m |
|
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| - | {{STRUCTURE_3k1r| PDB=3k1r | SCENE= }} | |
| - | ===Structure of harmonin NPDZ1 in complex with the SAM-PBM of Sans=== | |
| - | {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_20142502}} | |
| | | | |
| - | ==Disease== | + | ==Structure of harmonin NPDZ1 in complex with the SAM-PBM of Sans== |
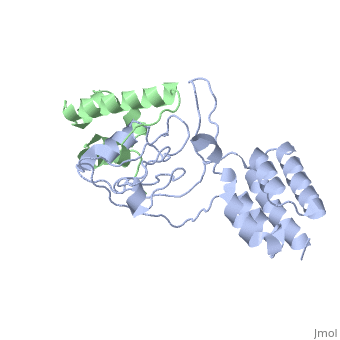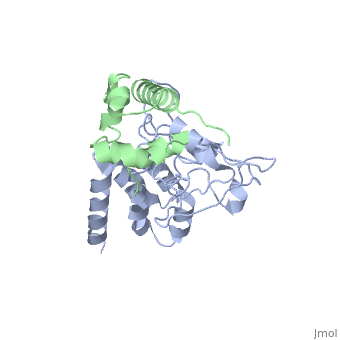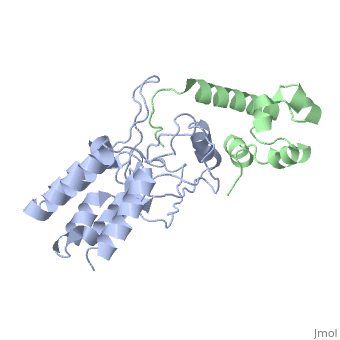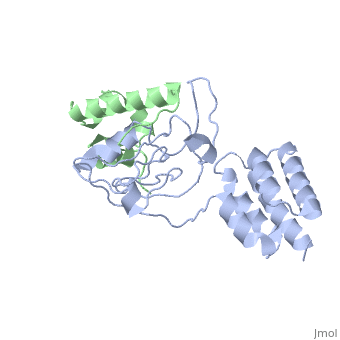
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/USH1C_HUMAN USH1C_HUMAN]] Defects in USH1C are the cause of Usher syndrome type 1C (USH1C) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/276904 276904]]; also known as Usher syndrome type I Acadian variety. USH is a genetically heterogeneous condition characterized by the association of retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural deafness. Age at onset and differences in auditory and vestibular function distinguish Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1), Usher syndrome type 2 (USH2) and Usher syndrome type 3 (USH3). USH1 is characterized by profound congenital sensorineural deafness, absent vestibular function and prepubertal onset of progressive retinitis pigmentosa leading to blindness.<ref>PMID:10973247</ref> Defects in USH1C are the cause of deafness, autosomal recessive, 18A (DFNB18A) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/602092 602092]]. A form of sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information.<ref>PMID:12107438</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/USH1G_HUMAN USH1G_HUMAN]] Defects in USH1G are the cause of Usher syndrome type 1G (USH1G) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/606943 606943]]. USH is a genetically heterogeneous condition characterized by the association of retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural deafness. Age at onset and differences in auditory and vestibular function distinguish Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1), Usher syndrome type 2 (USH2) and Usher syndrome type 3 (USH3). USH1 is characterized by profound congenital sensorineural deafness, absent vestibular function and prepubertal onset of progressive retinitis pigmentosa leading to blindness.<ref>PMID:21709241</ref><ref>PMID:12588794</ref><ref>PMID:20142502</ref><ref>PMID:16283141</ref> | + | <StructureSection load='3k1r' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3k1r]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> |
| | + | == Structural highlights == |
| | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3k1r]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3K1R OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3K1R FirstGlance]. <br> |
| | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> |
| | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3k1r FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3k1r OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3k1r PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3k1r RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3k1r PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3k1r ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | + | </table> |
| | + | == Disease == |
| | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/USH1C_HUMAN USH1C_HUMAN] Defects in USH1C are the cause of Usher syndrome type 1C (USH1C) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/276904 276904]; also known as Usher syndrome type I Acadian variety. USH is a genetically heterogeneous condition characterized by the association of retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural deafness. Age at onset and differences in auditory and vestibular function distinguish Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1), Usher syndrome type 2 (USH2) and Usher syndrome type 3 (USH3). USH1 is characterized by profound congenital sensorineural deafness, absent vestibular function and prepubertal onset of progressive retinitis pigmentosa leading to blindness.<ref>PMID:10973247</ref> Defects in USH1C are the cause of deafness, autosomal recessive, 18A (DFNB18A) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/602092 602092]. A form of sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information.<ref>PMID:12107438</ref> |
| | + | == Function == |
| | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/USH1C_HUMAN USH1C_HUMAN] Required for normal development and maintenance of cochlear hair cell bundles. Anchoring/scaffolding protein that is a part of the functional network formed by USH1C, USH1G, CDH23 and MYO7A that mediates mechanotransduction in cochlear hair cells. Required for normal hearing (By similarity). |
| | + | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | + | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| | + | Check<jmol> |
| | + | <jmolCheckbox> |
| | + | <scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/k1/3k1r_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> |
| | + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> |
| | + | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> |
| | + | </jmolCheckbox> |
| | + | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=3k1r ConSurf]. |
| | + | <div style="clear:both"></div> |
| | + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| | + | The hereditary hearing-vision loss disease, Usher syndrome I (USH1), is caused by defects in several proteins that can interact with each other in vitro. Defects in USH1 proteins are thought to be responsible for the developmental and functional impairments of sensory cells in the retina and inner ear. Harmonin/USH1C and Sans/USH1G are two of the USH1 proteins that interact with each other. Harmonin also binds to other USH1 proteins such as cadherin 23 (CDH23) and protocadherin 15 (PCDH15). However, the molecular basis governing the harmonin and Sans interaction is largely unknown. Here, we report an unexpected assembly mode between harmonin and Sans. We demonstrate that the N-terminal domain and the first PDZ domain of harmonin are tethered by a small-domain C-terminal to PDZ1 to form a structural and functional supramodule responsible for binding to Sans. We discover that the SAM domain of Sans, specifically, binds to the PDZ domain of harmonin, revealing previously unknown interaction modes for both PDZ and SAM domains. We further show that the synergistic PDZ1/SAM and PDZ1/carboxyl PDZ binding-motif interactions, between harmonin and Sans, lock the two scaffold proteins into a highly stable complex. Mutations in harmonin and Sans found in USH1 patients are shown to destabilize the complex formation of the two proteins. |
| | | | |
| - | ==Function==
| + | The structure of the harmonin/sans complex reveals an unexpected interaction mode of the two Usher syndrome proteins.,Yan J, Pan L, Chen X, Wu L, Zhang M Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 8. PMID:20142502<ref>PMID:20142502</ref> |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/USH1C_HUMAN USH1C_HUMAN]] Required for normal development and maintenance of cochlear hair cell bundles. Anchoring/scaffolding protein that is a part of the functional network formed by USH1C, USH1G, CDH23 and MYO7A that mediates mechanotransduction in cochlear hair cells. Required for normal hearing (By similarity). [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/USH1G_HUMAN USH1G_HUMAN]] Required for normal development and maintenance of cochlear hair cell bundles. Anchoring/scaffolding protein that is a part of the functional network formed by USH1C, USH1G, CDH23 and MYO7A that mediates mechanotransduction in cochlear hair cells. Required for normal hearing.<ref>PMID:21709241</ref><ref>PMID:12588794</ref>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | ==About this Structure==
| + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> |
| - | [[3k1r]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3K1R OCA].
| + | </div> |
| | + | <div class="pdbe-citations 3k1r" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> |
| | | | |
| - | ==Reference== | + | ==See Also== |
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID:020142502</ref><references group="xtra"/><references/>
| + | *[[Harmonin|Harmonin]] |
| | + | == References == |
| | + | <references/> |
| | + | __TOC__ |
| | + | </StructureSection> |
| | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| - | [[Category: Pan, L.]] | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Yan, J.]] | + | [[Category: Pan L]] |
| - | [[Category: Zhang, M.]] | + | [[Category: Yan J]] |
| - | [[Category: Ank repeat]] | + | [[Category: Zhang M]] |
| - | [[Category: Deafness]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Disease mutation]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hearing]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Non-syndromic deafness]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Protein-protein complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Retinitis pigmentosa]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Sensory transduction]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Structural protein]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Usher syndrome]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Vision]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Disease
USH1C_HUMAN Defects in USH1C are the cause of Usher syndrome type 1C (USH1C) [MIM:276904; also known as Usher syndrome type I Acadian variety. USH is a genetically heterogeneous condition characterized by the association of retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural deafness. Age at onset and differences in auditory and vestibular function distinguish Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1), Usher syndrome type 2 (USH2) and Usher syndrome type 3 (USH3). USH1 is characterized by profound congenital sensorineural deafness, absent vestibular function and prepubertal onset of progressive retinitis pigmentosa leading to blindness.[1] Defects in USH1C are the cause of deafness, autosomal recessive, 18A (DFNB18A) [MIM:602092. A form of sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information.[2]
Function
USH1C_HUMAN Required for normal development and maintenance of cochlear hair cell bundles. Anchoring/scaffolding protein that is a part of the functional network formed by USH1C, USH1G, CDH23 and MYO7A that mediates mechanotransduction in cochlear hair cells. Required for normal hearing (By similarity).
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The hereditary hearing-vision loss disease, Usher syndrome I (USH1), is caused by defects in several proteins that can interact with each other in vitro. Defects in USH1 proteins are thought to be responsible for the developmental and functional impairments of sensory cells in the retina and inner ear. Harmonin/USH1C and Sans/USH1G are two of the USH1 proteins that interact with each other. Harmonin also binds to other USH1 proteins such as cadherin 23 (CDH23) and protocadherin 15 (PCDH15). However, the molecular basis governing the harmonin and Sans interaction is largely unknown. Here, we report an unexpected assembly mode between harmonin and Sans. We demonstrate that the N-terminal domain and the first PDZ domain of harmonin are tethered by a small-domain C-terminal to PDZ1 to form a structural and functional supramodule responsible for binding to Sans. We discover that the SAM domain of Sans, specifically, binds to the PDZ domain of harmonin, revealing previously unknown interaction modes for both PDZ and SAM domains. We further show that the synergistic PDZ1/SAM and PDZ1/carboxyl PDZ binding-motif interactions, between harmonin and Sans, lock the two scaffold proteins into a highly stable complex. Mutations in harmonin and Sans found in USH1 patients are shown to destabilize the complex formation of the two proteins.
The structure of the harmonin/sans complex reveals an unexpected interaction mode of the two Usher syndrome proteins.,Yan J, Pan L, Chen X, Wu L, Zhang M Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 8. PMID:20142502[3]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Verpy E, Leibovici M, Zwaenepoel I, Liu XZ, Gal A, Salem N, Mansour A, Blanchard S, Kobayashi I, Keats BJ, Slim R, Petit C. A defect in harmonin, a PDZ domain-containing protein expressed in the inner ear sensory hair cells, underlies Usher syndrome type 1C. Nat Genet. 2000 Sep;26(1):51-5. PMID:10973247 doi:10.1038/79171
- ↑ Ahmed ZM, Smith TN, Riazuddin S, Makishima T, Ghosh M, Bokhari S, Menon PS, Deshmukh D, Griffith AJ, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB, Wilcox ER. Nonsyndromic recessive deafness DFNB18 and Usher syndrome type IC are allelic mutations of USHIC. Hum Genet. 2002 Jun;110(6):527-31. Epub 2002 May 3. PMID:12107438 doi:10.1007/s00439-002-0732-4
- ↑ Yan J, Pan L, Chen X, Wu L, Zhang M. The structure of the harmonin/sans complex reveals an unexpected interaction mode of the two Usher syndrome proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 8. PMID:20142502
|