We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 124
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
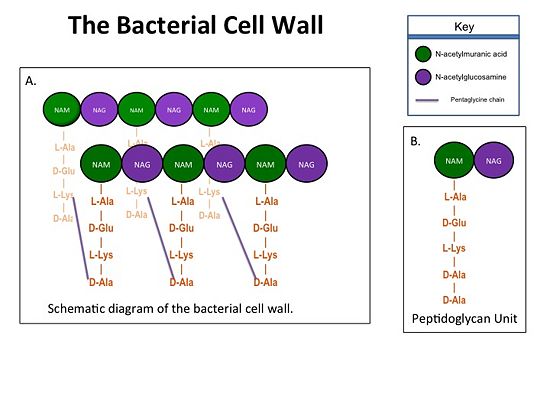
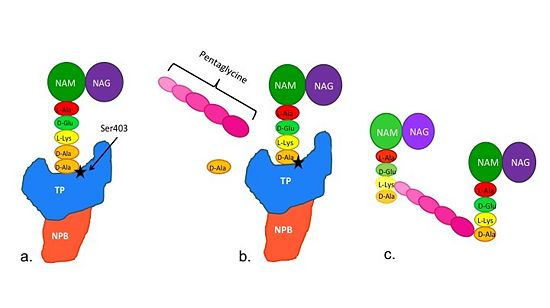
==='''Catalytic Mechanism of PBP2a'''=== | ==='''Catalytic Mechanism of PBP2a'''=== | ||
| - | [[Image:Schematic TP 3steps.jpg|thumb|alt= Alt text|Figure | + | [[Image:Schematic TP 3steps.jpg|thumb|alt= Alt text|Figure 2. Schematic showing Catalytic Mechanism of PBP2a |550px]] |
(a) The D-Ala-D-Ala side-chain substrate of the peptidoglycan accesses | (a) The D-Ala-D-Ala side-chain substrate of the peptidoglycan accesses | ||
the active site of the PBP2a. | the active site of the PBP2a. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
The entire process takes 4 milliseconds. | The entire process takes 4 milliseconds. | ||
| - | ==='''How | + | ==='''How Do Antibiotics Work?'''=== |
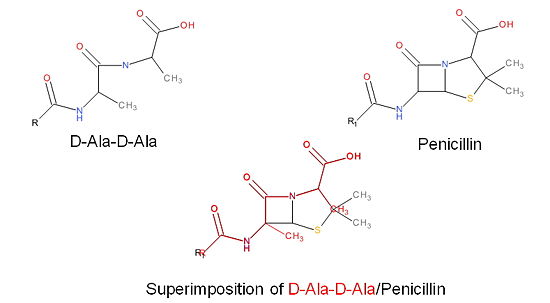
The β-lactam antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth by inhibiting PBPs and ultimately cell wall | The β-lactam antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth by inhibiting PBPs and ultimately cell wall | ||
synthesis. Specifically, β-lactams are molecular mimics of D-Ala-D-Ala, which is the normal | synthesis. Specifically, β-lactams are molecular mimics of D-Ala-D-Ala, which is the normal | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
inhibited by the β-lactam. As a result, the synthesis of the cell wall is inhibited which leads | inhibited by the β-lactam. As a result, the synthesis of the cell wall is inhibited which leads | ||
to cell lysis. | to cell lysis. | ||
| + | [[Image:Structures on penicillin and b lactam.jpg|thumb|alt= Alt text|Figure 3. Mechanism of action of β-lactams. A. Structure of a β-lactam (penicillin) showing the amide, carboxyl, and β-lactam ring groups β-lactam ring groups. B. Structure of the D-Ala-D-Ala substrate. C. Overlay of the D-Ala-D-Ala substrate in red with penicillin demonstrating molecular mimicry.|550 px]] | ||
| + | |||
==='''PBP2a and Ceftobiprole'''=== | ==='''PBP2a and Ceftobiprole'''=== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||