Exo-alpha-1,5-L-Arabinanase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='2w5o' size='450' scene='Exo-alpha-1,5-L-Arabinanase/Arabinanase_bgblack/1' caption='α-L-arabinofuranosidase complex with arabinobiose, ethane diol, PEG and sulfate (PDB code [[2w5o]])'> |
| - | + | ||
[[Image:Arabinanase_2d.jpg|left|300 px]] | [[Image:Arabinanase_2d.jpg|left|300 px]] | ||
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
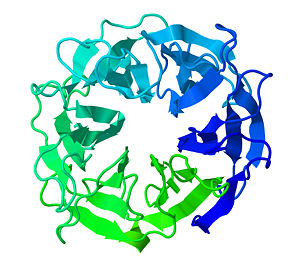
[[Exo-alpha-1,5-L-Arabinanase|Exo-α-1,5-L-Arabinanase]] (Arb93A) ([[EC]] 3.2.1.55) is an enzyme from the GH93 family encoded by the gene fg03054.1. The CAZY data base describes the enzymes of this family as α-1,5-L-arabinanases which are essential glycoside hydrolases participating in the complete hydrolysis of α-1,5-L-arabinofuranosic linkages in hemicellulose. This is important since hemicellulose is a major compound in plant biomass that is used in many industrial processes such as bioethanol or pharmaceutical production. Thus the potential practical application of those enzymes in various industrial processes gives them a great interest in the industry domain. | [[Exo-alpha-1,5-L-Arabinanase|Exo-α-1,5-L-Arabinanase]] (Arb93A) ([[EC]] 3.2.1.55) is an enzyme from the GH93 family encoded by the gene fg03054.1. The CAZY data base describes the enzymes of this family as α-1,5-L-arabinanases which are essential glycoside hydrolases participating in the complete hydrolysis of α-1,5-L-arabinofuranosic linkages in hemicellulose. This is important since hemicellulose is a major compound in plant biomass that is used in many industrial processes such as bioethanol or pharmaceutical production. Thus the potential practical application of those enzymes in various industrial processes gives them a great interest in the industry domain. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 15: | ||
==Enzymatic functioning of exo-α-1,5-L-arabinanase== | ==Enzymatic functioning of exo-α-1,5-L-arabinanase== | ||
| - | + | ||
The active site is located in a deep acidic L-shaped crevice in the centre of the β-propeller. The contacts between the sugar and Arb93A are shown <scene name='Exo-alpha-1,5-L-Arabinanase/Exo-arabinanase_poket/3'>here</scene> | The active site is located in a deep acidic L-shaped crevice in the centre of the β-propeller. The contacts between the sugar and Arb93A are shown <scene name='Exo-alpha-1,5-L-Arabinanase/Exo-arabinanase_poket/3'>here</scene> | ||
A movement of about 1Å is observed for some loops close to the active site to accommodate the sugar. | A movement of about 1Å is observed for some loops close to the active site to accommodate the sugar. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of exo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase
Bibliography
- Carapito R, Imberty A, Jeltsch JM, Byrns SC, Tam PH, Lowary TL, Varrot A, Phalip V. Molecular basis of arabinobio-hydrolase activity in phytopathogenic fungi: crystal structure and catalytic mechanism of Fusarium graminearum GH93 exo-alpha-L-arabinanase. J Biol Chem. 2009 May 1;284(18):12285-96. Epub 2009 Mar 6. PMID:19269961 doi:10.1074/jbc.M900439200
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Leo-Paul Tisserant, Michal Harel, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Anne-Sophie Kirstetter, Jaime Prilusky