We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Fibrinogen binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
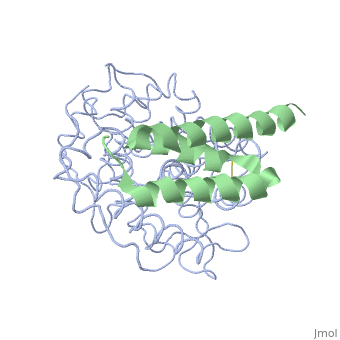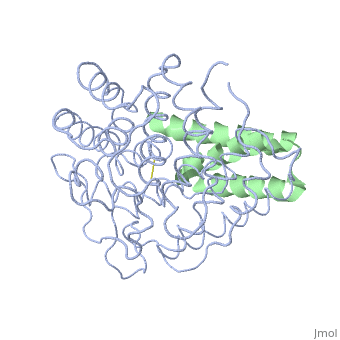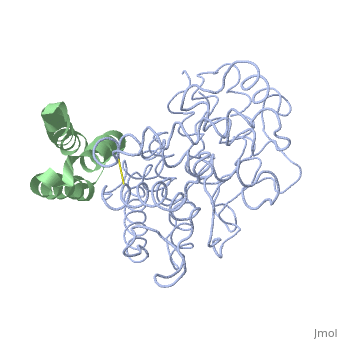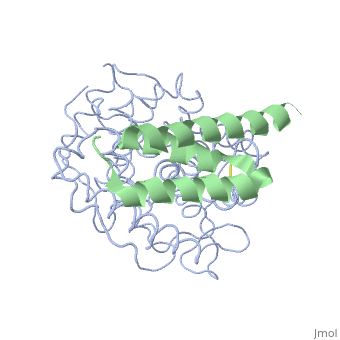
| + | <StructureSection load='2gox' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Efb (green) complex with complement C3 α chain fragment (grey) (PDB entry [[2gox]])' scene=''> | ||
== Extra cellular fibrinogen binding protein- Efb == | == Extra cellular fibrinogen binding protein- Efb == | ||
| - | + | ''Staphylococcous Aureus'' is a bacterium that is commonly found on human skin and respiratory tracts; however, when it becomes pathogenic it can cause many diseases: skin infections, respiratory diseases(pneumonia), food poisoning. It is a Gram positive, cluster forming coccus, non-motile, facultative Anaerobe and a leading cause of nosocomial infection. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus More about Staph Aureus] | |
'''Complement System''' is part of the innate immune system and helps aid [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibodies antibodies] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phagocytic_cells phagocytic cells] to kill off pathogenic cells. Complement system contains 30 proteins produced in the liver and are secreted into the body. Key proteins that are in the complement system that Efb inhibits:<br> | '''Complement System''' is part of the innate immune system and helps aid [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibodies antibodies] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phagocytic_cells phagocytic cells] to kill off pathogenic cells. Complement system contains 30 proteins produced in the liver and are secreted into the body. Key proteins that are in the complement system that Efb inhibits:<br> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
[http://www.bioscience.org/2009/v1s/af/11/fig1.jpg cascade process] | [http://www.bioscience.org/2009/v1s/af/11/fig1.jpg cascade process] | ||
| - | '''Efb function''' is a protein that is secreted by Staphylococcous Aureus which mimics the natural proteins in the body that inhibit the complement system. These proteins are called regulator of complement activation(RCA). In general, RCA proteins suppress the activation of C3 and C4 by dissociating the subunits of C3 and/or C5 convertases or by acting as cofactors for factor I–dependent cleavage of C3b and/or C4b. <ref>PMID: 17351618</ref> Efb has been shown to bind to the C3d domain of C3 and C3B, inhibiting its function. | + | '''Efb function''' is a protein that is secreted by Staphylococcous Aureus which mimics the natural proteins in the body that inhibit the complement system. These proteins are called regulator of complement activation(RCA). In general, RCA proteins suppress the activation of C3 and C4 by dissociating the subunits of C3 and/or C5 convertases or by acting as cofactors for factor I–dependent cleavage of C3b and/or C4b. <ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> Efb has been shown to bind to the C3d domain of C3 and C3B, inhibiting its function. |
| - | + | ||
==Structural motifs== | ==Structural motifs== | ||
The overall dimensions of Efb-C were approximately 40x25x20 A° and 15.6 kDa, with the N-terminal a1 helix (K106–H125) connected | The overall dimensions of Efb-C were approximately 40x25x20 A° and 15.6 kDa, with the N-terminal a1 helix (K106–H125) connected | ||
| - | through a short loop to the a2 helix (V127–L139), followed by the C-terminal a3 helix (K145–Q161), and terminating in a random coil conformation. All three helices were packed in a canonical three-helix bundle fold, with most of the nonpolar side chains directed inward.<ref>PMID: 17351618</ref> [http://p8888-ucelinks.cdlib.org.proxy.library.ucsb.edu:2048/sfx_local?&url_ver=Z39.88-2004&rfr_id=info%3Asid%2Fucsb.worldcat.org%3Aworldcat&rft_val_fmt=info%3Aofi%2Ffmt%3Akev%3Amtx%3Ajournal&req_dat=%3Csessionid%3E&rfe_dat=%3Caccessionnumber%3E123919124%3C%2Faccessionnumber%3E&rft_id=info%3Aoclcnum%2F123919124&rft_id=urn%3AISSN%3A1529-2908&rft.aulast=Hammel&rft.aufirst=M&rft.atitle=A+structural+basis+for+complement+inhibition+by+Staphylococcus+aureus.&rft.jtitle=Nature+immunology&rft.date=2007&rft.volume=8&rft.issue=4&rft.spage=430&rft.epage=7&rft.issn=1529-2908&rft.genre=article&rft.sici=1529-2908%28200704%298%3A4%3C430%3AASBFCI%3E2.0.TX%3B2-7&req_id=info:rfa/oclc/institutions/211&req_dat=%3Cip%3E128.111.121.42%3C%2Fip%3E&req_id=info%3Arfa%2Foclc%2FInstitutions%2F211 Figure 1] Many RCA proteins like factor H contain a short consensus repeat or complement-control protein beta-type fold but Efb does not. Its structure is entirely helical and therefore defined a previously unrecognized fold class for complement regulatory proteins. <ref>PMID: 17351618</ref> | + | through a short loop to the a2 helix (V127–L139), followed by the C-terminal a3 helix (K145–Q161), and terminating in a random coil conformation. All three helices were packed in a canonical three-helix bundle fold, with most of the nonpolar side chains directed inward.<ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> [http://p8888-ucelinks.cdlib.org.proxy.library.ucsb.edu:2048/sfx_local?&url_ver=Z39.88-2004&rfr_id=info%3Asid%2Fucsb.worldcat.org%3Aworldcat&rft_val_fmt=info%3Aofi%2Ffmt%3Akev%3Amtx%3Ajournal&req_dat=%3Csessionid%3E&rfe_dat=%3Caccessionnumber%3E123919124%3C%2Faccessionnumber%3E&rft_id=info%3Aoclcnum%2F123919124&rft_id=urn%3AISSN%3A1529-2908&rft.aulast=Hammel&rft.aufirst=M&rft.atitle=A+structural+basis+for+complement+inhibition+by+Staphylococcus+aureus.&rft.jtitle=Nature+immunology&rft.date=2007&rft.volume=8&rft.issue=4&rft.spage=430&rft.epage=7&rft.issn=1529-2908&rft.genre=article&rft.sici=1529-2908%28200704%298%3A4%3C430%3AASBFCI%3E2.0.TX%3B2-7&req_id=info:rfa/oclc/institutions/211&req_dat=%3Cip%3E128.111.121.42%3C%2Fip%3E&req_id=info%3Arfa%2Foclc%2FInstitutions%2F211 Figure 1] Many RCA proteins like factor H contain a short consensus repeat or complement-control protein beta-type fold but Efb does not. Its structure is entirely helical and therefore defined a previously unrecognized fold class for complement regulatory proteins. <ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> |
==Interactions== | ==Interactions== | ||
<scene name='Extra_cellular_fibrinogen_binding_protein/R131_and_n138/1'>Two amino acids</scene> of Efb were noted as extremely important in achieving binding with the C3d domain, <scene name='Extra_cellular_fibrinogen_binding_protein/R131/2'>R131</scene> and <scene name='Extra_cellular_fibrinogen_binding_protein/N138/1'>N138</scene>. Mutations by site-directed mutagenesis to these two points showed lack of complex formation and showed that other residues of Efb were not enough to drive complex formation. It was also observed that the a2 helix was mostly interacting with the C3d complex.<br> | <scene name='Extra_cellular_fibrinogen_binding_protein/R131_and_n138/1'>Two amino acids</scene> of Efb were noted as extremely important in achieving binding with the C3d domain, <scene name='Extra_cellular_fibrinogen_binding_protein/R131/2'>R131</scene> and <scene name='Extra_cellular_fibrinogen_binding_protein/N138/1'>N138</scene>. Mutations by site-directed mutagenesis to these two points showed lack of complex formation and showed that other residues of Efb were not enough to drive complex formation. It was also observed that the a2 helix was mostly interacting with the C3d complex.<br> | ||
| - | Efb-C blocks the formation of the functional C3b opsonin by binding tightly to the thioester-containing domain of native C3 and by perturbing the overall solution conformation of the molecule to one that is incapable of being processed into C3b. <ref>PMID: 17351618</ref> | + | Efb-C blocks the formation of the functional C3b opsonin by binding tightly to the thioester-containing domain of native C3 and by perturbing the overall solution conformation of the molecule to one that is incapable of being processed into C3b. <ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> |
==Future Possibilities== | ==Future Possibilities== | ||
| - | Possible new anti-staph. aureus compounds can be synthesized that target the Efb-C3 interaction. It can also be used as a model in clinical settings to block complement activation. Knowing the two binding sites, R131 and N138, is a good starting point for screening of new bioactive peptides. <ref>PMID: 17351618</ref> | + | Possible new anti-staph. aureus compounds can be synthesized that target the Efb-C3 interaction. It can also be used as a model in clinical settings to block complement activation. Knowing the two binding sites, R131 and N138, is a good starting point for screening of new bioactive peptides. <ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | *Fibrinogen binding protein | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[3doa]] – SaFba – ''Staphylococcus aureus'' <br /> | |
| + | **[[1r19]] – SeFba – ''Staphylococcus epidermitis'' <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2gom]] – SaFba C terminal<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3t49]], [[4h6i]] – SaFba residues 49-116<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4h6h]] – SaFba residues 4-85<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1n67]] – SaFba A<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3au0]] – SaFba B N2N3 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4f24]] – SaFba B residues 197-542<br /> | ||
| - | + | *Fibrinogen binding protein binary complex | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[2gox]] – SaFba C terminal + complement C3<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3d5r]], [[3d5s]] – SaFba C terminal (mutant) + complement C3 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2vr3]] – SaFba A N2N3 (mutant) + fibrinogen γ chain peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3asw]] – SaFba A N2N3 (mutant) + keratin peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4f1z]] – SaFba B N2N3 + keratin peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4f20]] – SaFba B N2N3 + dermokine peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3at0]] – SaFba B N2N3 (mutant) + fibrinogen α chain peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4f27]] – SaFba B N2N3 + fibrinogen α chain peptide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3t4a]] – SaFba residues 49-116 + complement C3<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1r17]] – SeFba + fibrinopeptide <br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of fibrinogen binding protein
Updated on 23-June-2024
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Hammel M, Sfyroera G, Ricklin D, Magotti P, Lambris JD, Geisbrecht BV. A structural basis for complement inhibition by Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Immunol. 2007 Apr;8(4):430-7. Epub 2007 Mar 11. PMID:17351618 doi:10.1038/ni1450
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Rahul Gunasekera, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky