Tyrosine kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (103 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
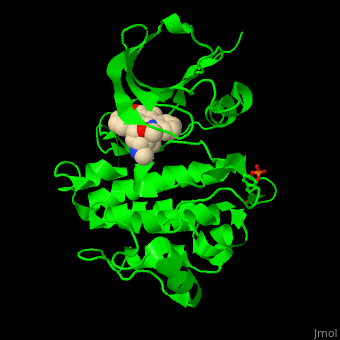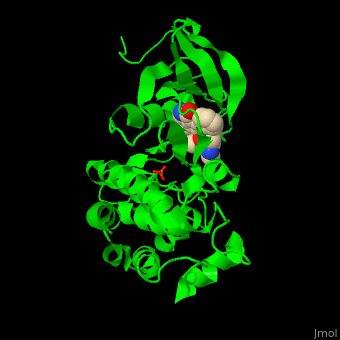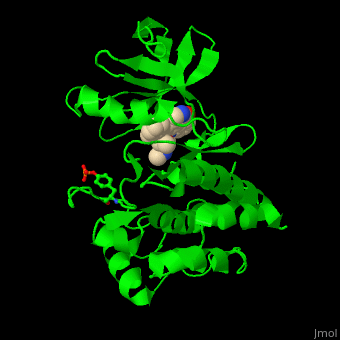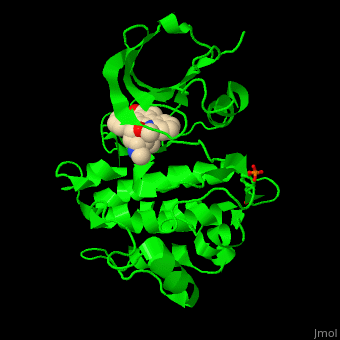
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='48/483859/Cv/1' caption='Human Fyn tyrosine kinase kinase domain with phosphotyrosine in stick model complex with inhibitor staurosporine (PDB code [[2dq7]]).' pspeed='8'> | |
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | ==Function== | ||
| - | '''Tyrosine kinase''' (TK) transfers a phosphate group from ATP to tyrosine residues of proteins. | + | '''Tyrosine kinase''' (TK) transfers a phosphate group from ATP to tyrosine residues of proteins<ref>PMID:10966463</ref>. TKs are classified as [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|receptor-TK]] which are membrane-attached and cytoplasmic non-receptor TKs. Staurosporine inhibits TK and prevents ATP binding to it.<br /> |
| - | + | For '''Abelson tyrosine kinase''' see:<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Bcr-Abl and Imatinib (STI571 or Gleevec)]]<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Imatinib]] (Gleevec)<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Dasatinib]] (Sprycel)<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Nilotinib]] (Tasigna)<br /> | |
| - | + | For '''Bruton's tyrosine kinase''' see:<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Ibrutinib]] (Imbruvica)<br /> | |
| - | + | For '''Src tyrosine kinase'''<ref>PMID:15504335</ref> see:<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[SRC]]<br /> | |
| - | + | For '''Kit tyrosine kinase''' (or SCF or stem cell factor) see:<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[SCF-KIT]]<br /> | |
| - | + | For '''Tyk tyrosine kinase''' see:<br /> | |
| - | '' | + | *[[Student Project 5 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015]]<br /> |
| - | + | *[[Ephrin receptor|Ephrin receptors]] belong to the receptor tyrosine kinases. | |
| - | + | For '''Focal adhesion kinase''' see:<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Focal adhesion kinase]] | |
| - | + | *'''Csk tyrosine kinase''' (or C-terminal Src kinase) has a role in regulating apoptosis, survival, proliferation<ref>PMID:36578781</ref>. | |
| - | + | *'''Fgr tyrosine kinase''' has a role in regulating diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and liver steatosis<ref>PMID:32943786</ref>. | |
| - | + | *'''Syk tyrosine kinase''' (or spleen tyrosine kinase) has a role in adaptive immun receptor signalling<ref>PMID:20467426</ref>. | |
| - | + | *'''Mer tyrosine kinase''' has a role in macrophage physiology like regulating cytokine secretion and clearance of apoptotic cells<ref>PMID:19386698</ref>. | |
| - | + | *'''Hck tyrosine kinase''' activates kinase-dependent and caspase-mediated apoptosis<ref>PMID:14551197</ref>. | |
| - | + | See also | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | *[[Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase]]<br /> | |
| - | + | *[[Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Pharmacokinetics]]<br /> | |
| - | '' | + | *[[Treatments:TYKI References]]<br /> |
| - | + | *[[Oncogenes & Tumor Suppressor Genes]] | |
| - | + | *[[Cancer]] | |
| - | [[ | + | *[[Ephrin Type-A Receptor]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | '' | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | '' | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | '' | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | For references see [[Treatments:TYKI References]]. |
| - | + | ==Relevance== | |
| - | + | Bcr-Abl inhibitors are used against chronic myelogenous leukemia (CLM)<ref>PMID:19538165</ref>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | == | + | ==Disease== |
| + | Mutated TK can cause unregulated growth of the cell and their inhibitors can be effective cancer treatment<ref>PMID:17311534</ref>. | ||
| - | + | == Structural highlights == | |
| + | TK contains, starting from the N-terminal, SH4 – a membrane attachment domain; SH3 and SH2 domains which are a sequence-specific phosphotyrosine binding domains with roles in protein-protein interactions and the SH1 catalytic kinase domain. The <scene name='48/483859/Cv/6'>staurosporine inhibitor binds the kinase domain</scene> of Fyn TK which contains a <scene name='48/483859/Cv/7'>phosphotyrosine</scene>, in the <scene name='48/483859/Cv/8'>groove between the N- and C-lobes</scene><ref>PMID:16782058</ref>. | ||
| - | == | + | ==Traditional Chinese medicine as dual guardians against hypertension and cancer? <ref>DOI 10.1080/07391102.2012.680030</ref> == |
| - | + | <scene name='Journal:JBSD:14/Cv/2'>Src kinase</scene> functions as a signal protein and is implicated in various diseases. The carboxyl terminal of Src kinase is important in regulating conformation and activity of Src. Src protein is locked as an inward folding conformation through binding between the phosphorylated Tyr527 and the SH2 domain under normal inactive conditions. Src is activated when dephosphorylation of Tyr527 and phosphorylation of Tyr419 occurs. | |
| - | + | From N-terminal to C-terminal, Src is composed of a <scene name='Journal:JBSD:14/Cv/3'>smaller amino-terminal lobe</scene> (<span style="color:violet;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">residues 270–340; colored in violet</span>) which binds adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and a <scene name='Journal:JBSD:14/Cv/5'>larger carboxyl-terminal lobe</scene> (<span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">residues 345–523; colored in green</span>) which binds with substrates. The ATP binding site is also partially located in the larger lobe. By regulating the alpha-helix structure, the large lobe can move toward or away from the small lobe, opening or closing the cleft between the two lobes. The Src catalytic site is located within the cleft. An open conformation allows the entrance of ATP into the cleft and exit of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) from the cleft. Drugs that can either interact with the residues (404–432) on the activation loop or inhibit the activation loop from moving away and opening the cleft as a result of Tyr419 phosphorylation can effectively inhibit Src activity. | |
| + | In this ''in vivo'' study, <scene name='Journal:JBSD:14/Cv/7'>Angeliferulate</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBSD:14/Cv/8'>HMID</scene> have multiple stable interactions with the two Src cleft loops while simultaneously interacting with Asp407, hindering the activation loop from activation. Considering the aforementioned interactions with Src and high affinity with EGFR, HER2, and HSP90, we suggest that Angeliferulate and HMID which both originate from the TCM ''Angelica sinensis'' may have potential as multi-targeting drug leads. | ||
| - | + | ==3D structures of tyrosine kinase== | |
| - | + | [[Tyrosine kinase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | == | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ==References== | |
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||