Molecular Playground/C-Raf
From Proteopedia
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<applet load='3omv' size='[450,338]' frame='true' align='right' | <applet load='3omv' size='[450,338]' frame='true' align='right' | ||
caption='C-Raf complex with inhibitor [[3omv]]' scene=''User:Thuy V. Nguyen/Sandbox103/Loadedfrompdb/4'/> | caption='C-Raf complex with inhibitor [[3omv]]' scene=''User:Thuy V. Nguyen/Sandbox103/Loadedfrompdb/4'/> | ||
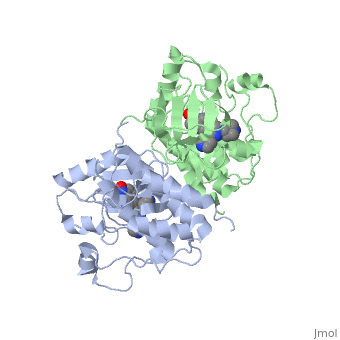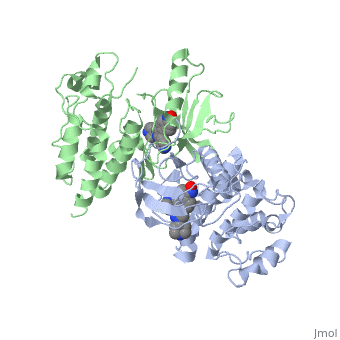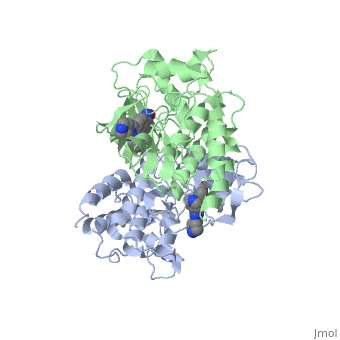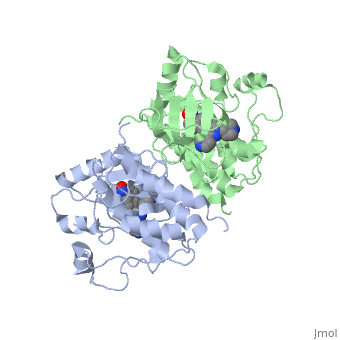
| - | '''C-Raf''' (Raf1) is one of the isoforms of Raf serine/threonine kinase. The others are A-Raf and B-Raf. The Raf-kinase is activated by Ras protein. Activated Raf will trigger the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK, which regulates some transcription factors that induce gene expression required for cell proliferation. Raf1 activation is found in 50% of renal cell carcinoma and 100% of hepatocellular carcinoma (Scott Wilhelm et al., 2006). [[Sorafenib]] is an FDA approval small molecule for Raf1 inhibitor. | + | '''C-Raf''' (Raf1) is one of the isoforms of Raf serine/threonine kinase. The others are A-Raf and B-Raf. The Raf-kinase is activated by Ras protein. Activated Raf will trigger the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK, which regulates some transcription factors that induce gene expression required for cell proliferation. Raf1 activation is found in 50% of renal cell carcinoma and 100% of hepatocellular carcinoma (Scott Wilhelm et al., 2006). [[Sorafenib]] is an FDA approval small molecule for Raf1 inhibitor. Sorafenib also binds to B-Raf. |
| + | <scene name='Molecular_Playground/C-Raf/B-raf/2'>THE COMPLEX OF WILD TYPE B-RAF AND BAY439006 (Sorafenib)</scene> | ||
==3D structures of C-Raf== | ==3D structures of C-Raf== | ||
Current revision
>One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst in the Peyton group and on display at the Molecular Playground.
|
C-Raf (Raf1) is one of the isoforms of Raf serine/threonine kinase. The others are A-Raf and B-Raf. The Raf-kinase is activated by Ras protein. Activated Raf will trigger the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK, which regulates some transcription factors that induce gene expression required for cell proliferation. Raf1 activation is found in 50% of renal cell carcinoma and 100% of hepatocellular carcinoma (Scott Wilhelm et al., 2006). Sorafenib is an FDA approval small molecule for Raf1 inhibitor. Sorafenib also binds to B-Raf.
3D structures of C-Raf
1rfa – hCRAF-1 Ras-binding domain – human – NMR
3omv - hCRAF-1 kinase domain
1gua - hCRAF-1 Ras-binding domain + Rap1A (mutant) + guanosyl-imido-triphosphate
3kuc - hCRAF-1 Ras-binding domain + Rap1A (mutant)
3kud - hCRAF-1 Ras-binding domain + GTPase Hras