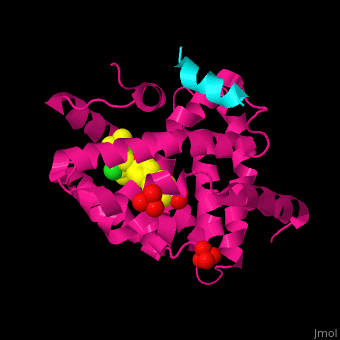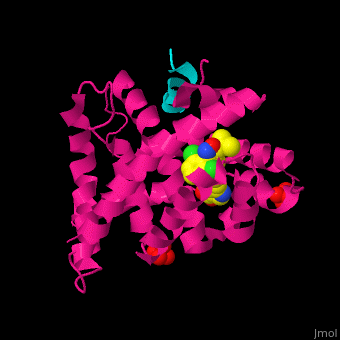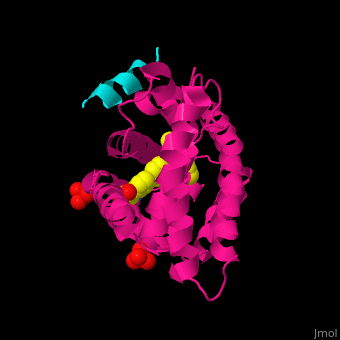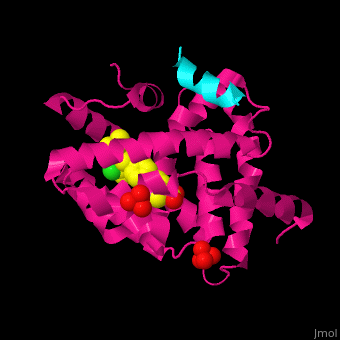Bile acid receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='3ruu' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human FXR ligand-binding domain complex with non-steroidal agonist and nuclear receptor coactivator 1 peptide (...) |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human FXR ligand-binding domain (magenta) complex with non-steroidal agonist, nuclear receptor coactivator 1 peptide (cyan) and sulfate ions (PDB entry [[3ruu]])' scene='54/545859/Cv/1'> | |
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | |
| + | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Bile acid receptor or farnesoid X receptor''' (FXR) binds bile acids, then translocates to the nucleus, forms a dimer and binds to hormone response elements. This causes up- or down-regulation of certain genes involved in cholesterol metabolism, lipid homeostasis and absorption of fats and vitamins. FXR ligand-binding domain (LBD) binds chenodeoxycholic acid (CDC), lithocholic acid and deoxycholic acid. | + | '''Bile acid receptor or farnesoid X receptor''' (FXR) binds bile acids, then translocates to the nucleus, forms a dimer and binds to hormone response elements (see [[Nuclear receptors]]). This causes up- or down-regulation of certain genes involved in cholesterol metabolism, lipid homeostasis and absorption of fats and vitamins. FXR ligand-binding domain (LBD) binds chenodeoxycholic acid (CDC), lithocholic acid and deoxycholic acid. <ref>PMID:23982684</ref> |
| - | + | See also [[Intracellular receptors]] | |
| - | + | == Disease == | |
| + | |||
| + | FXR is involved in pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer and type II diabetes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | FXR and other bile acid receptors are targets for the treatment of dyslipidemia, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='54/545859/Cv/3'>Structure</scene> of human FXR ligand-binding domain (deeppink) complex with non-steroidal agonist, nuclear receptor coactivator 1 peptide (cyan) and sulfate ions (PDB entry [[3ruu]]). <ref>PMID:21890356</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of bile acid receptor== | ||
| + | [[Bile acid receptor 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | [[ | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Schaap FG, Trauner M, Jansen PL. Bile acid receptors as targets for drug development. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Jan;11(1):55-67. doi:, 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.151. Epub 2013 Aug 27. PMID:23982684 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.151
- ↑ Akwabi-Ameyaw A, Caravella JA, Chen L, Creech KL, Deaton DN, Madauss KP, Marr HB, Miller AB, Navas F 3rd, Parks DJ, Spearing PK, Todd D, Williams SP, Wisely GB. Conformationally constrained farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists: Alternative replacements of the stilbene. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Aug 11. PMID:21890356 doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.08.034