Nuclear receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
| - | + | SEE [[Nuclear receptors]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
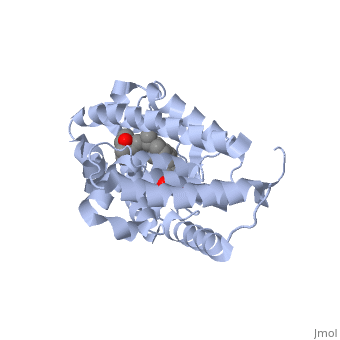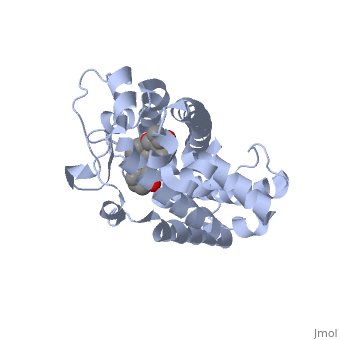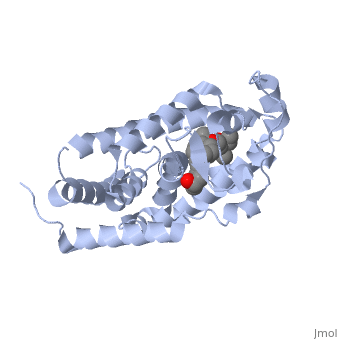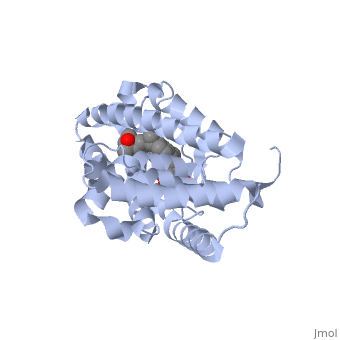
<StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of the LBD of a VDR (vitamin D receptor) complexed to 1alpha,25(OH)(2)D(3) and the 20-epi analogs(PDB entry [[1ie8]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of the LBD of a VDR (vitamin D receptor) complexed to 1alpha,25(OH)(2)D(3) and the 20-epi analogs(PDB entry [[1ie8]])' scene=''> | ||
The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. | The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. | ||
| - | It is a globular domain | + | It is a globular domain, mainly alpha |
<scene name='Nuclear_receptor/Nr-lbd-/1'>well folded</scene> | <scene name='Nuclear_receptor/Nr-lbd-/1'>well folded</scene> | ||
| - | + | composed of | |
| + | <scene name='Nuclear_receptor/Nr-lbd-alpha/1'>12 alpha-helices</scene> | ||
| + | arranged in a three layered sandwich, and a <scene name='Nuclear_receptor/Nr-lbd-beta/1'>beta-sheet</scene>. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
the nuclear receptors facts book [1]
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Vincent Laudet, Hinrich Gronemeyer, "The nuclear receptor factsbook", Publisher Academic Press, 2002