Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
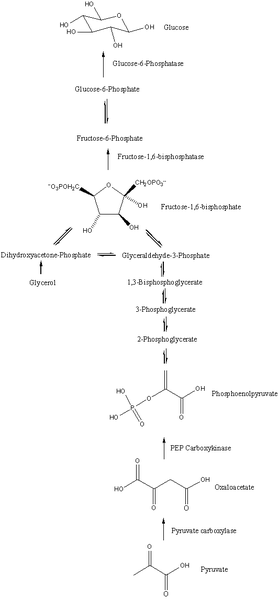
[[Image:279px-Gluconeogenesis.png|350px|right|thumb| Synthesis of Glucose During Gluconeogenesis]] | [[Image:279px-Gluconeogenesis.png|350px|right|thumb| Synthesis of Glucose During Gluconeogenesis]] | ||
| - | [[Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis|Gluconeogesis]] is a metabolic pathway which results in the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates such as glycerol, | + | [[Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis|Glycogen Metabolism]] maintains blood glucose level through synthesis or degradation of glycogen in the liver <ref>DOI:10.1038/emm.2015.122</ref>. [[Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis|Gluconeogesis]] is a metabolic pathway which results in the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and select amino acids<ref>Stryer, Biochemistry, Section 16.3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22591/</ref>. It is one of the major mechanisms present in humans which prevents blood glucose levels from dropping too low. |
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Articles in Proteopedia concerning [[Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis]] include: | Articles in Proteopedia concerning [[Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis]] include: | ||
Current revision
Glycogen Metabolism maintains blood glucose level through synthesis or degradation of glycogen in the liver [1]. Gluconeogesis is a metabolic pathway which results in the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and select amino acids[2]. It is one of the major mechanisms present in humans which prevents blood glucose levels from dropping too low.
References
- ↑ Han HS, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, Koo SH. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp Mol Med. 2016 Mar 11;48:e218. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.122. PMID:26964834 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/emm.2015.122
- ↑ Stryer, Biochemistry, Section 16.3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22591/
Articles in Proteopedia concerning Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis include:
- Aldolase
- Biotin Protein Ligase
- Calmodulin
- Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase
- Glycogen Phosphorylase
- Hexokinase Structure & Mechanism
To view automatically seeded indices concerning Glycogen Metabolism & Gluconeogenesis See:
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David Canner, Lynmarie K Thompson, Karsten Theis, Jaime Prilusky