Enzyme I of the S. aureus PTS
From Proteopedia
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='2wqd' size='450' side='right' scene='Enzyme_I_of_the_S._aureus_PTS/Saei_domains/7' caption='Enzyme I of the phosphotransferase system (PDB code [[2wqd]])'> | ||
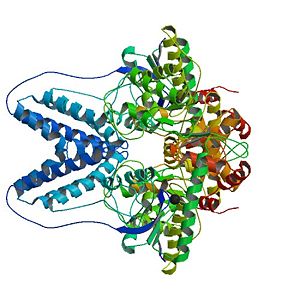
[[Image:2wqd bio r 500.jpg|300px|left|thumb| Biological Assembly of the two asymmetric units of Enzyme I of the S. aureus PTS (PEP Phosphotransferase System), [[2wqd]]]] | [[Image:2wqd bio r 500.jpg|300px|left|thumb| Biological Assembly of the two asymmetric units of Enzyme I of the S. aureus PTS (PEP Phosphotransferase System), [[2wqd]]]] | ||
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
| - | + | ||
Here we report the crystal structure of [[Enzyme I (EI) from Staphylococcus aureus]] which is the first component involved in the Sugar Phosphotransferase System (PTS) reaction cascade. EI is an enzyme of 572 residues and its tertiary structure is composed of 48% α helix and of 13% β-sheet. The crystal structure was obtained with a resolution of 2,40Ǻ. | Here we report the crystal structure of [[Enzyme I (EI) from Staphylococcus aureus]] which is the first component involved in the Sugar Phosphotransferase System (PTS) reaction cascade. EI is an enzyme of 572 residues and its tertiary structure is composed of 48% α helix and of 13% β-sheet. The crystal structure was obtained with a resolution of 2,40Ǻ. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== I.The Sugar Phosphotransferase System == | == I.The Sugar Phosphotransferase System == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
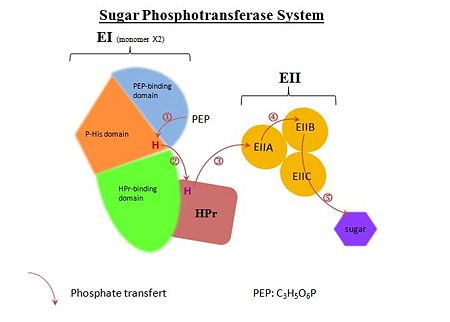
PTS have two functions in organisms, the first one is the control of sugar consumption, the second one is the control of the carbon metabolism. PTS is composed of four phosphoproteins, whose aim is to regulate the transfer of a phosphyl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to sugar which can then move into the cell. PEP is the phosphate stock in this system. The phosphate transfer occurs by five phosphorylation steps : | PTS have two functions in organisms, the first one is the control of sugar consumption, the second one is the control of the carbon metabolism. PTS is composed of four phosphoproteins, whose aim is to regulate the transfer of a phosphyl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to sugar which can then move into the cell. PEP is the phosphate stock in this system. The phosphate transfer occurs by five phosphorylation steps : | ||
| Line 23: | Line 18: | ||
In vivo, the transferred phosphate come from PEP, but in vivo it can come from ATP or acetyl phosphate too. | In vivo, the transferred phosphate come from PEP, but in vivo it can come from ATP or acetyl phosphate too. | ||
| - | [[Image:Pts EI.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Pts EI.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] |
| - | + | ||
== II. Structure of Enzyme I == | == II. Structure of Enzyme I == | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='2wqd' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of ''S. aureus'' EI' scene='Enzyme_I_of_the_S._aureus_PTS/Saei_domains/7' > | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
EI is active only in its homodimeric form of 64kDa. As we said, EI consists of a N- and a C-terminal domain. | EI is active only in its homodimeric form of 64kDa. As we said, EI consists of a N- and a C-terminal domain. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 35: | ||
-There is 920 Ǻ² of solvent accessible surface between the P-His with its phosphorylated His191 and the EIC domains with its PEP binding site. | -There is 920 Ǻ² of solvent accessible surface between the P-His with its phosphorylated His191 and the EIC domains with its PEP binding site. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | + | __NOTOC__ | |
== III.Staphylococcus aureus vs Escherichia coli == | == III.Staphylococcus aureus vs Escherichia coli == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
The X-ray structure of S. aureus EI (SaEI) has been recently solved but structures of other bacterias have been reported before, for instance E. coli EI structure (EcEI). Although SaEI and EcEI X-ray structures are nearly the same, some differences have been observed. | The X-ray structure of S. aureus EI (SaEI) has been recently solved but structures of other bacterias have been reported before, for instance E. coli EI structure (EcEI). Although SaEI and EcEI X-ray structures are nearly the same, some differences have been observed. | ||
| - | |||
[[Image:tableau SaEI EcEI.jpg]] | [[Image:tableau SaEI EcEI.jpg]] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 47: | ||
== Conclusion: == | == Conclusion: == | ||
| - | |||
Knowing the structure of S. aureus EI allows a better comprehension of the PTS mechanism. But progresses could be still done such as the possible phenomena which induce the motions of the different domains. | Knowing the structure of S. aureus EI allows a better comprehension of the PTS mechanism. But progresses could be still done such as the possible phenomena which induce the motions of the different domains. | ||
| - | |||
== Reference == | == Reference == | ||
| Line 68: | Line 54: | ||
Oberholzer AE, Schneider P, Siebold C, Baumann U, Erni B. (2009).Crystal structure of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:Sugar phosphotransferase system in the dephosphorylated state. J Biol Chem | Oberholzer AE, Schneider P, Siebold C, Baumann U, Erni B. (2009).Crystal structure of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:Sugar phosphotransferase system in the dephosphorylated state. J Biol Chem | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19801641?dopt=Abstract PMID: 19801641] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19801641?dopt=Abstract PMID: 19801641] | ||
| - | |||
== 3D Structures of EI == | == 3D Structures of EI == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
III.Staphylococcus aureus vs Escherichia coli
The X-ray structure of S. aureus EI (SaEI) has been recently solved but structures of other bacterias have been reported before, for instance E. coli EI structure (EcEI). Although SaEI and EcEI X-ray structures are nearly the same, some differences have been observed.
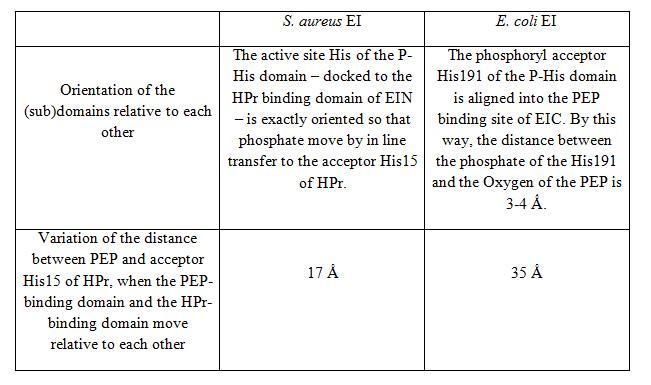
These two X-ray structures could actually be two possible conformations of the Enzyme I, corresponding to two steps of the phosphotransfer from PEP to HPr. EcEI structure correspond to the conformation II and SaEI structure correspond to the conformation I.
Thus, two modest rigid body motions can be described :
Conclusion:
Knowing the structure of S. aureus EI allows a better comprehension of the PTS mechanism. But progresses could be still done such as the possible phenomena which induce the motions of the different domains.
Reference
Oberholzer AE, Schneider P, Siebold C, Baumann U, Erni B. (2009).Crystal structure of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:Sugar phosphotransferase system in the dephosphorylated state. J Biol Chem PMID: 19801641
3D Structures of EI
2wqd S. aureus EI phosphorylated structure
2hwg E. coli phosphorylated and Mg2+-oxalate bound structure
Links
Proteopedia page : Enzyme I of the Phosphoenolpyruvate:Sugar Phosphotransferase System (E. coli and S. carnosus)