C-terminal portion of human eIF4GI
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1ug3' size='400' side='right' scene | + | <StructureSection load='1ug3' size='400' side='right' scene='3d3m/Al1/1' | caption="Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G C-terminal [[1ug3]]"> |
[[Image:1ug3.png|left|200px]] | [[Image:1ug3.png|left|200px]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
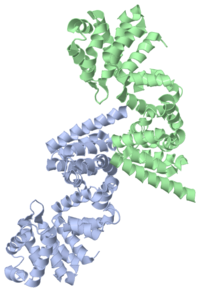
The X-ray structure of the C-terminal region of human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) has been determined at 2.2 A resolution, revealing two atypical HEAT-repeat domains. eIF4G recruits various translation factors and the 40S ribosomal subunit to the mRNA 5' end. In higher eukaryotes, the C terminus of eIF4G (4G/C) supports translational regulation by recruiting eIF4A, an RNA helicase, and Mnk1, the kinase responsible for phosphorylating eIF4E. Structure-guided surface mutagenesis and protein-protein interaction assays were used to identify binding sites for eIF4A and Mnk1 within the HEAT-repeats of 4G/C. p97/DAP5, a translational modulator homologous to eIF4G, lacks an eIF4A binding site in the corresponding region. The second atypical HEAT domain of the 4G/C binds Mnk1 using two conserved aromatic/acidic-box (AA-box) motifs. Within the first AA-box, the aromatic residues contribute to the hydrophobic core of the domain, while the acidic residues form a negatively charged surface feature suitable for electrostatic interactions with basic residues in Mnk1. | The X-ray structure of the C-terminal region of human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) has been determined at 2.2 A resolution, revealing two atypical HEAT-repeat domains. eIF4G recruits various translation factors and the 40S ribosomal subunit to the mRNA 5' end. In higher eukaryotes, the C terminus of eIF4G (4G/C) supports translational regulation by recruiting eIF4A, an RNA helicase, and Mnk1, the kinase responsible for phosphorylating eIF4E. Structure-guided surface mutagenesis and protein-protein interaction assays were used to identify binding sites for eIF4A and Mnk1 within the HEAT-repeats of 4G/C. p97/DAP5, a translational modulator homologous to eIF4G, lacks an eIF4A binding site in the corresponding region. The second atypical HEAT domain of the 4G/C binds Mnk1 using two conserved aromatic/acidic-box (AA-box) motifs. Within the first AA-box, the aromatic residues contribute to the hydrophobic core of the domain, while the acidic residues form a negatively charged surface feature suitable for electrostatic interactions with basic residues in Mnk1. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | Bellsolell L, Cho-Park PF, Poulin F, Sonenberg N, Burley SK. Two structurally atypical HEAT domains in the C-terminal portion of human eIF4G support binding to eIF4A and Mnk1. Structure. 2006 May;14(5):913-23. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16698552 16698552] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | <applet load='D3m.pdb' size='500' frame='true' align='right' scene='3d3m/Al1/1' /> | ||
| - | |||
'''Protease cleavage sites''' (especially caspase cleavage sites) are frequently situated in '''flexible, unstructured regions''' of proteins. In eIF4GI, eIF2Bε, and eIF5, where the caspase cleavage site is absent, <scene name='3d3m/Al1/2'>this region</scene> is structured and characterized by an α3-α4 interunit loop. The superposition of <font color='blue'><b>α3 and α4 of eIF4GI</b></font> ([[1ug3]], <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>) to <font color='orange'><b>α3 (orange)</b></font> and <font color='lime'><b>α4 (lime)</b></font> of C-terminal domain of human DAP5/p97 (DAP5-CTD, [[3d3m]]) is shown. | '''Protease cleavage sites''' (especially caspase cleavage sites) are frequently situated in '''flexible, unstructured regions''' of proteins. In eIF4GI, eIF2Bε, and eIF5, where the caspase cleavage site is absent, <scene name='3d3m/Al1/2'>this region</scene> is structured and characterized by an α3-α4 interunit loop. The superposition of <font color='blue'><b>α3 and α4 of eIF4GI</b></font> ([[1ug3]], <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>) to <font color='orange'><b>α3 (orange)</b></font> and <font color='lime'><b>α4 (lime)</b></font> of C-terminal domain of human DAP5/p97 (DAP5-CTD, [[3d3m]]) is shown. | ||
There are only 3 pairs of <scene name='3d3m/Al1/3'>interacting residues</scene> between α3 and α4 of DAP5-CTD. In contrast, there are more interactions at the <scene name='3d3m/Al1/4'>loop</scene> stabilizing the interaction between α3 and α4 in eIF4GI. | There are only 3 pairs of <scene name='3d3m/Al1/3'>interacting residues</scene> between α3 and α4 of DAP5-CTD. In contrast, there are more interactions at the <scene name='3d3m/Al1/4'>loop</scene> stabilizing the interaction between α3 and α4 in eIF4GI. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Reference
- Bellsolell L, Cho-Park PF, Poulin F, Sonenberg N, Burley SK. Two structurally atypical HEAT domains in the C-terminal portion of human eIF4G support binding to eIF4A and Mnk1. Structure. 2006 May;14(5):913-23. PMID:16698552 doi:10.1016/j.str.2006.03.012