):987-9. PMID:11533692 doi:10.1038/nm0901-987
|